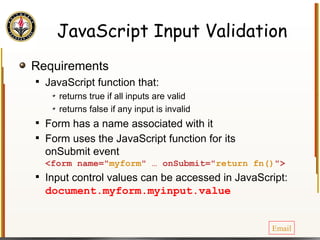
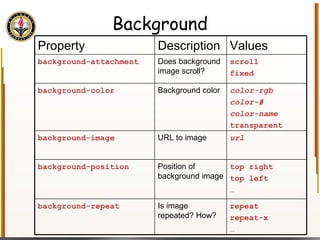
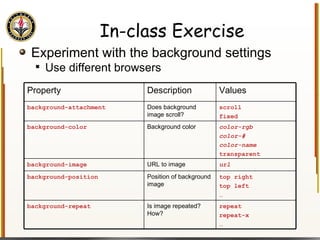
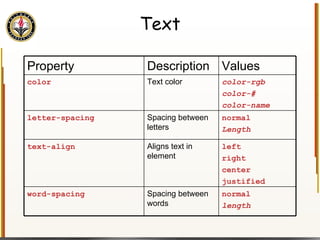
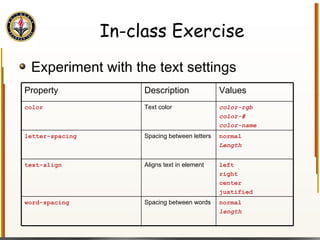
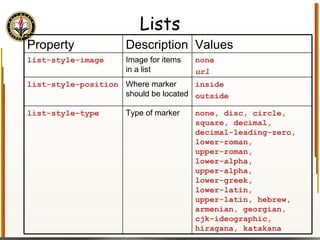
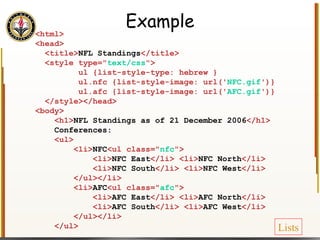
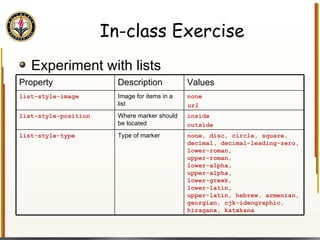
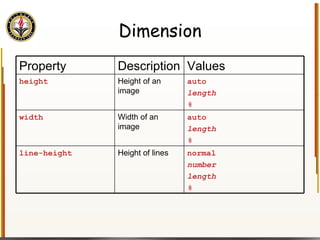
The document provides an overview of HTML and CSS, detailing their structure, essential tags, and usage for web page creation. It includes examples of HTML file structure, formatting tags, links, tables, and images, along with exercises for practical understanding. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of markup languages in web development, particularly HTML's role as a standard for internet pages.



























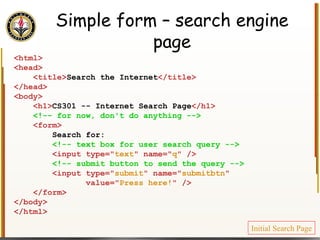


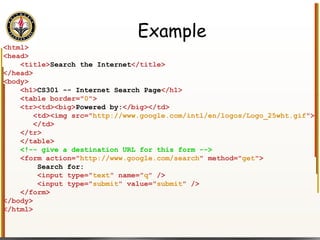

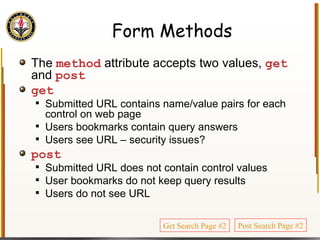
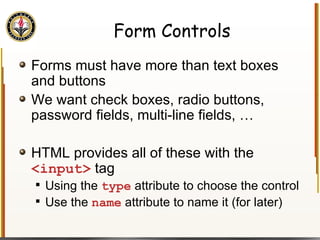



























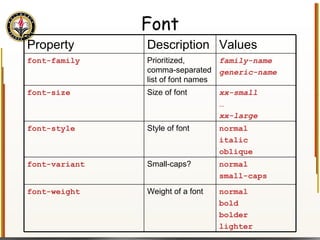

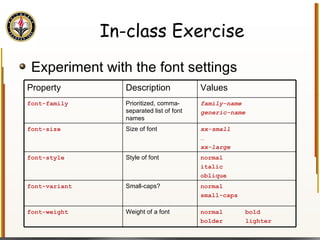
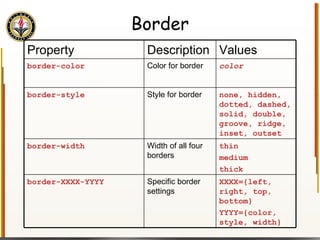

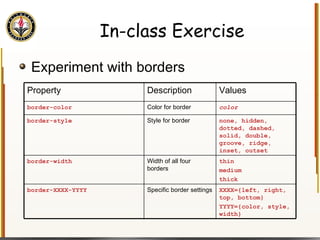







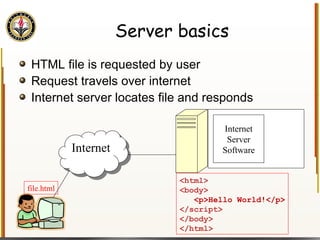
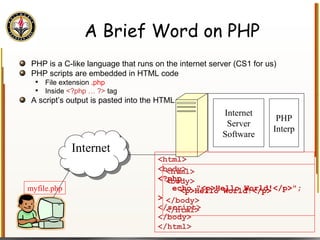
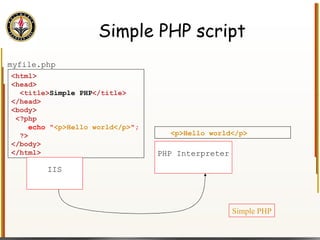

![Handling Input Example <html> <head> <title> Simple PHP </title> </head> <body> <?php echo "<p>Hello world</p>\n"; if (isset($_REQUEST["name"])) { echo "<p>Welcome back " . $_REQUEST["name"]; } else { ?> <form action="name.php" method="GET"> <input type="textbox" name="name"> <br /><input type="submit" value="Login"> </form> <?php } ?> </body> </html> Name PHP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/HTML_CSS-090224183818-phpapp01/85/HTML-CSS-90-320.jpg)