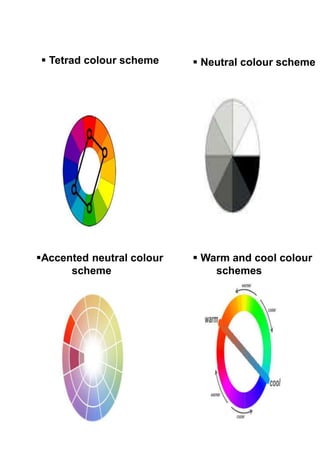
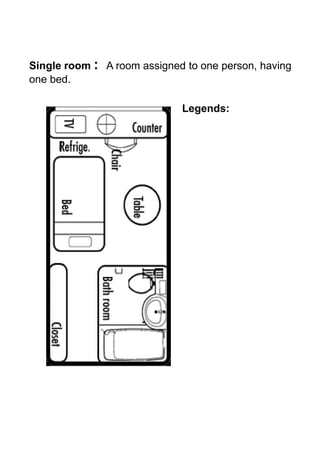
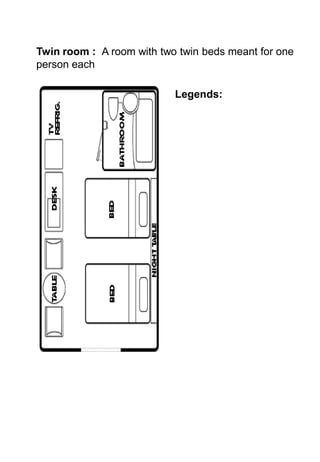
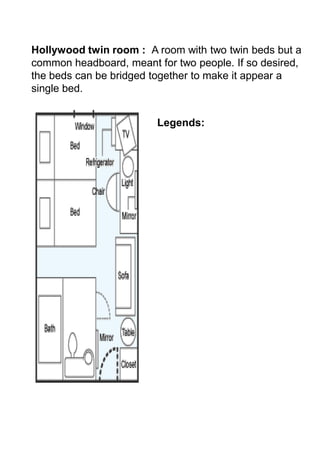
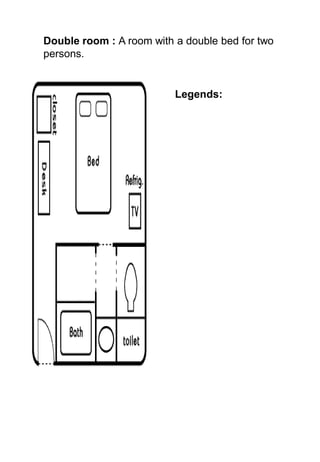
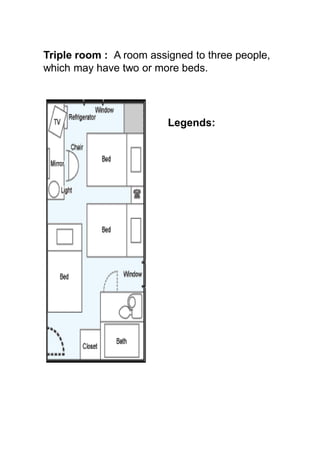
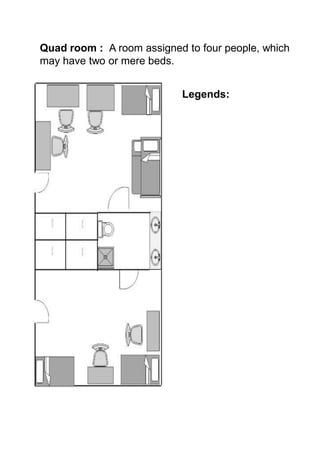
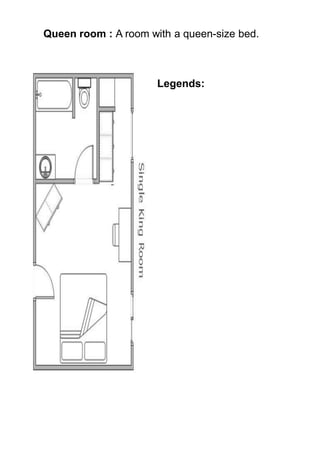
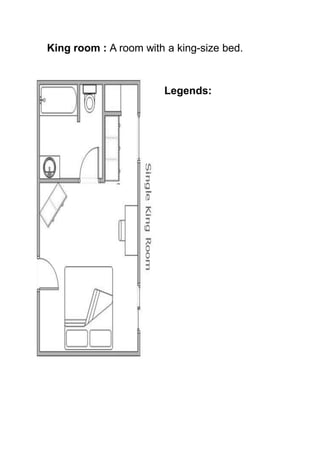
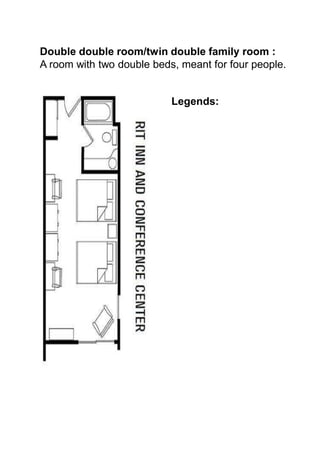
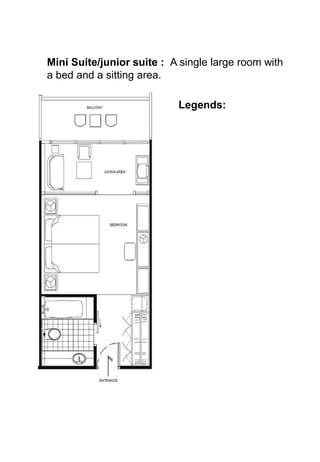
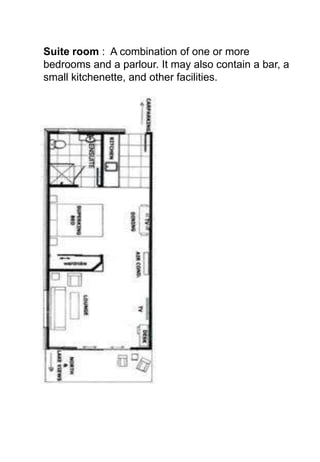
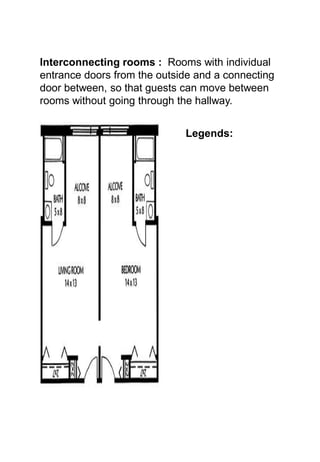
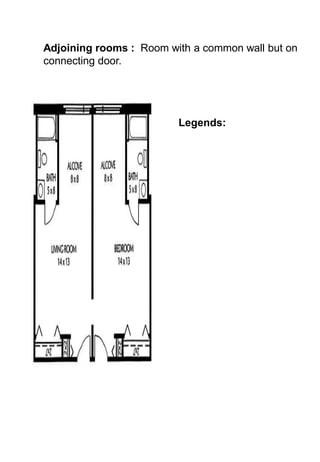
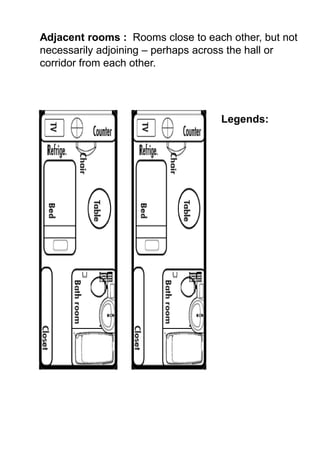
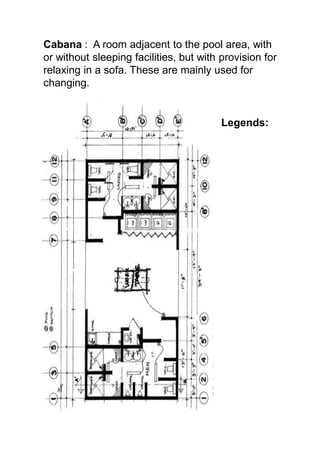
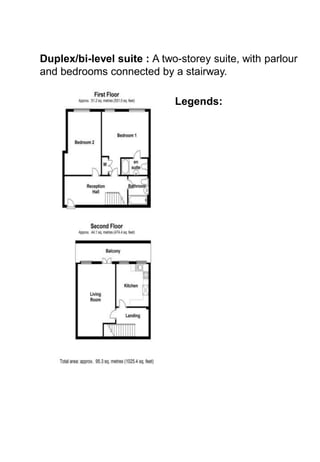
