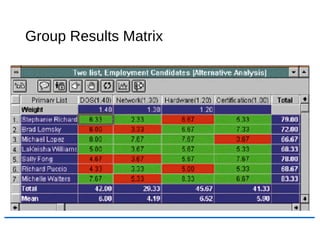
The document discusses decision support systems (DSS) and their role in aiding decision-making for both structured and unstructured problems. It details characteristics, capabilities, and types of DSS and emphasizes their integration in organizations, particularly with web-based systems. Additionally, it covers group decision support systems (GDSS) and executive support systems (ESS), highlighting their specific features and advantages.