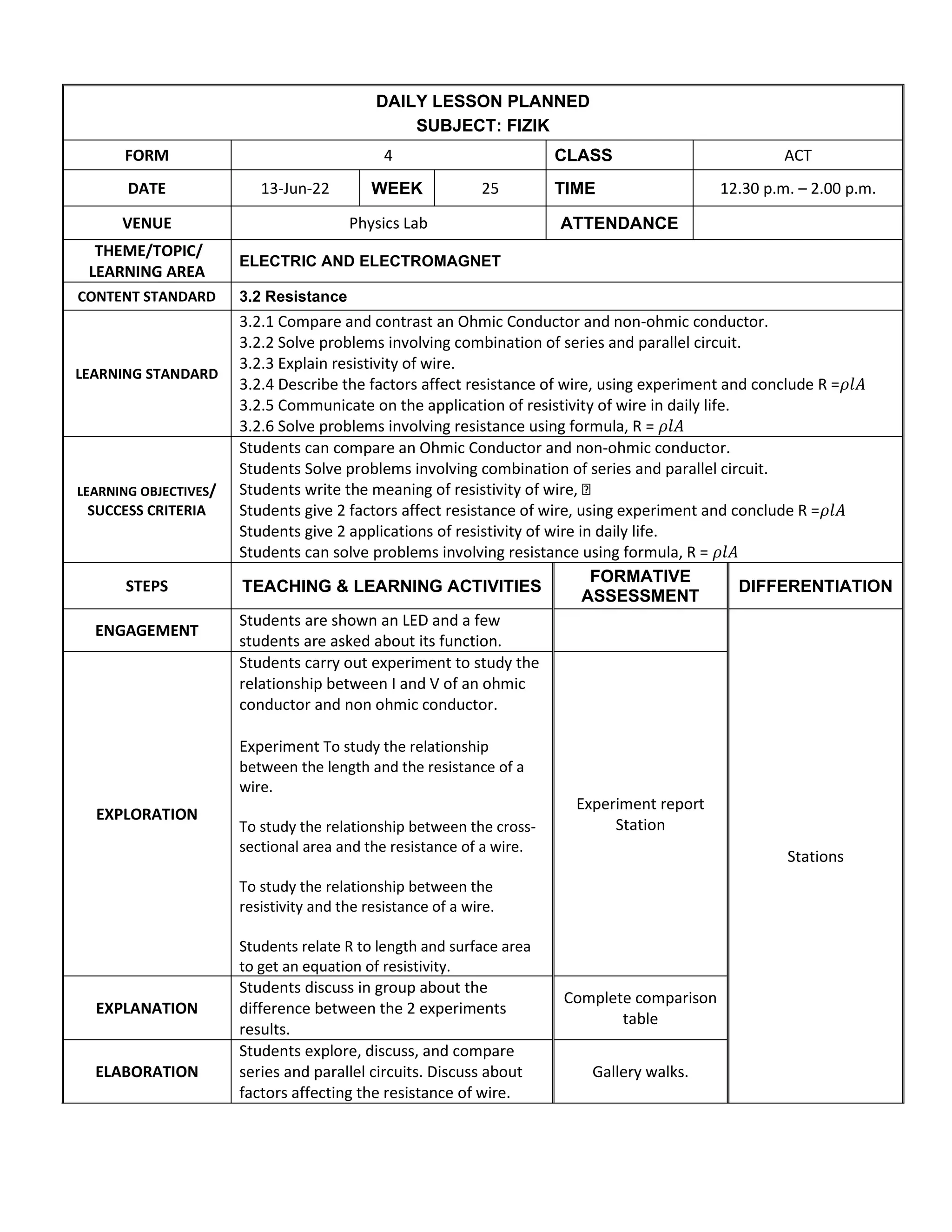
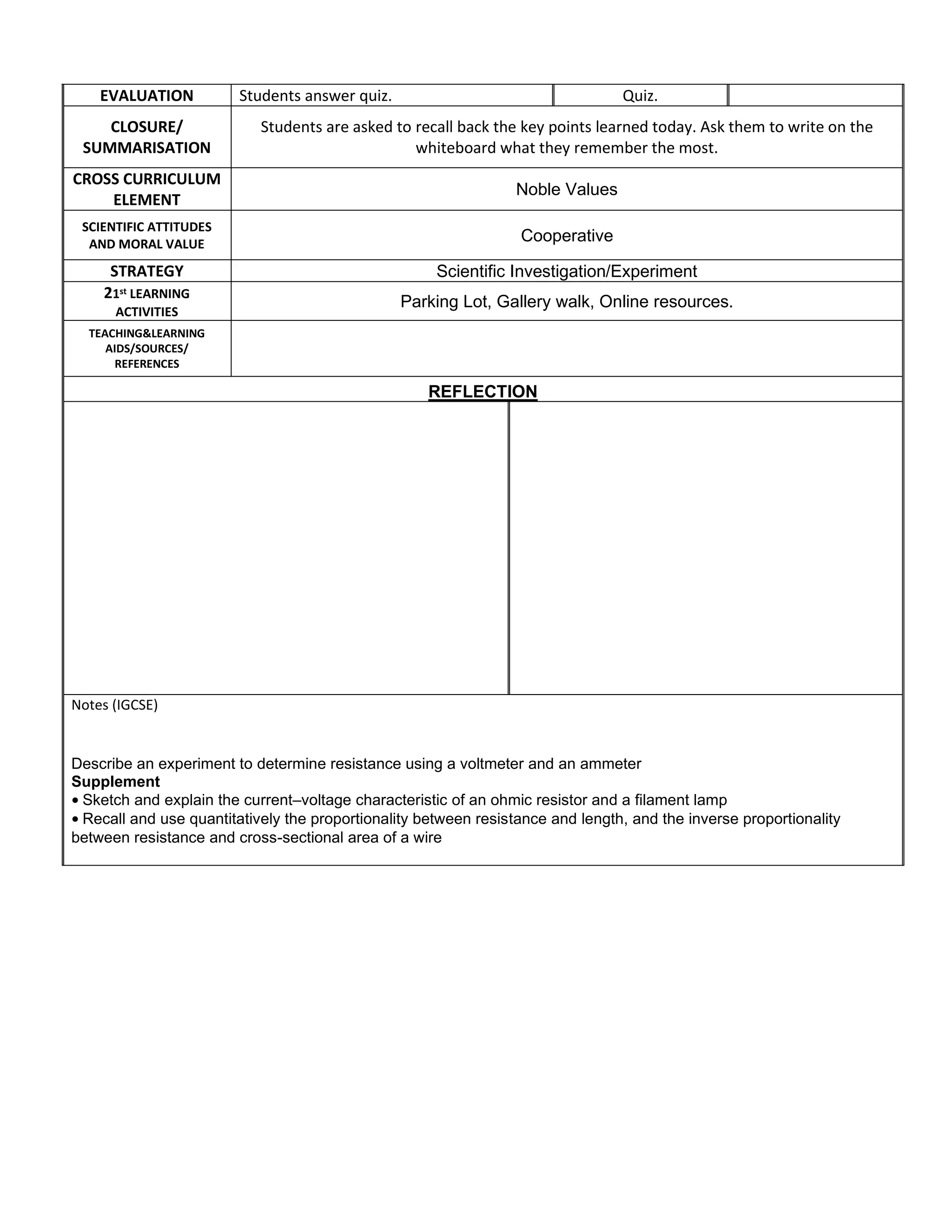
This document outlines a daily lesson plan for a Form 4 physics class on electric and electromagnetism. The lesson focuses on resistance, with learning standards around comparing Ohmic and non-Ohmic conductors, solving series and parallel circuit problems, and understanding the factors that affect resistance. Students will conduct experiments on the relationships between resistance and length/area of a wire. They will also explore and discuss series and parallel circuits and the factors affecting resistance. Formative assessment includes an experiment report and quiz.