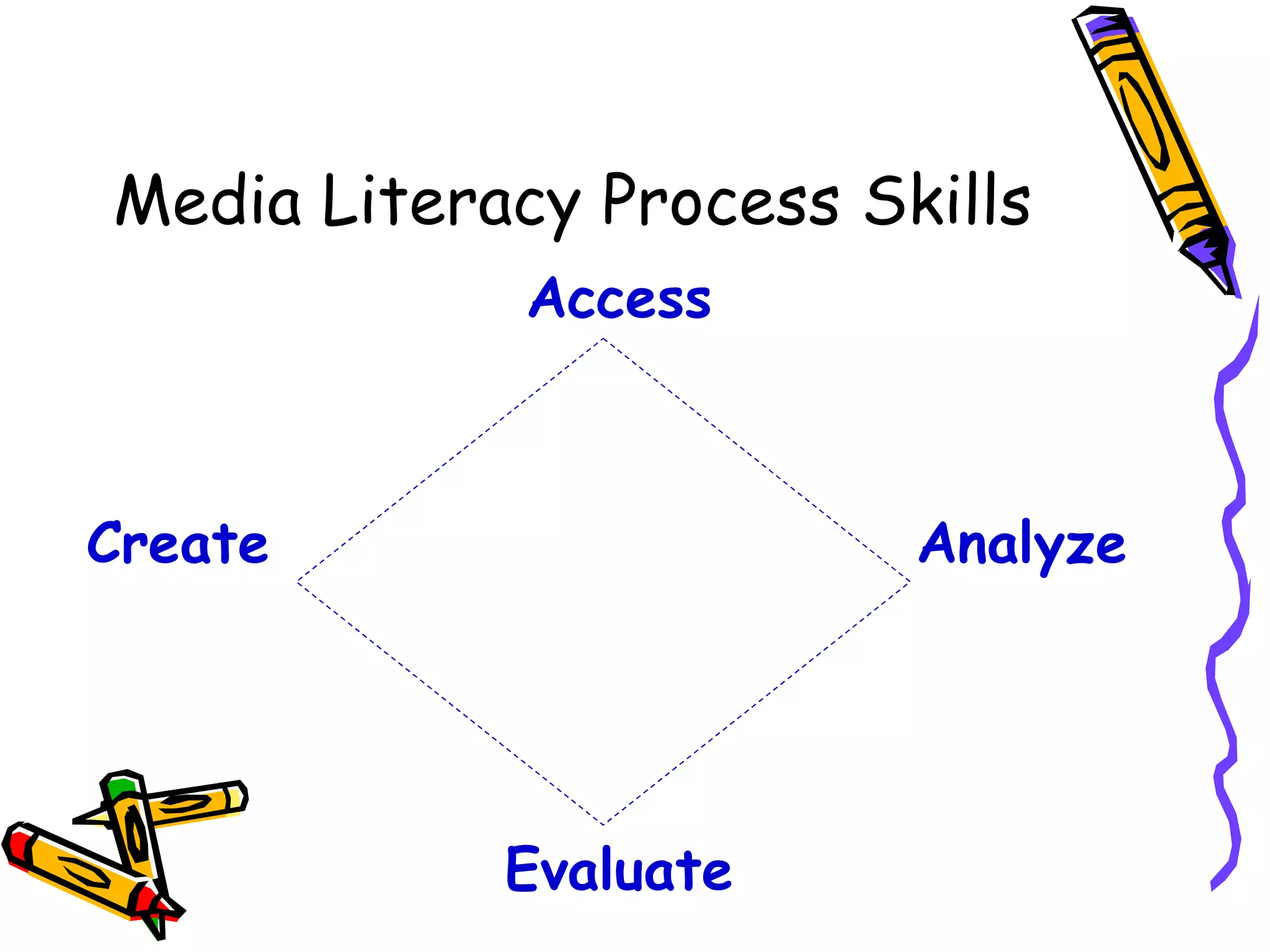
The document discusses media literacy and provides statistics about media consumption habits. It notes that the average American watches over 4 hours of television per day and sees 2 million commercials by age 65. By age 18, children have watched 17,000 hours of television. The document defines media literacy as the ability to access, analyze, evaluate and create media. It explains the key skills involved - accessing information from different sources, analyzing messages by comparing/contrasting and identifying facts vs opinions, evaluating the quality and value of messages, and creating new media content.