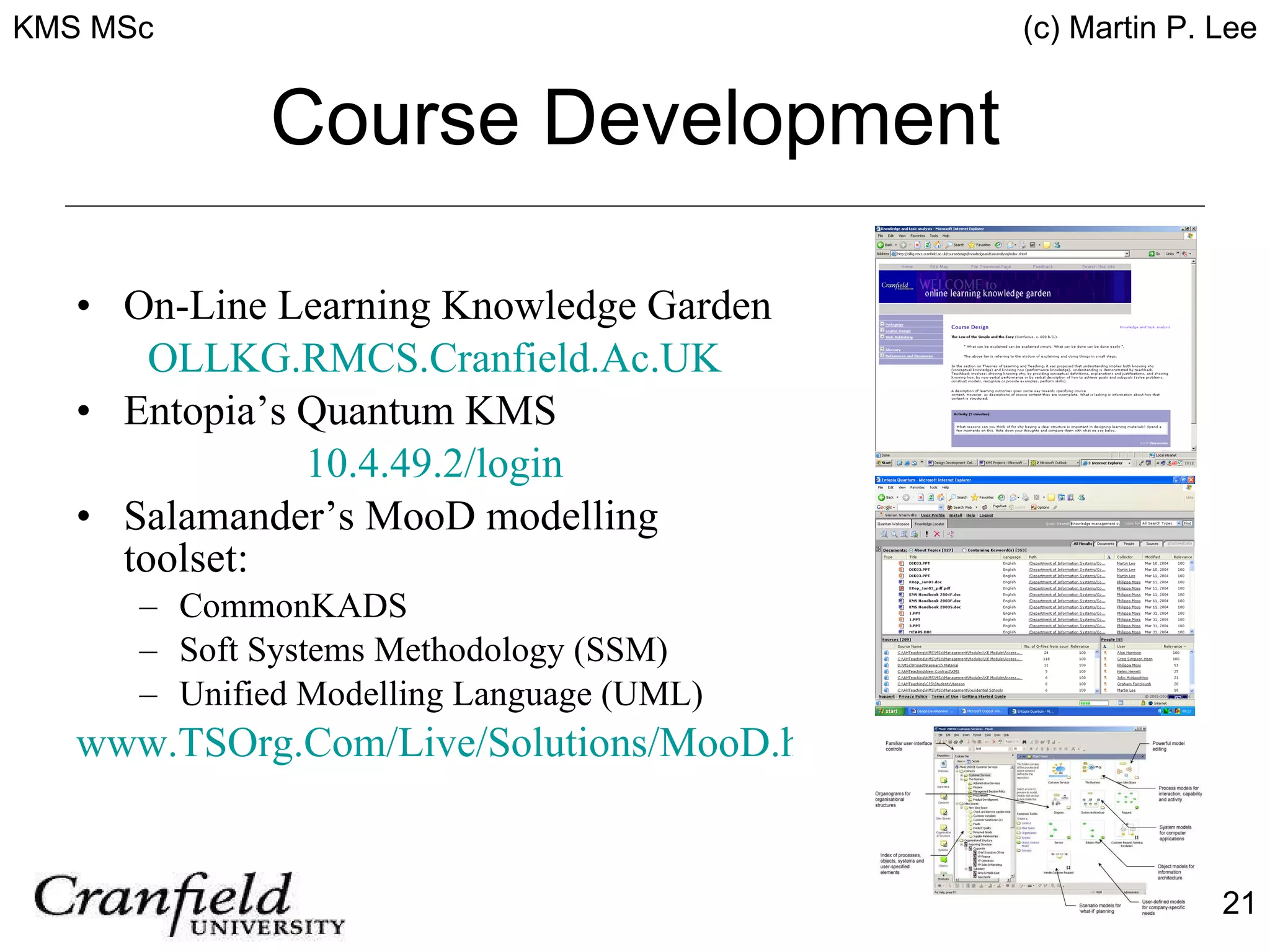
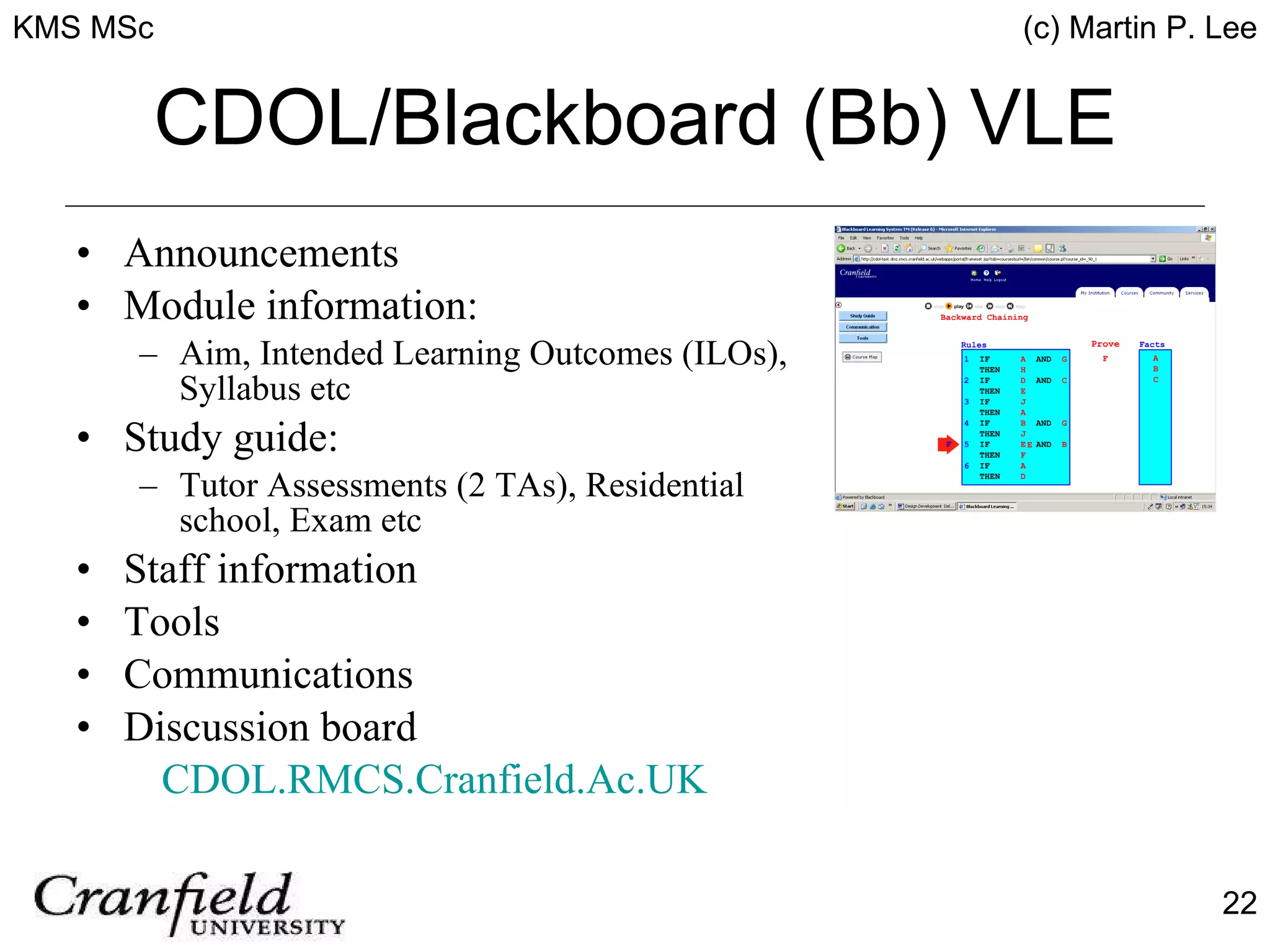
The document describes an innovative blended Master's in Knowledge Management Systems (KMS) offered by Cranfield University and the Royal Military College of Science. The course is designed to equip learners with the foundations of knowledge management through 10 modules covering topics like organizational knowledge, knowledge management systems, knowledge discovery and more. It uses a blended learning approach including online and residential components, and applies knowledge management principles in its design to provide an interactive learning experience. The course has been successfully implemented and evaluated, being adopted by the British Army as well.