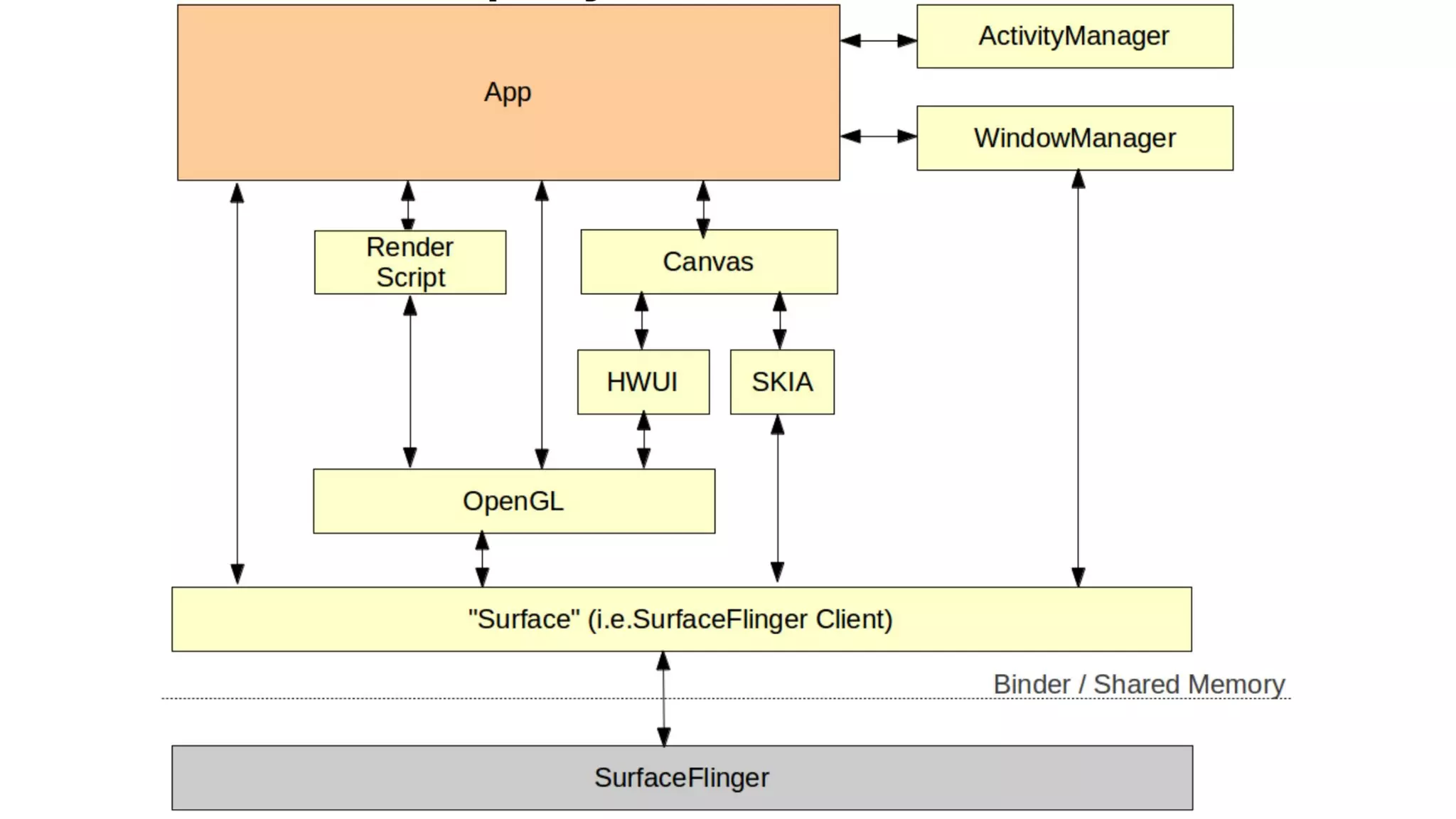
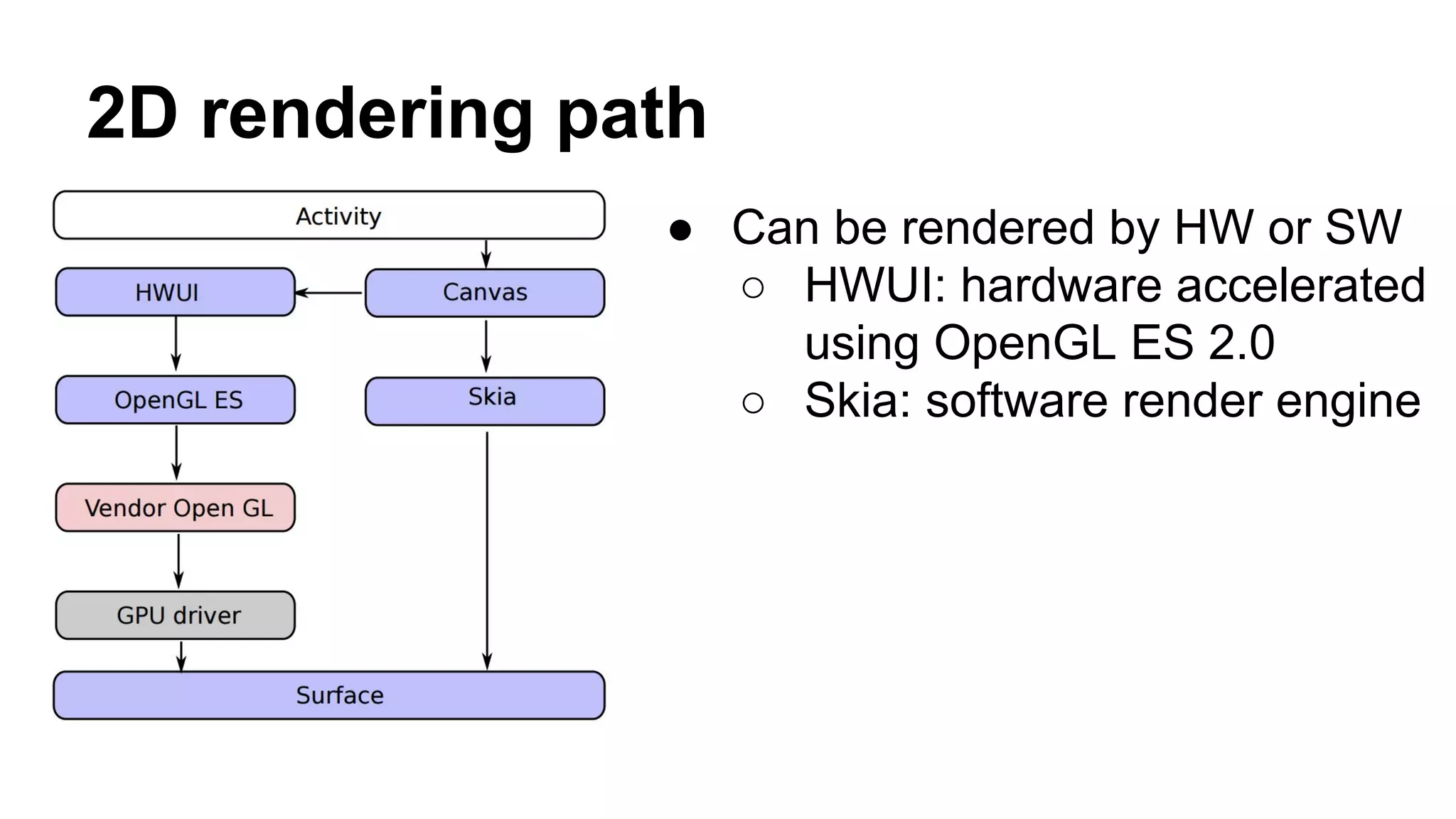
