Embed presentation

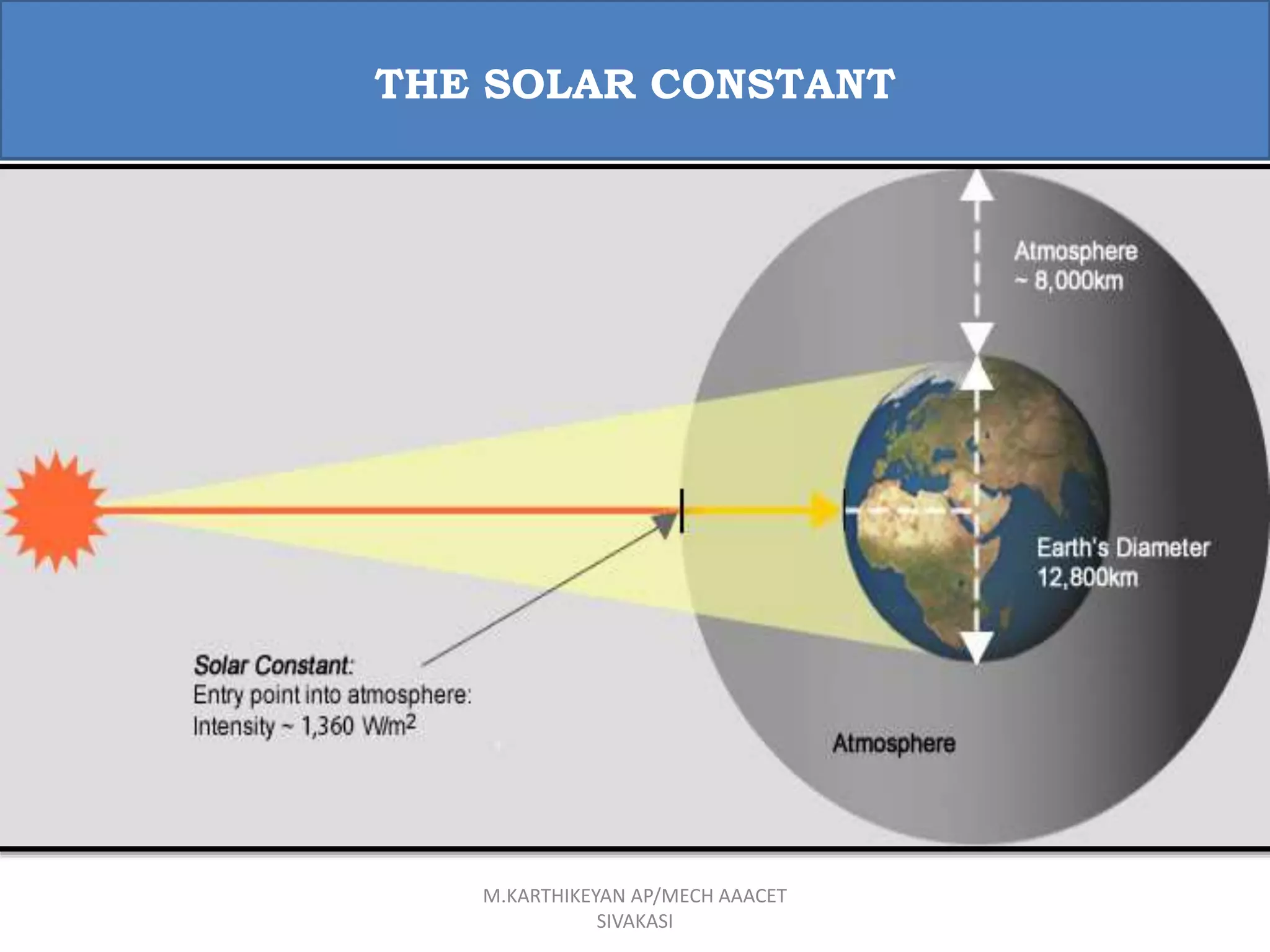
![ The rate at which solar energy arrives at the top of the atmosphere
is called the solar constant.
[or]
Solar constant is the amount of energy received in unit time on a
unit area perpendicular to the sun’s direction at the mean distance
of the earth from the sun.
M.KARTHIKEYAN AP/MECH AAACET
SIVAKASI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oro551-res-unit1-thesolarconstant-190711071239/75/Oro551-res-unit-1-the-solar-constant-3-2048.jpg)

This document discusses principles of solar radiation. It covers the role of solar energy, environmental impacts, physics of the sun, and measurements of solar radiation. Specifically, it defines the solar constant as the rate at which solar energy arrives at the top of the atmosphere, which is approximately 1.367 kW/m2. It also provides equivalent units of the solar constant in kcal/m2/hr and Btu/ft2/hr.


![ The rate at which solar energy arrives at the top of the atmosphere
is called the solar constant.
[or]
Solar constant is the amount of energy received in unit time on a
unit area perpendicular to the sun’s direction at the mean distance
of the earth from the sun.
M.KARTHIKEYAN AP/MECH AAACET
SIVAKASI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oro551-res-unit1-thesolarconstant-190711071239/75/Oro551-res-unit-1-the-solar-constant-3-2048.jpg)
