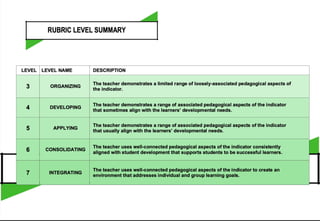
This document provides indicators and descriptors for evaluating a teacher's proficiency and application of content knowledge. It includes 4 indicators rated on a scale from 1 to 7.
Indicator 1 addresses a teacher's knowledge of content within and across curriculum areas. Higher ratings require more accurate, in-depth and broad content knowledge as well as making connections between areas.
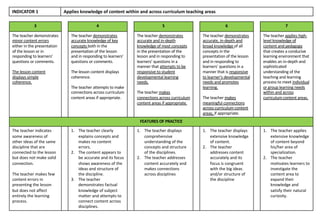
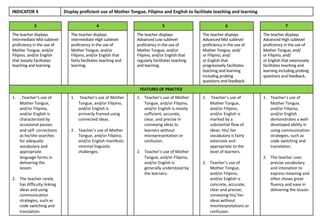
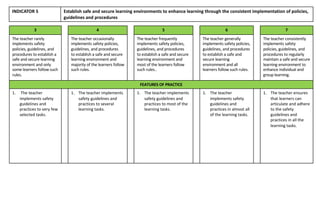
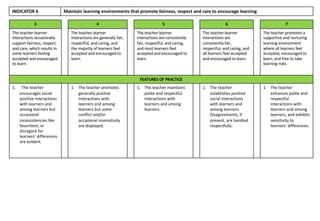
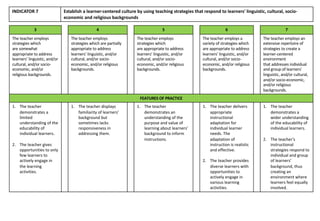
Indicator 2 focuses on using a range of teaching strategies to enhance literacy and numeracy skills. More effective strategies are consistently used to meet individual learner needs.
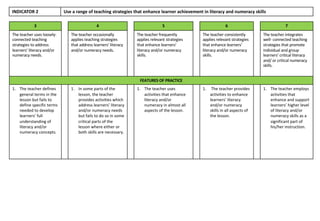
Indicator 3 examines applying strategies to develop critical thinking and higher-order skills. Higher ratings involve more complex, analytical questions and activities.
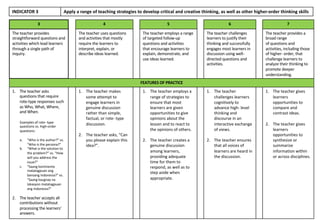
Indicator 4 evaluates proficiency in the languages of instruction. Advancing levels












![[Appendix C-02] Proficient COT-RPMS SY 2023-2024.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendixc-02proficientcot-rpmssy2023-2024-230827054106-da1a9521/85/Appendix-C-02-Proficient-COT-RPMS-SY-2023-2024-pdf-21-320.jpg)