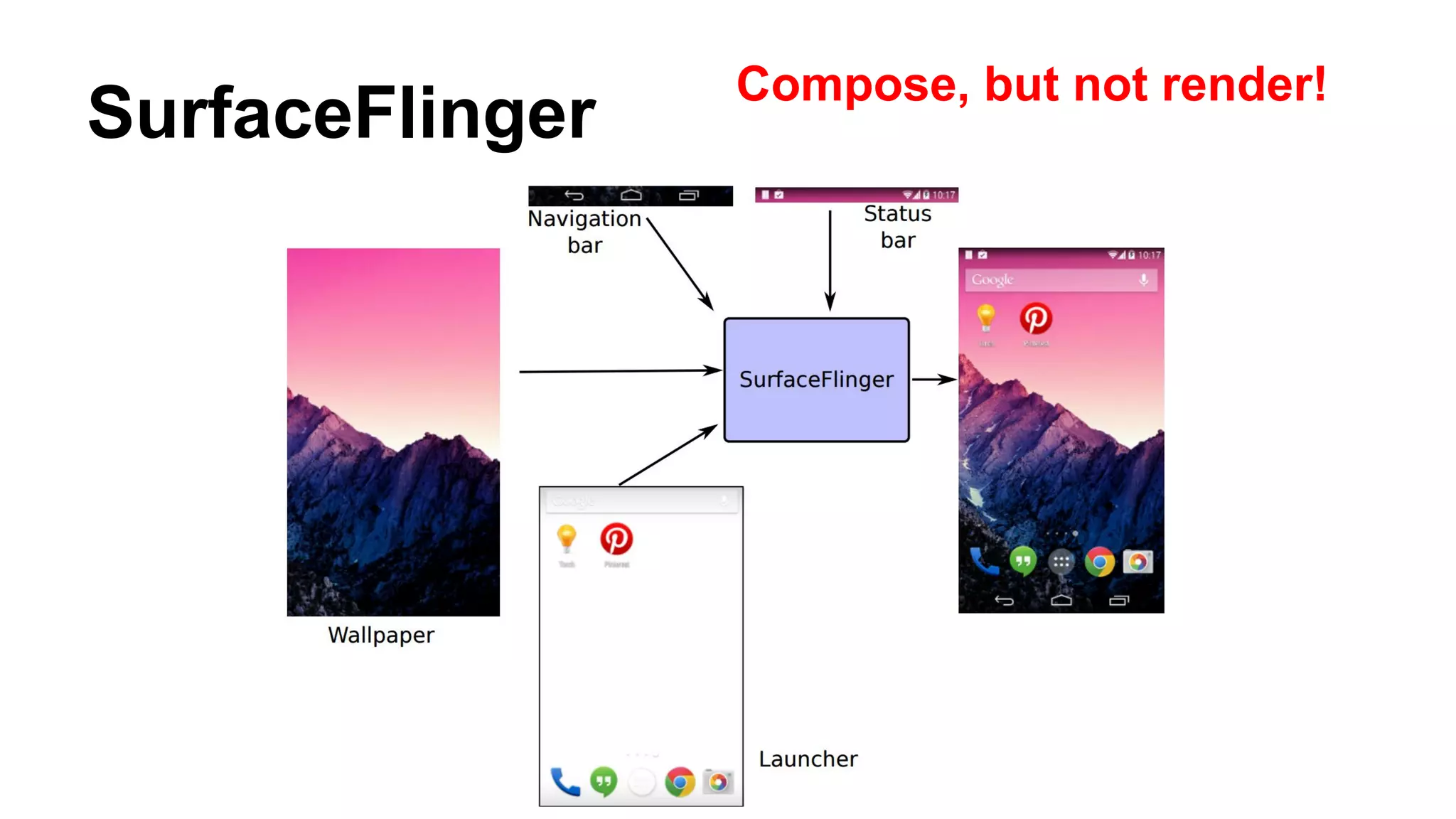
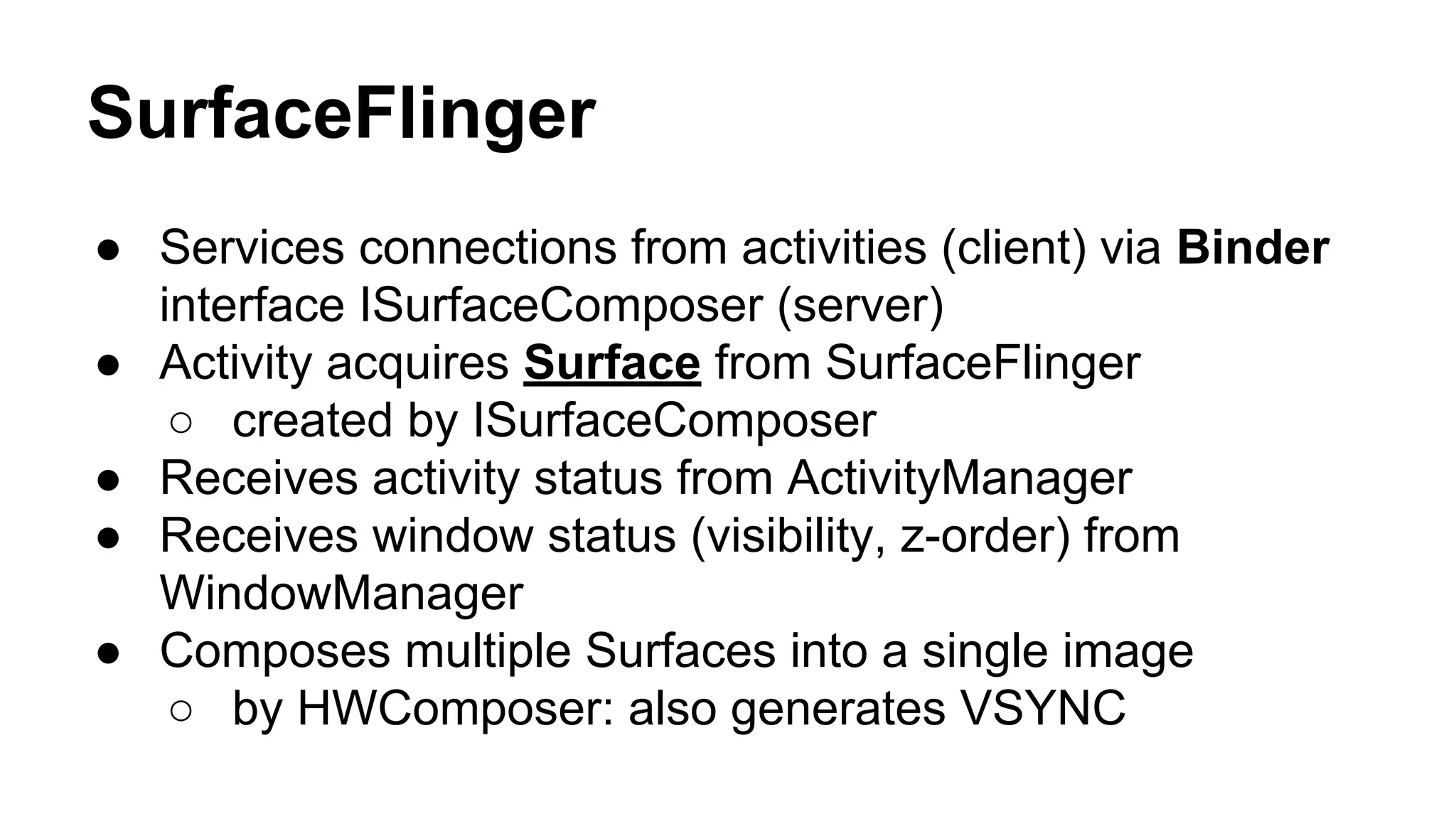
