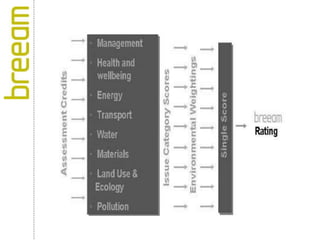
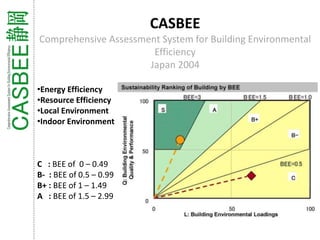
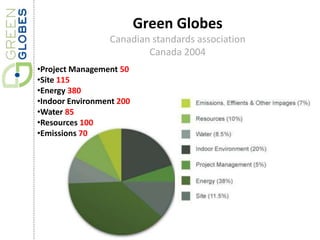
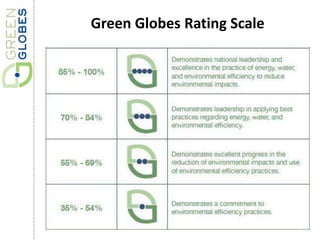
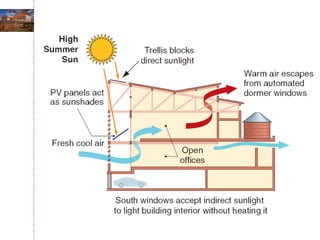
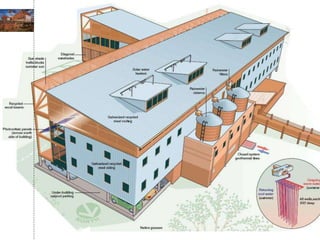
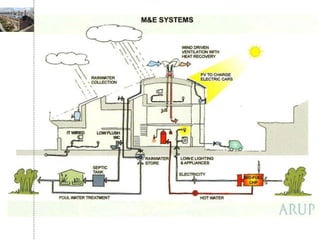
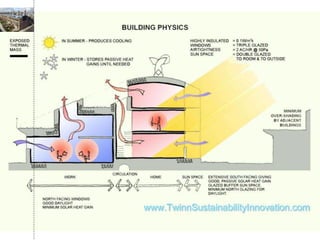
Green building rating systems evaluate buildings based on criteria like energy use, water efficiency, carbon emissions, indoor environmental quality, and transportation. Some examples of rating systems described are BREEAM (UK), LEED (US), Green Star (Australia), CASBEE (Japan), and Green Globes (Canada). Buildings are given ratings on a scale (e.g. pass, good, very good for BREEAM) based on their performance in the criteria. Examples are provided of highly rated buildings under BREEAM and LEED that implemented sustainable design strategies like renewable energy, water recycling, and energy efficient materials.