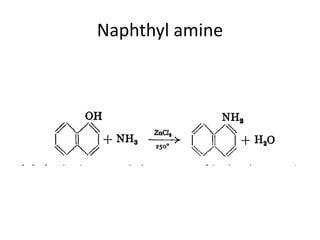
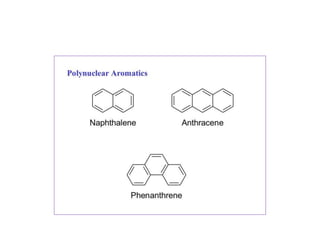
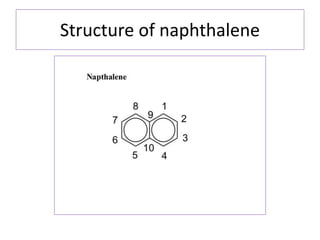
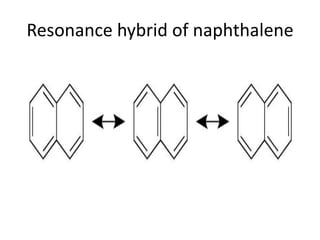
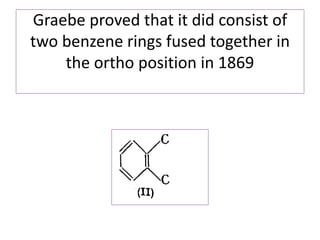
1) Naphthalene consists of two benzene rings fused together in the ortho position.
2) It is obtained from coal tar and purified by distillation.
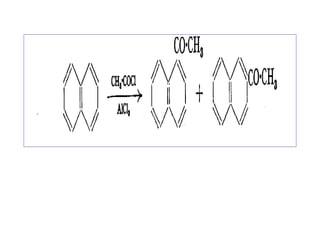
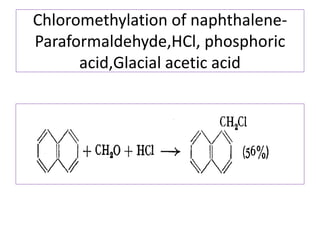
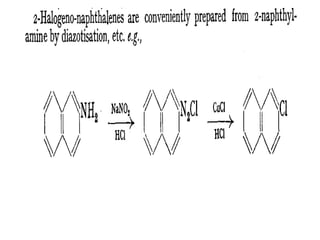
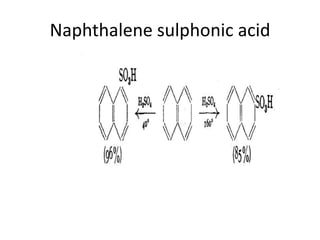
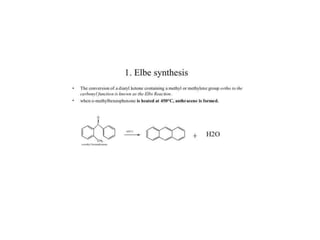
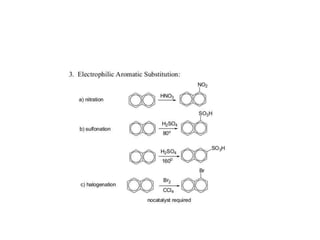
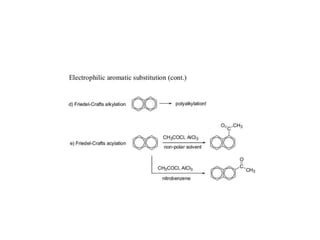
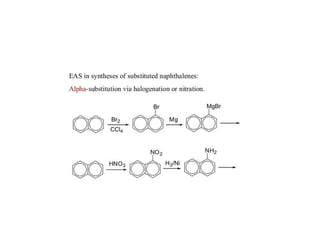
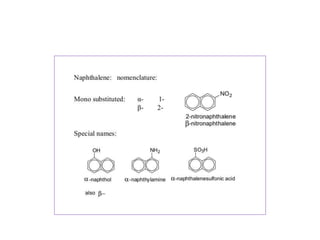
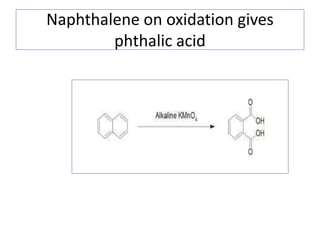
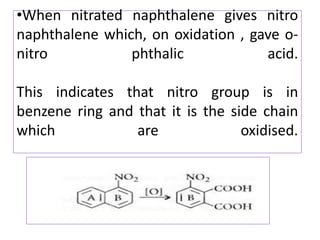
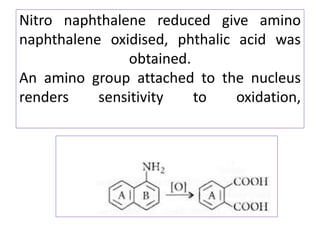
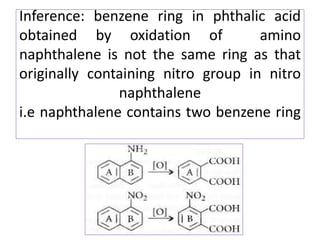
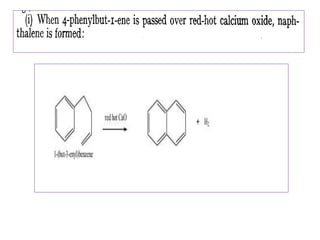
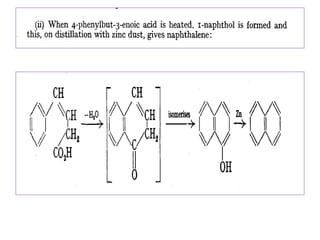
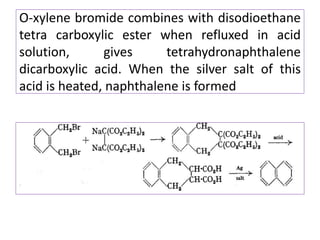
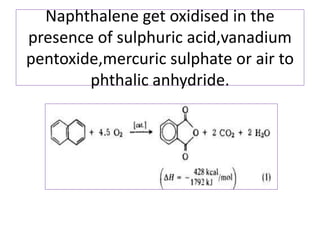