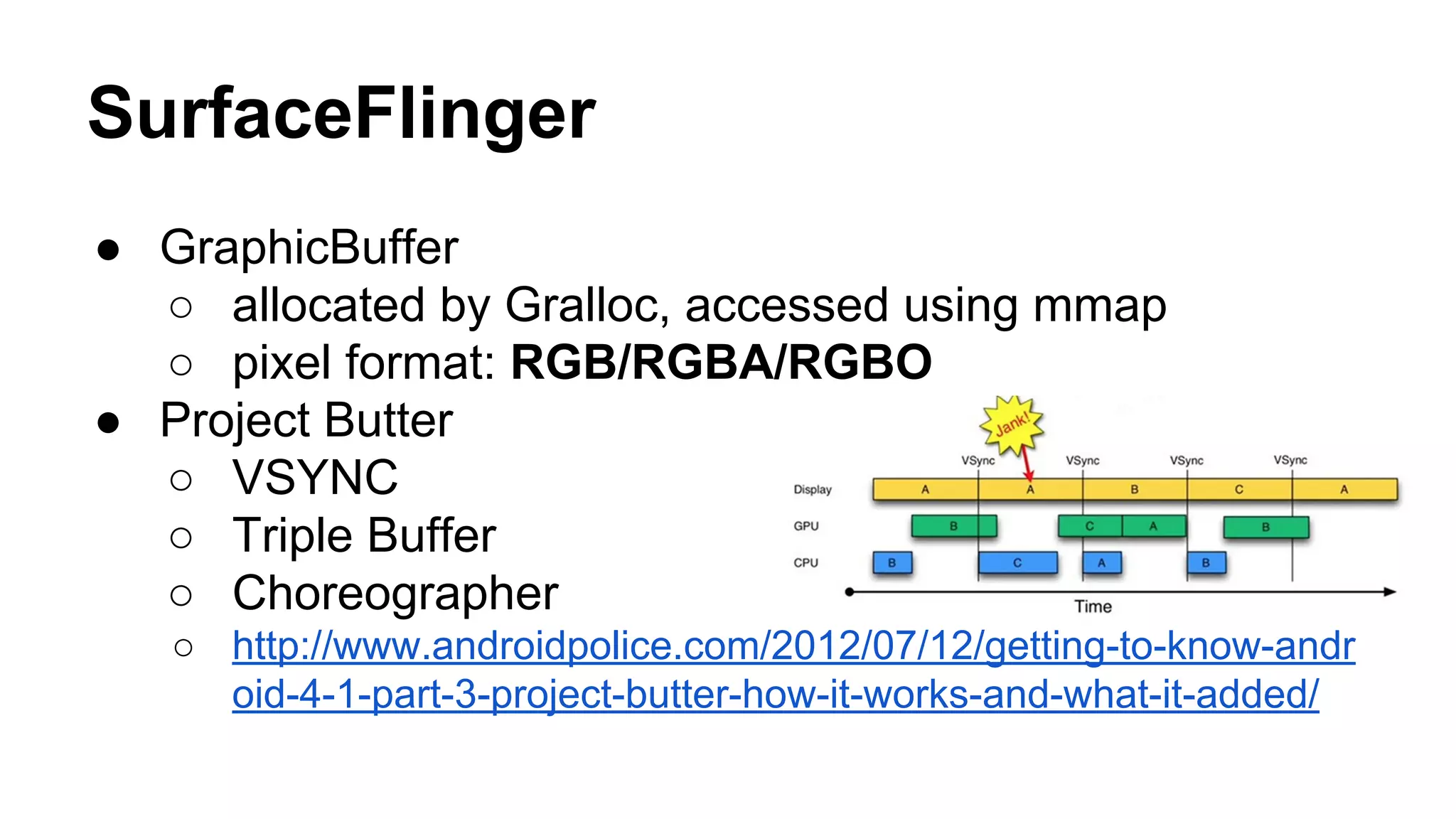
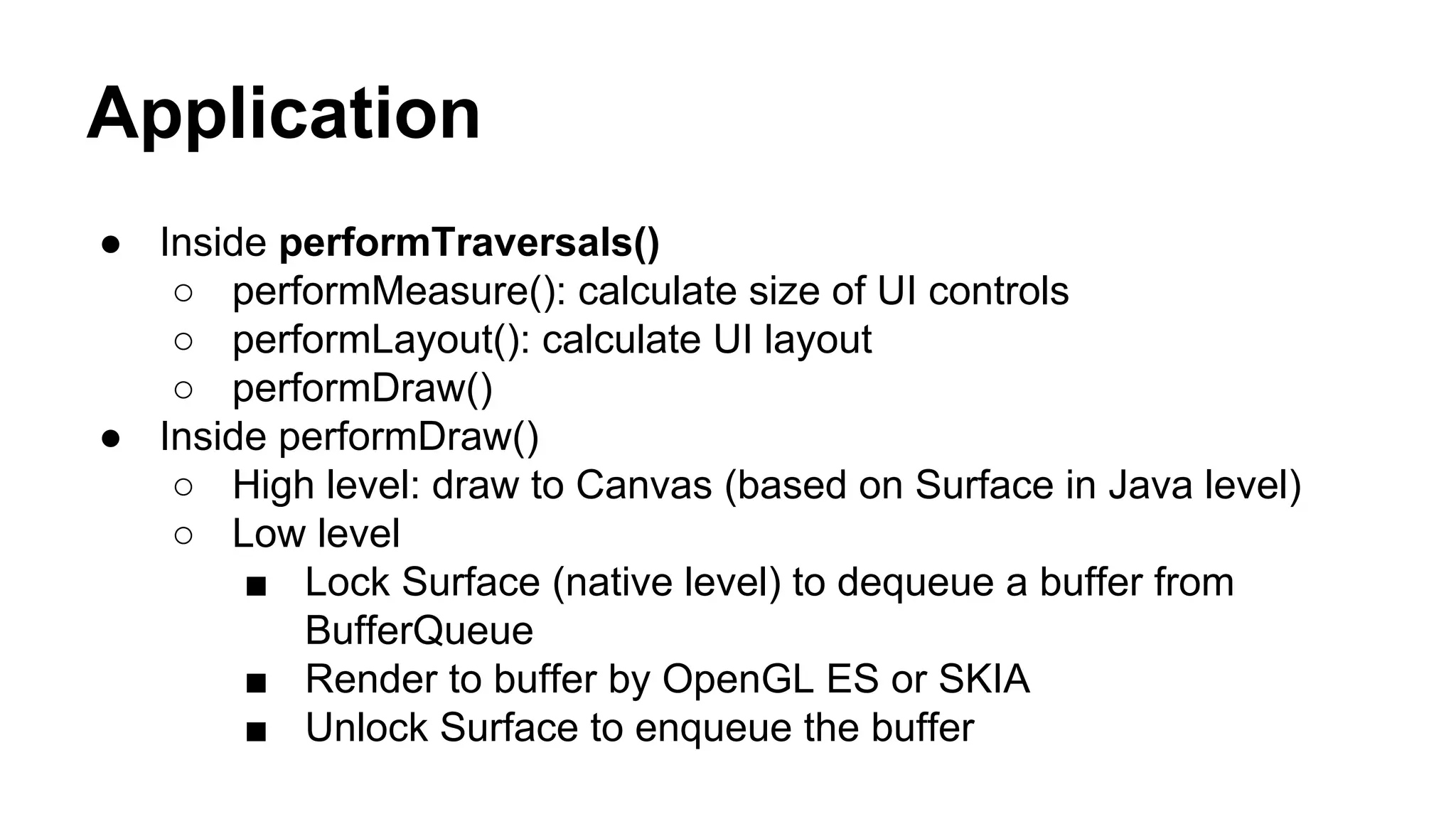
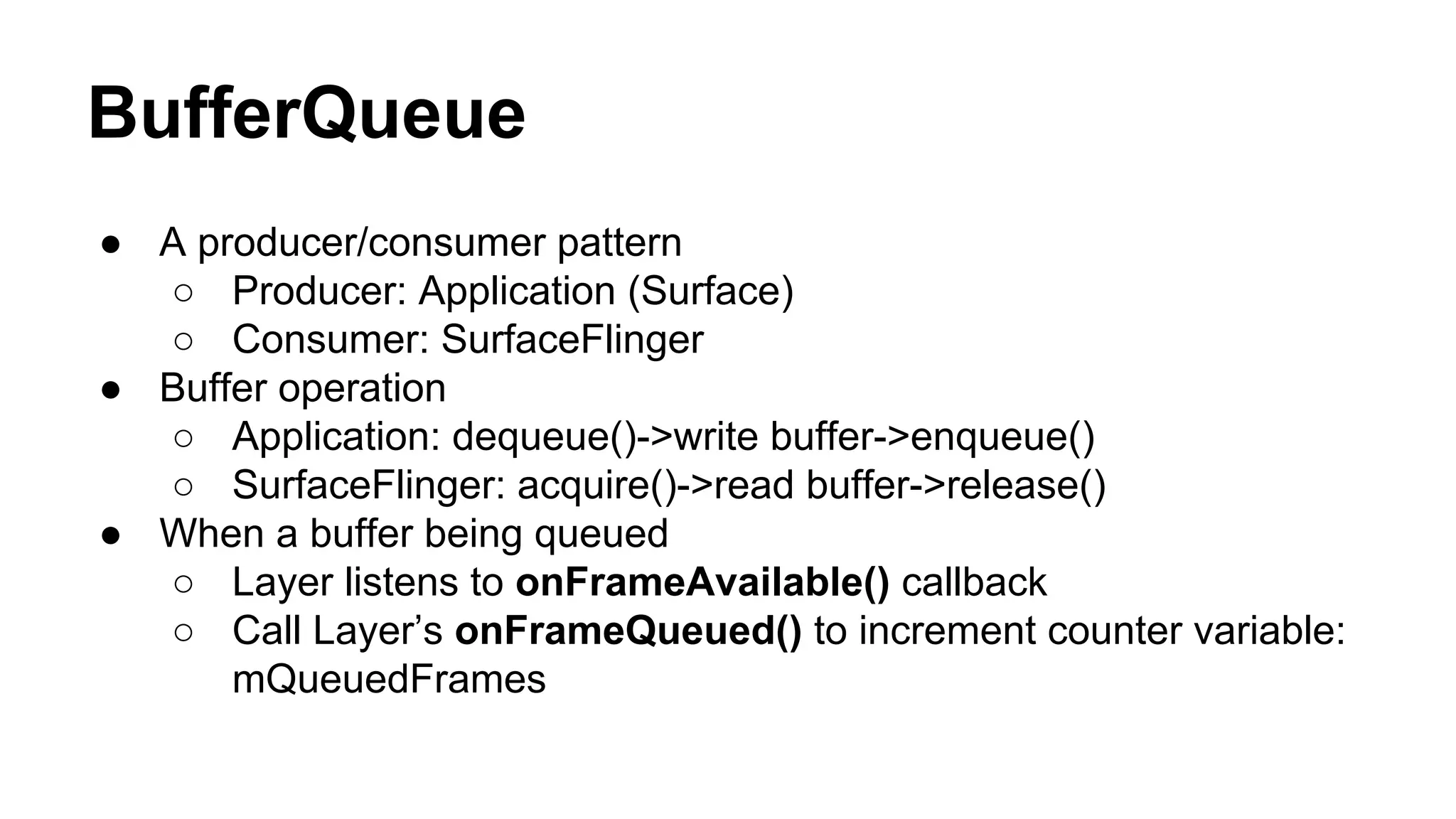
