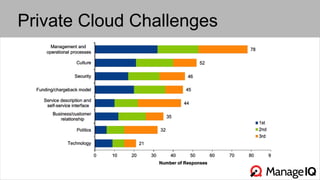
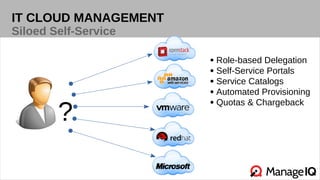
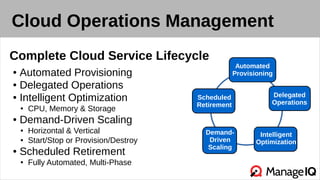
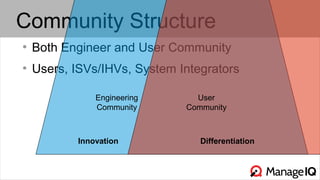
The document discusses hybrid cloud management using ManageIQ, emphasizing the importance of open source in addressing challenges related to private cloud infrastructure and customer demands. It outlines key features such as automated provisioning, role-based delegation, and demand-driven scaling, while highlighting the community-driven development and collaboration with various partners. Future releases will enhance support for multiple technologies and provide comprehensive APIs for integration.