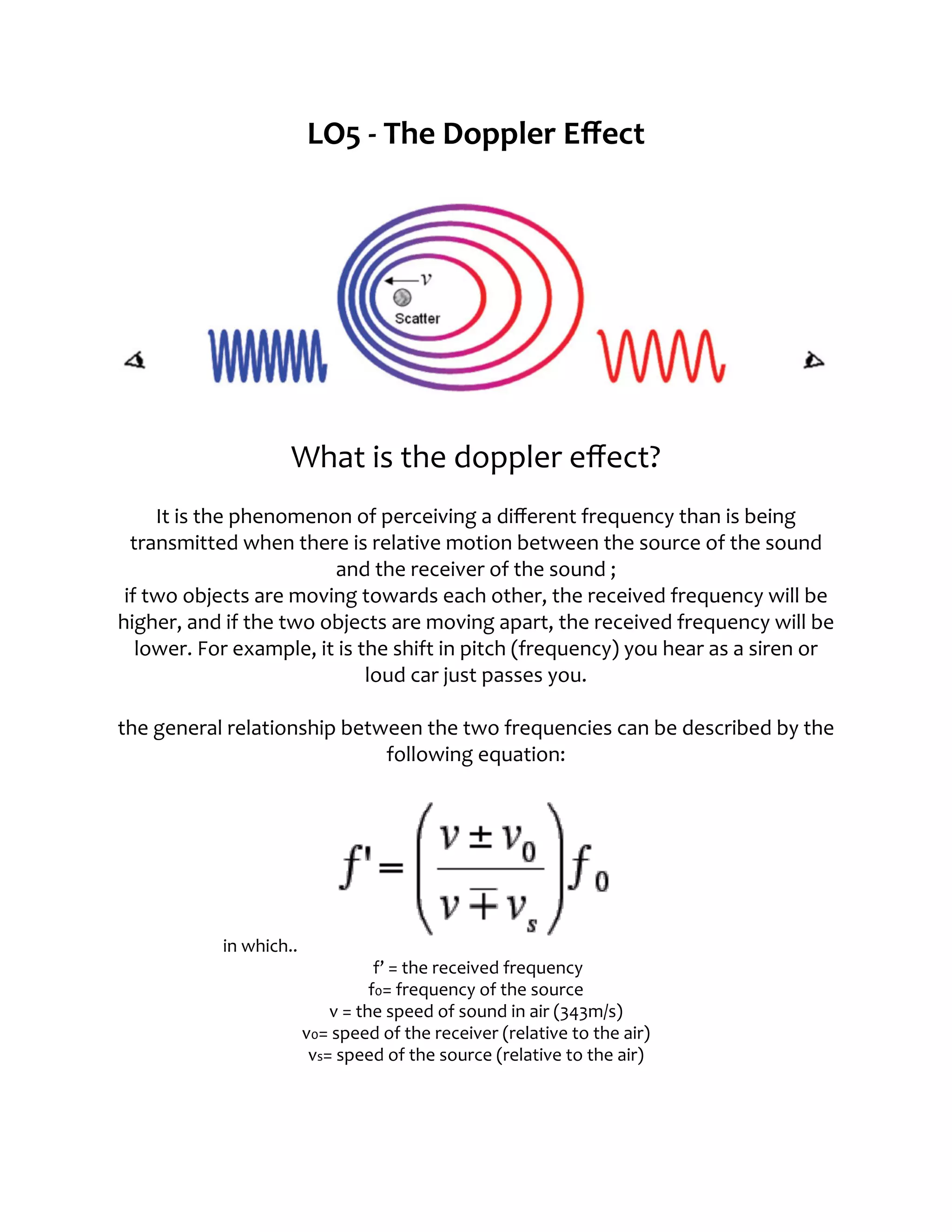
The document discusses the Doppler effect, which is when there is a difference between the perceived and transmitted frequency of a sound due to relative motion between the source and receiver. It explains that the perceived frequency is higher if the source is moving towards the receiver, and lower if moving away, due to the change in distance over time. An equation is provided to calculate the relationship between the transmitted and received frequencies based on the speed of sound and speeds of the source and receiver relative to the air. An example problem is then given about using the Doppler effect to determine if a mosquito is approaching or receding based on the perceived frequency of its buzzing.