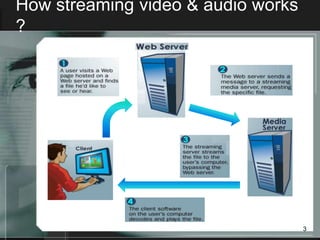
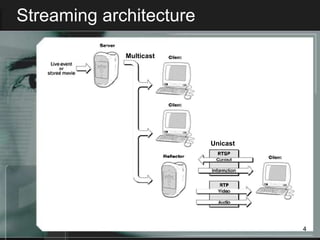
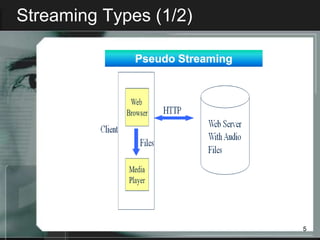
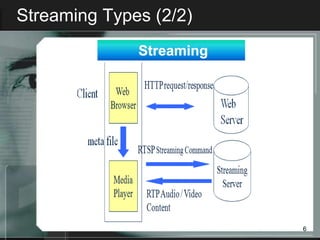
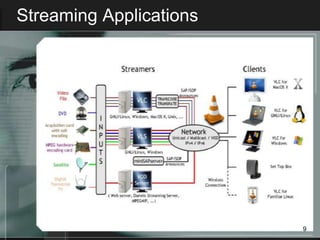
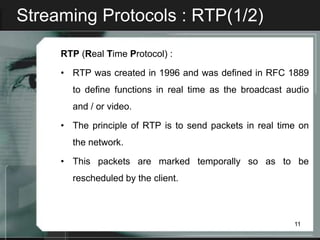
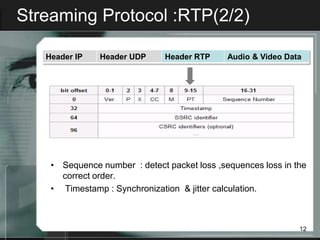
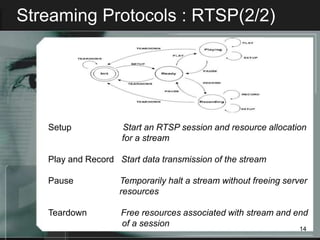
Streaming allows audio and video content to be delivered over the internet without requiring users to wait for files to fully download. It works by segmenting files into packets that are played as they are received. There are two main types of streaming architectures: multicast, which broadcasts content to multiple clients simultaneously, and unicast, which delivers private streams to each client individually. Common streaming applications include video on demand, web-based TV, music distribution, and internet radio. Key streaming protocols are HTTP, FTP, RTP for real-time transport, and RTSP for controlling multimedia delivery and providing functions like play, pause and stop.