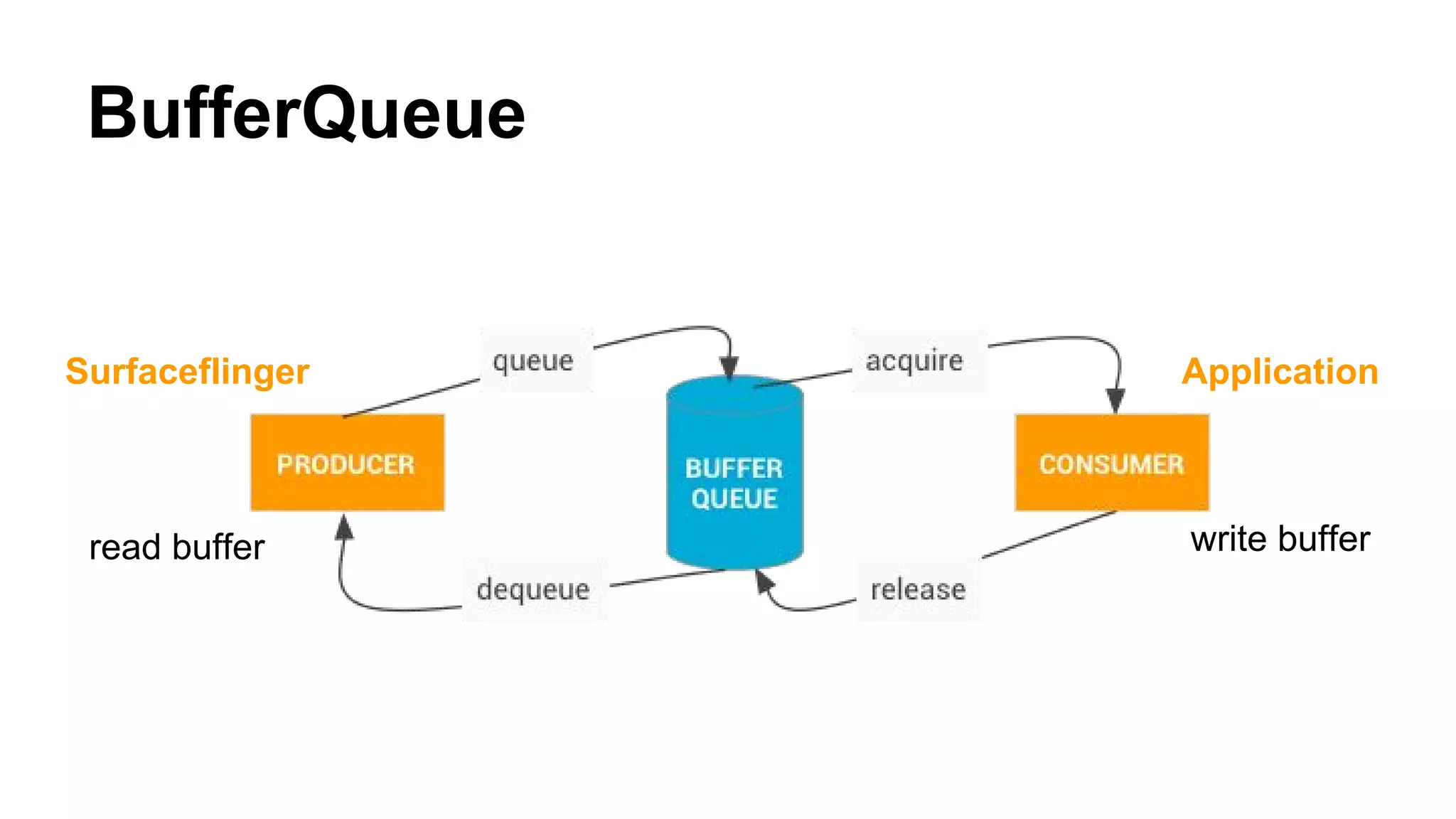
The Android graphics architecture uses SurfaceFlinger to composite surfaces from apps into the final display. Apps draw to surfaces using a canvas, which can target OpenGL or a software renderer. Views define a display list of drawing commands. SurfaceFlinger receives surfaces from apps and window status from WindowManager to composite surfaces in z-order before each VSYNC signal.