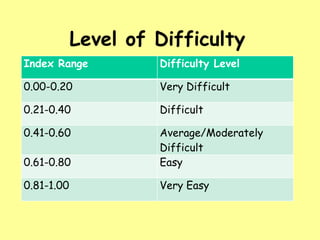
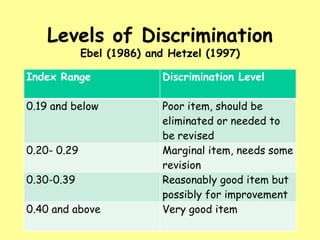
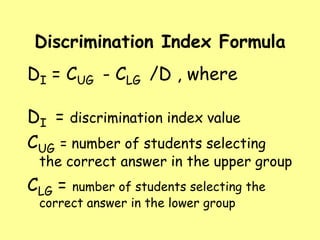
This document discusses item analysis, which examines student responses to test questions. There are two types: quantitative, which uses statistics like difficulty and discrimination indices, and qualitative, which involves expert review. Difficulty index measures the proportion of students answering correctly, ranging from very difficult to very easy. Discrimination index measures an item's ability to distinguish high-scoring from low-scoring students. Qualitative analysis involves experts proofreading tests for issues like ambiguity before administration.