RIVER CIVILIZATIONS.
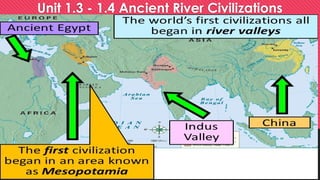
- 1. Unit 1.3 - 1.4 Ancient River Civilizations Case studies
- 2. Do Now: Think About It… Hazlo ahora: piensa en eso ... Why would most of the earliest civilizations develop near rivers??? ¿Por qué la mayoría de las civilizaciones más antiguas se desarrollarían cerca de los ríos? 1) 2) 3)
- 3. Ancient ‘Mesopotamia’ Introduction Video to Mesopotamia Mesopotamia literally means “The land between two rivers.” Tigris and Euphrates!
- 4. Introduction Video to Ancient Mesopotamian Civilization
- 5. Today Mesopotamia is in Iraq!
- 6. We are here!
- 7. The World’s First Civilization! -- 3300 B.C ‘Sumer’ in Mesopotamia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u-n84sDBEB4 (3 minute Video) -- Ancient Sumerians Invented Writing and the Wheel! -- They also created the first ever written story! THE EPIC OF GILGAMESH
- 8. Ancient Sumerian Civilization! 3300 B.C
- 9. First Writing: ‘Cuneiform’ Wedge Writing! Press down on clay with a specific instrument! Developed out of pictographs!
- 10. Social “Stratification” in Mesopotamia Because of ‘Surpluses’ not everyone has to be a farmer or produce their own food! When people have enough food, they can branch out and do other things!
- 12. Ziggurats were built to worship the Gods!
- 13. The World’s First Empire By the year 2300 B.C, the Sumerians were invaded and conquered by a King Named Sargon and his people named the Akkadians. The Akkadians built the first ever Empire! They did this by conquering more and more cities and land. Instead of cities governing themselves, the Akkadian Empire made one single government! With Sargon as the king, or emperor, huge amounts of land were controlled!
- 15. Down Goes Sargon! Here comes Hammurabi! Soon after Sargon died, the Akkadian empire fell apart due to outside invaders and poor governance! By the year 1790 B.C however, an Empire was once again in Mesopotamia. This time, the legendary king Hammurabi established the Babylonian Empire!
- 16. Think-Pair-Share What would be the benefit of having laws written down?? What would some issues be with laws or social rules not being written down?
- 17. Hammurabi’s Code! King Hammurabi is famous in world history for his creation of the first ‘codified’ or written law code around 1790 B.C! Before King Hammurabi, no laws were written down! An eye for an eye!!! An arm for an arm! However! Consequences also depended on your social status in society!!! If you were a wealthy noble, you often only had to pay a fine!
- 18. Summary of Mesopotamian Civilization! ○ Tigris & Euphrates Rivers ○ Monarchy – King ○ Slaves, peasants, artisans & merchants, warriors & priests, royal family-- Social Stratification ○ Cuneiform (writing), Epic of Gilgamesh, Hammurabi’s Code ○ Phoenicians → Alphabet ○ Sumer -- Babylon -- Akkad
- 19. River Valley Civilization 2 Ancient Egypt 2,575 B.C to 332 B.C
- 20. Ancient Egypt lasted for a MIND BLOWING amount of time… (Around 2,200 Years) -- 2,200 years of Civilization in Egypt! -- All before the birth and life of Jesus Christ around 4 B.C *** Think about this… The United States has been a country since 1776, that’s about 250 Years ago Ancient Egyptian civilization lasted almost 9 times (9x) as long as the United States has existed as a country!!!
- 21. Where? Egypt is located in Northeastern Africa!
- 22. Where? (Continued) The Mediterranean Sea is located just North of Egypt! This eventually allowed Ancient Egyptians to TRADE with other peoples and cultures, leading to CULTURAL DIFFUSION!
- 23. Why did Civilization arise there??? THE NILE RIVER!!! The Nile River was very predictable! It always flooded at the same times of year, allowing The Ancient Egyptians to plan how much food they’d have! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GPXXeypfI5A (1 Min Nile Video)
- 24. The Nile From Space!!!
- 25. Why??? Natural Barrier! The Nile provided The Ancient Egyptians with everything they needed for survival. Just outside the areas of land made liveable by The Nile however, was dry and barren desert!
- 26. Mummies! Pharaohs and other egyptians with wealth and power would have themselves mummified! What? Writing and Religion! Hieroglyphics! Egyptian scribes would write down just about anything important! >>>
- 27. Document Analysis (Reading) WIth a partner or alone, work through the document written by The Ancient Greek Historian ‘Herodotus.’ ***Although historians and archaeologists still study the construction of the pyramids, they agree that this process involved tens of thousands of workers working across two to three decades on each. Construction involved cutting, moving, and setting large stones with chisels, ropes, oxen, and ramps. *** https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TWaReNkjTLk
- 28. What? Scribes (continued) Ancient Egyptians knew how important the scribes were. In the social classes, scribes were near the top of the chart. Scribes didn’t have to pay taxes, be part of the military or do any of the manual labor!
