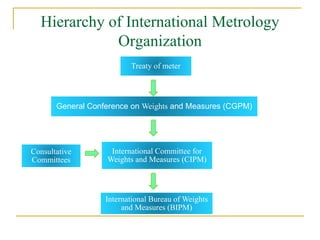
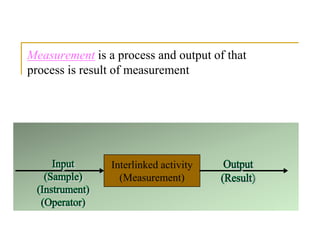
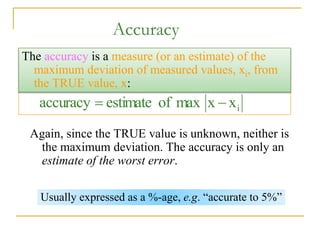
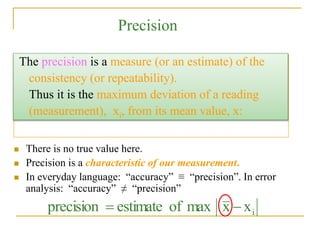
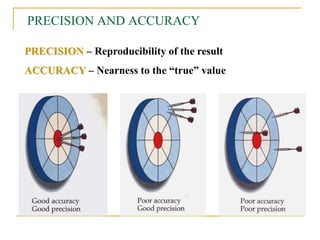
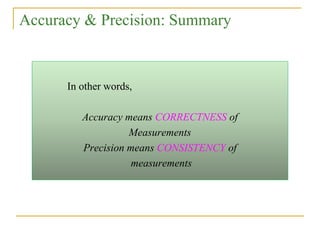
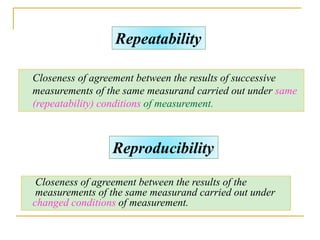
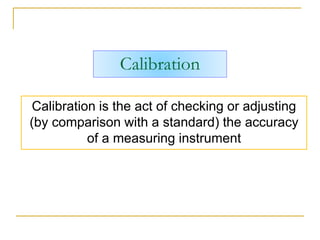
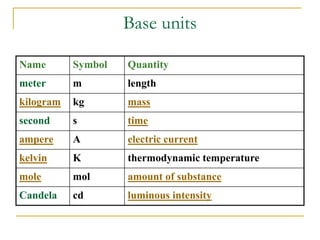
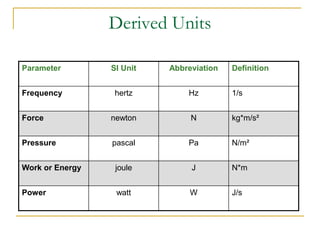
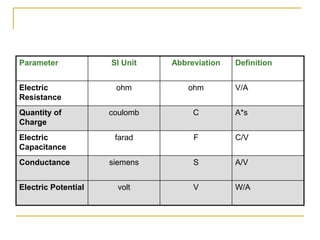
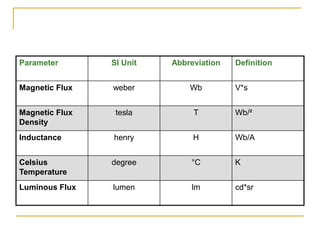
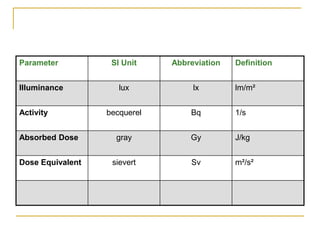
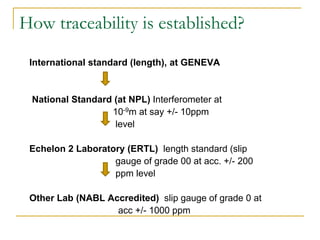
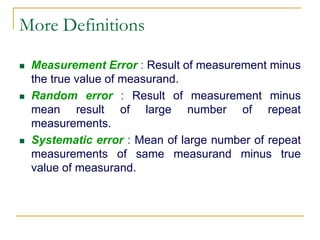
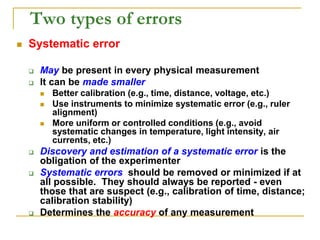
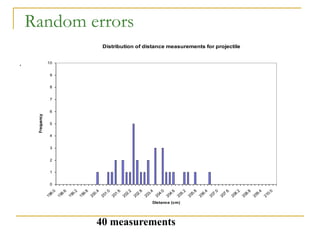
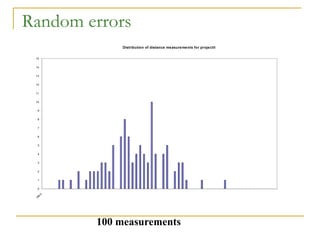
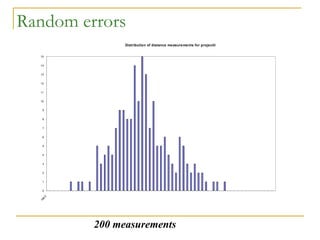
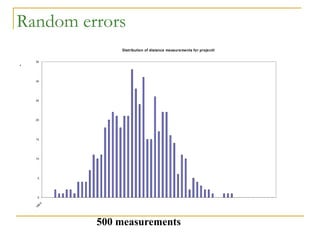
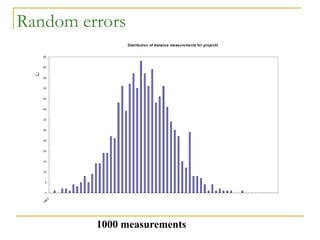
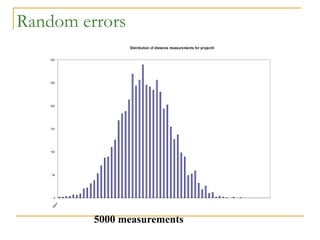
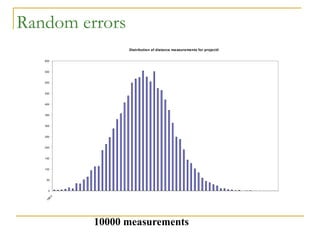
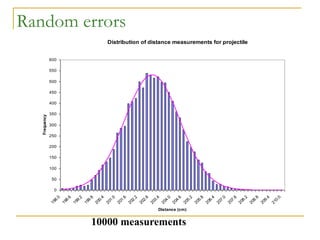
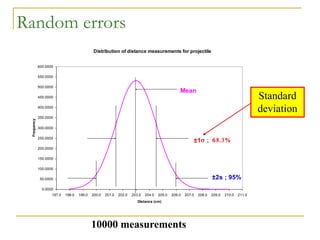
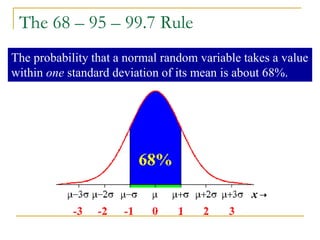
