Current Commutated Chopper: Working, Advantages and Design
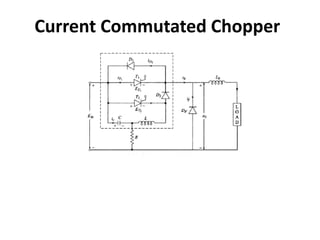
- 2. What is meant by current commutation? • Chopper is used to change the dc level of voltage, it is dc/dc converter. • In current commutated chopper , as the name suggests, chopper is commutated by current pulse. • In this process, a current pulse is made to flow in the reverse direction through the conducting thyristor and when the net thyristor current becomes zero, it is turned off.
- 3. • Some assumption are: Load current is constant. SCR and Diodes are ideal switches. RC is so large such that it can be treated as open circuit during the commutation interval. • The energy for commutation comes from energy stored in capacitor. • Capacitor is charges to Edc , so that energy for commutation is available.
- 4. At to Thyristor T1 is turned on by gate pulse g1.
- 5. • Main thyristor T1 is fired at t=0 so that load current and output voltage is IO and VS respectively from t0 to t1 . • With the turning on of T1 commutation circuitry remain inactive. • Commutation process begins with turning on of T2. • The commutation process is divided in various modes as follows.
- 6. (a) Mode I, t1<t<t2 At t2 At first the T2 is turned on - T2 is fired through gate and turned on. Capacitor C is charged to -Edc – As T2 is on, the capacitor inductor series circuit is shorted and so the capacitor is charged to negative voltage -Edc .
- 7. (a) Mode II, t2<t<t3 The capacitor C is fully charged, and current reverses, and so T2 is turned off - When the capacitor is charged, it provides -Edc voltage reverse bias to T2 thyristor, so T2 is turned off. Now the current flows opposite through the thyristor T1 - The capacitor, charged to negative Edc, pushes current ic opposite to T1. Here ic doesn't not flow through diode, because the forward voltage of diode is more than that of drop accross thyristor T1.
- 8. (a) Mode III, t3<t<t4 T1 is turned off- Now the ic turns off T1. So the impedance offered by T1 is more than diode, and the current ic flows through diode.
- 9. (a) Mode IV, t4<t<t5 The D1 is reversed biased - The current ic slowly decrease, and when ic=Io, the diode D1 is no longer forward biased. So the diode is turned off.
- 10. (a) Mode IV, t5<t<t6 C is charged to +Edc : C is overcharged, free wheeling diode is forward biased and Eo is reduced to zero. Io=ic+ifd.
- 11. The commutation period is complete. The T1 is turned on by gate pulse. And again T2 is turned on, capacitor charges to negative potential and cycle repeats.
- 12. What are the advantages of current commutated chopper? • The capacitor always remains charged with the correct polarity. • Commutation is reliable as load current is less than the peak commutation current ICP. • The auxiliary thyristor T2 is naturally commutated as its current passes through zero value.
- 15. Design Consideration : Finding values of L & C (i) Peak Commutating Current ICP > Load Current IO. The oscillating current in commutation circuit is given by ……….. (1) (ii) Circuit turn off time must be greater than turn off time of main Thyristor. tIt L C Vi oCPosc sinsin osCP I L C VI os xI L C V o CP I I x xI I II t ttt o CP oCP co c 1 sinsin sin 2 11 1 1 1 34
- 16. Circuit turn off time for main Thyristor ………………. (2a) ………………..(2b) The above relation reveals that as load current Io increases , turn off time of main thyristor decreases. So, ……………....(3) Substitution of above value in eq (1) …………………(4) )sin2( 1 )2( 1 1 0 1 CP o c o c I I t t L t C LCt x c xc )](sin2[ )](sin2[ 11 11 )](sin2[ )](sin2[ 11 11 xo cs o x cs xI tV L xI t L V
- 17. • From eq. (3) • Subsituting this value in eq (1) ……………….(5) C tL x c )](sin2[ 11 11 )](sin2[ )](sin2[ 11 11 xs co x c s o V txI C C t V xI
- 18. Total Communication Interval: (t6-t1)= (t2-t1) + (t4-t2) + (t5-t4) + (t6-t5) • (t2-t1): time period of half cycle of oscillating current • (t4-t2) : Sine current waveform of ic is examined • (t5-t4) : Increase in voltage across C during (t5-t4) = Vs - Vs sin(90-θ1) LC o LC o )( 1 1 o s o s ss o I CV I CVtt tt VV CI 11 45 45 1 cos1)90sin(1 )( )( )90sin(
- 19. • (t6-t5) : ic is assumed to be Iocosωot. • (t6-t1) : total commutation interval LCtt o 22 1 )( 56 o s o s I CVLC I CVLC 2sin 2 2 5 cos1 2 5 1 2 1 1 1 Turn off time: for main thyristor For auxilary thyristor LC LCtt x 11 134 sin2 2 LCLCttt xC 11 1124 sin
- 20. Peak Capacitor Voltage • Maximum capacitor VCP is reached at t6 which is equal to voltage at t5 + voltage rise due to the energy transfer from L to C during t6 - t5 • At t5 energy in L is ½ L Io 2 and at t6 this energy is transferred to C. Thus C L IVV C L IV LICV osCP oc oc 22 2 1 2 1
- 21. Numerical problems a) For a current commutated chopper, peak commutating current is twice the maximum possible load current. The source voltage is 230 V dc and main SCR turn off time is 30 µsec. For a maximum load current of 200A, calculate (i) The values of the commutating inductor and capacitor. (ii) Maximum capacitor voltage and (iii) The peak commutating current. SOLUTION: Given x=2, tq = 30 µsec tC = tq + Δt taking Δt= 30 µsec, tC =(30+30) µsec=60 µsec (i) Value of inductor )](sin2[ 11 xo cs xI tV L
- 22. Value of capacitor (ii) Peak capacitor voltage (iii) Peak commutating current HL 473.16 )](sin2[2002 1060230 2 11 6 FC V txI C xs co 822.49 )](sin2[230 sec302002 )](sin2[ 2 11 11 voltsV C L IVV CP osCP 345 822.49 473.16 200230 AxII oCP 4002002
- 23. b. A current commutated chopper is fed from a dc source of a 230V. Its commutating components are L=20µH and C=50µF. Is a load current of 200A is assumed constant during commutating process, then compute the following; (i) Turn off time of main thyristor (ii) Total commutation interval (iii) Turn off time of auxiliary thyristor SOLUTION: (i) Peak commutating current Turn off time of main thyristor 8183.1 200 33.363 33.363 50 20 230 CP O CP sCP I I x AI L C VI sec52.62105020)](sin2[ )](sin2[ 12 8183.1 11 11 c xc t LCt
- 24. (ii) Total commutation interval (iii) Turn off time of auxiliary O CP O I I 365.33 33.363 200 sinsin 11 1 sec427.239 10477.91095.229 200 363.33cos1 2301050101000 180 365.33 2 5 66 66 O sec931.80101000 180 365.33 sin 6 11 1 LCLC x
- 25. THANKS….!