- 29. How did we figure out how to read Hieroglyphics??? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yeQ-6eyMQ_o (3 Minute Rosetta Stone Video) The Rosetta Stone was found in 1799! The writing on the top half of the stone is in Ancient Hieroglyphics! The bottom half is in Ancient Greek! This allowed historians to figure out how to read hieroglyphics!!!
- 30. Summary!!! ○ Nile (VERY predictable) ○ Monarchy – pharaoh ○ Slaves, peasants, artisans & merchants, warriors & priests, royal family, pyramids ○ Hieroglyphics (Rosetta Stone) ○ Upper & Lower, Memphis, Valley of the Kings
- 31. Document Reading Ancient River Civs! Page 35 -- Read the excerpt from ‘The Epic of Gilgamesh’ Answer just question 1 Page 65 -- Read Documents A and B, Answer questions 1 -3
- 32. Indus Valley and Chinese Civilizations Un1.4 https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=DbnxPY3D1Pg 2 ½ minute video (boring voice) 3300 - 1700 B.C
- 33. Where? Modern Day India!
- 35. Mohenjo-Daro (Crash Course 2 min video) Cities! What?
- 36. What? Although the Indus Valley people used written language, we have no way to decipher____________ it.
- 37. What? Social Stratification! Social Structure Caste system with four main classes People were born into social classes that could not be changed. ○ Brahmins (priests and the king) ○ Kshatriyas (warriors and aristocrats - rulers) ○ Vaishyas (cultivators, artisans, and merchants) ○ Shudras (peasants and serfs)
- 38. Down Goes Indus Valley Civilization!!! -- 1700 B.C The Indus Valley Civilization ended around the year 1700 B.C. Historians believe that changing climate lead to massive Drought!! The people who live in the area now are not descendants of the Indus Valley Civilization. They most likely migrated in from elsewhere!
- 39. Indus Valley Civilization Summary!!! ○ Indus River ○ Little known (standardization in bricks & roads, major engineering projects) ○ Little known – variety of material possession – social hierarchy ○ Undeciphered ○ Mohenjo-Daro & Harappa (Largest Cities)
- 40. ‘Do Now’ Name 5 of the characteristics that make up a civilization!! Full sentence… “Five of the characteristics that make up a civilization are….”
- 41. Ancient China 1.5 Notes
- 42. Where is China?
- 43. Why There? 1. Geographical Barriers! China has mountains to the West, The Pacific Ocean to the east, and a Desert to the North! 2. This lead to early Chinese people thinking that they were the center of the world! 3. So much so that they called themselves “The Middle Kingdom.”
- 44. Why There? 1. Rivers!!! Duh!!! 2. Two rivers helped early chinese people, travel, farm, and trade within China! 3. The Yellow (Huang) and the Chang! 4. Very early on in Chinese history people started to farm and settle along these two rivers!
- 45. What? 1. There were many different kingdoms in China before it became unified (under the control of one government)! 2. These kingdoms would fight for territory and control over parts of China. This lead Historians to call that period of Chinese history as The _Warring__ Kingdoms period. 3. Around 1122 B.C (Before Christ) a kingdom named the __ZHOU___attacked and overthrew the kingdom of Shang. 4. They justified this by what they called THE MANDATE OF HEAVEN.
- 46. ‘The Mandate of Heaven’ 1. Mandate of Heaven means “The Divine Right to Rule.” 2. The Chinese believed that as long as the government did a good job, it kept the Mandate of Heaven. 3. If rulers became weak or corrupt, they would lose The Mandate of Heaven and be overthrown!
- 47. Zhou Rule… #Weak The Zhou Dynasty did rule China longer than any other government in China’s history. However, it’s rule was more so in name than in actual power. During the Zhou’s “rule” there were many smaller kings and kingdoms that fought against one another for power and honor!
- 48. What? China United! China is eventually united in the year 221 B.C by the Emperor Qin. Hence the name CHINa. But more on that another day!
- 49. What? Confucius! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-c53OBwnsbI (2 Minute Crash Course Confucius) Chinese Religion is based largely on the teachings of a man named Confucius. Confucius was born in 551 B.C. His views were more philosophical than religious. In other words, he was more concerned with life here on earth than an afterlife or belief in God or gods.
- 50. What? Taoism! Taoism offered up the more spiritual religious view in comparison to Confucius’ teachings! Taoism is all about unity with nature! The Taoists believe that people should not concern themselves with daily human affairs, but instead focus on being one with the universe.
- 52. ○ Yellow River (“China’s Sorrow”) ○ Monarch ○ Bronze metallurgy ○ Oracle bones, keep pictographs (never alphabetic) ○ Shang, Zhou
- 53. Choose 1 region (Mesopotamia, Egypt, Indus Valley, or China & discuss how it meets the criteria of a “civilization”? THINK-PAIR-SHARE Full Sentences, you can write this on the same paper as your DO NOW!!!