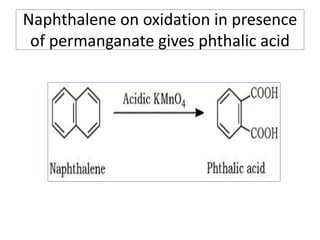
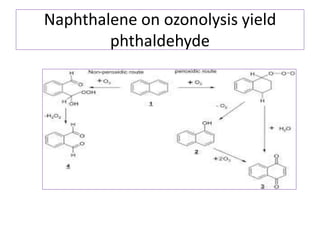
3) Naphthalene undergoes substitution and oxidation reactions. Common substitution products include nitro-, amino-, and sulfonated-naphthalenes. Oxidation of naphthalene produces phthalic acid.






![Fries rule
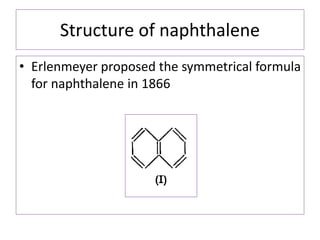
• The most stable form of polynuclear aromatic
compound is that form which has maximum
number of benzenoid ring i.e three double
bonds in each individual ring.
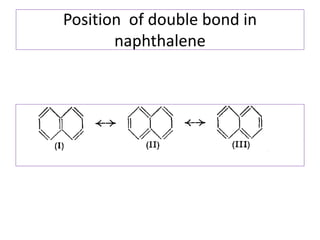
• According to fries naphthalene has structure I
[ has two benzenoid ring] and not the
structure of II and III [ has one benzenoid ring]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naphthalene-201119044255/85/Naphthalene-25-320.jpg)


![• Introduction of second substituent can give
rise to homonuclear substitution [ substitution
in the same ring] or heteronuclear
substitution [ second substitution in another
ring]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naphthalene-201119044255/85/Naphthalene-36-320.jpg)