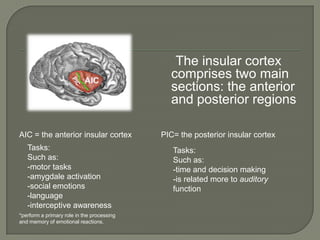
The insular cortex is located between the temporal and parietal lobes. It is involved in processing emotions, tastes, motor skills, and social behavior. It comprises anterior and posterior regions. Studies have shown the insular cortex is activated during risky decision making, anxiety, interoception, motor control, homeostasis, and social emotions. One study found damage to the insular cortex resulted in a person's inability to distinguish tastes but still have preferences. Another study found insular cortex activity when viewing others in pain. A third study found romantic rejection activated reward and motivation areas, including the insular cortex, similarly to addiction. Dysfunctions of the insular cortex are associated with various mood and mental disorders.