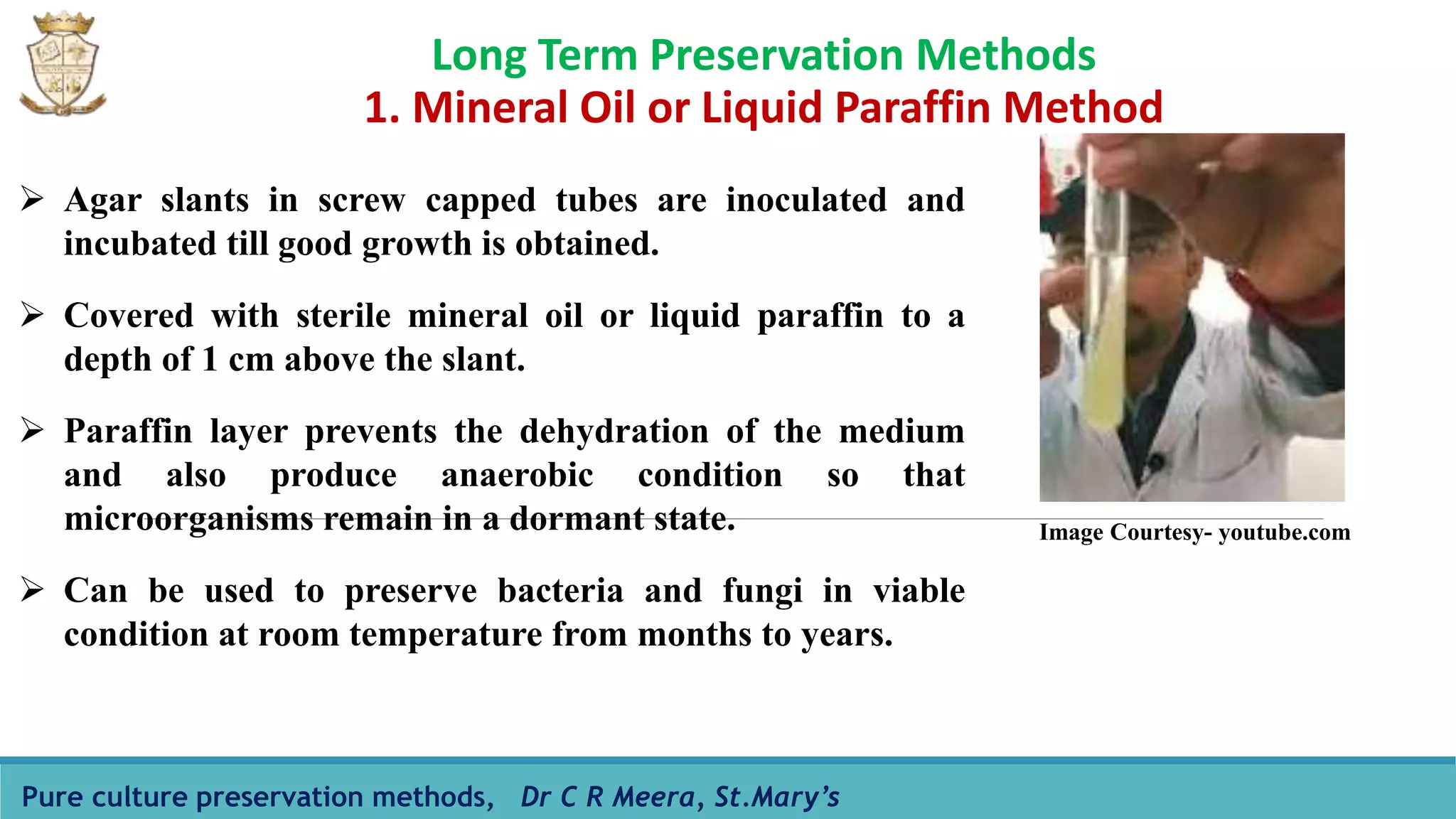
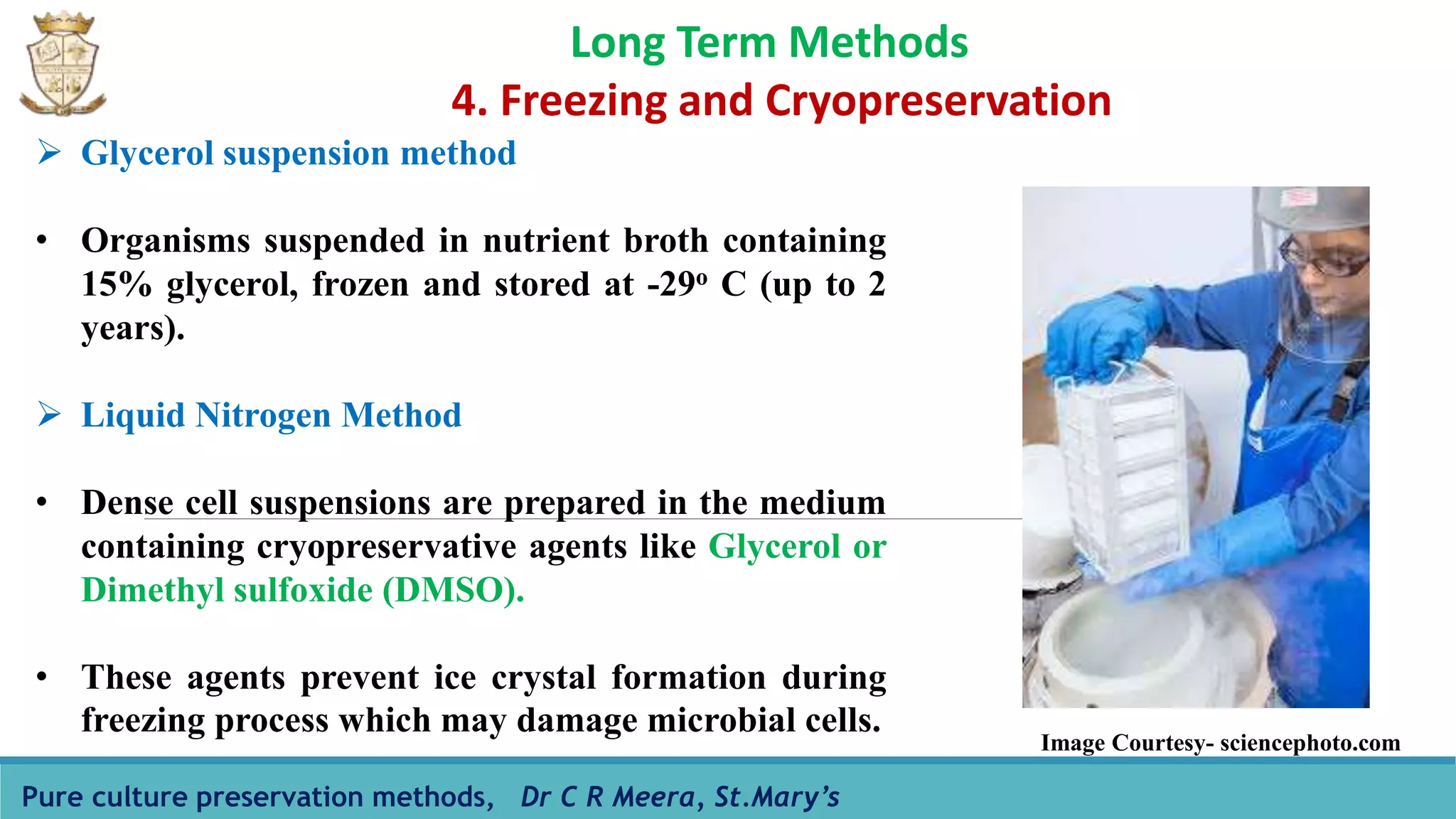
The document discusses various methods for preserving pure cultures of microorganisms, emphasizing the importance of maintaining viable cultures for laboratory and research applications. It details both short-term and long-term preservation techniques, including agar slant cultures, mineral oil storage, saline suspension, drying in vacuum, cryopreservation, and lyophilization, along with their advantages and limitations. The primary goal of these methods is to prevent contamination and maintain the genetic integrity of the cultures over extended periods.