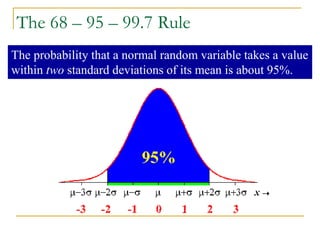
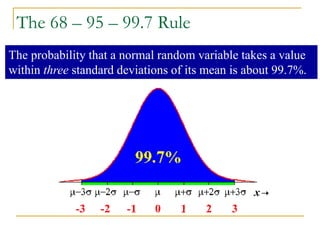
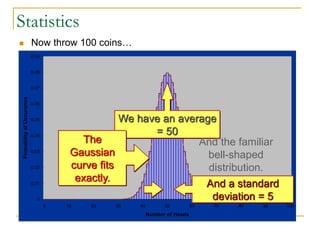
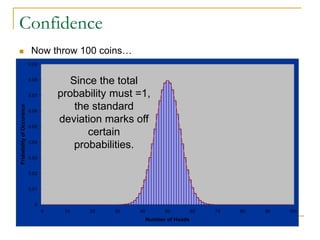
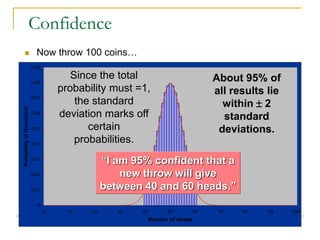
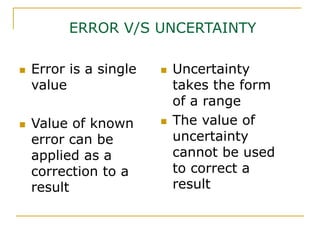
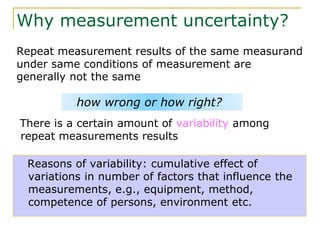
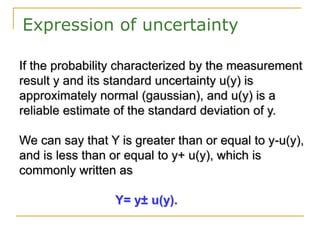
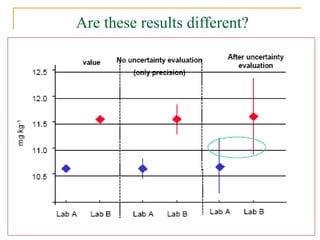
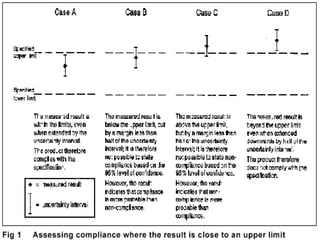
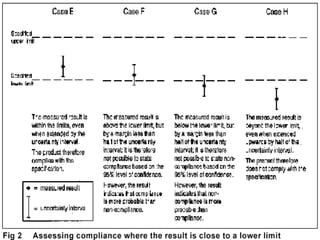
The document discusses measurement uncertainty and inter-laboratory comparisons. It defines key terms like metrology, traceability, accuracy, precision, random and systematic errors. Metrology is the science of measurement and embraces experimental and theoretical determinations at any level of uncertainty. The International System of Units (SI) provides standardized units for measurements. Traceability ensures measurement results can be linked to international standards through an unbroken chain of comparisons. Random errors are due to chance and average out over many measurements, while systematic errors remain constant or change in a known way.