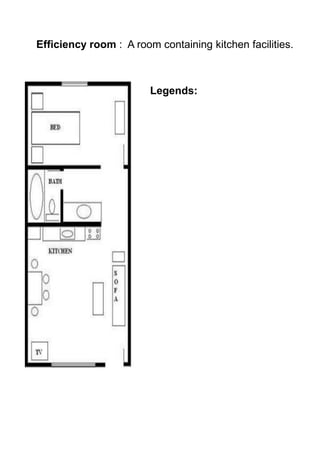
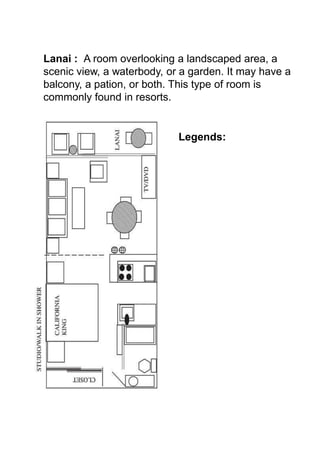
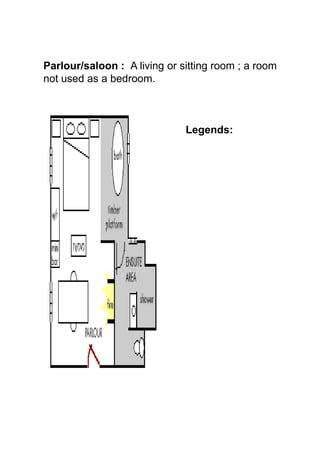
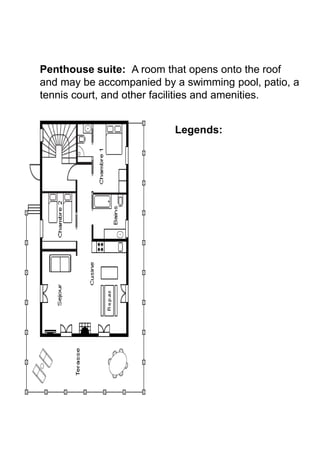
The document discusses hotel room layouts and types. It begins by defining layout and describing the objectives and strategic importance of layout. It then classifies different types of layouts and describes various color schemes used in hotel room design. The document outlines the four main operational sectors in hotels and notes that housekeeping generates 50% of hotel revenue. It provides details on over 20 different types of hotel rooms, including single, twin, queen, king, suite, connecting and adjoining rooms. Diagrams illustrate examples of common room layouts.