The document discusses production possibility frontiers (PPF), comparative advantage, and absolute advantage in international trade. It provides examples to illustrate the concepts. Specifically:
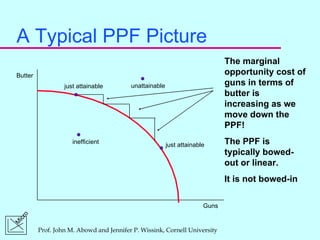
1) A PPF shows the maximum amounts of two goods an economy can produce while fully utilizing its resources, and the marginal opportunity cost of a good increases as we move down the PPF.
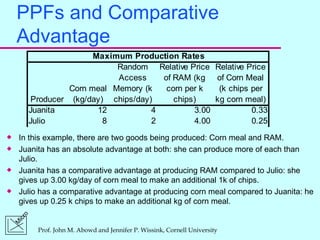
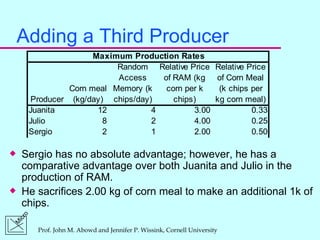
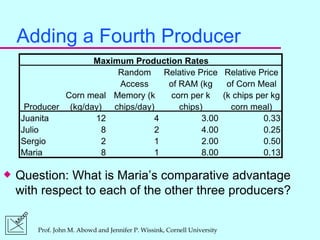
2) Comparative advantage refers to the good a country can produce at a lower opportunity cost than another country. Specialization and trade allow gains for all countries based on comparative rather than absolute advantage.
3) Absolute advantage means a country can produce more of a good using the same resources. Comparative advantage depends on opportunity costs even if a country has no