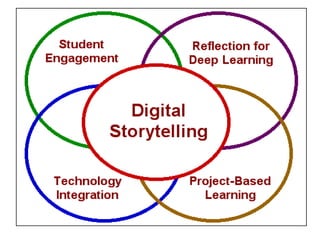
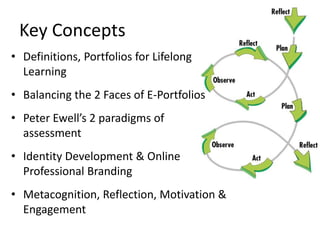
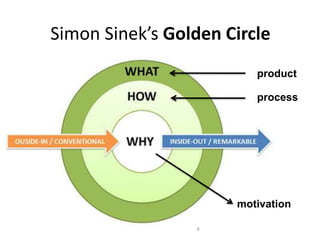
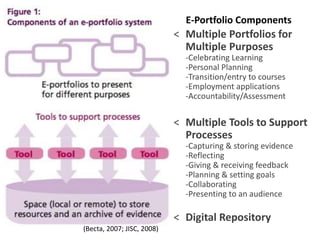
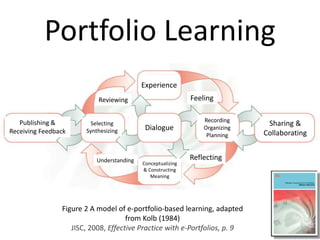
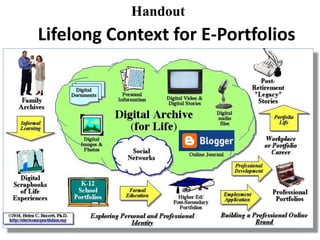
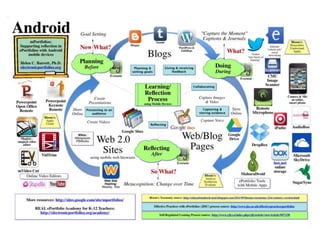
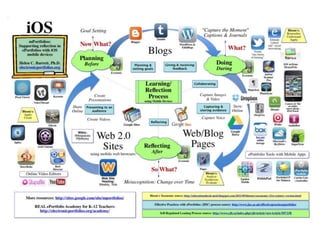
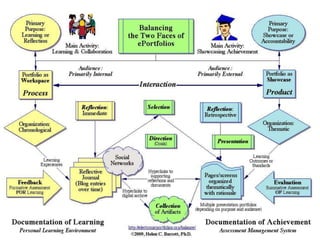
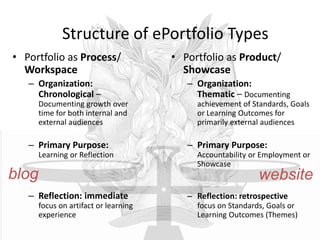
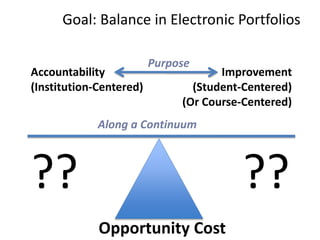
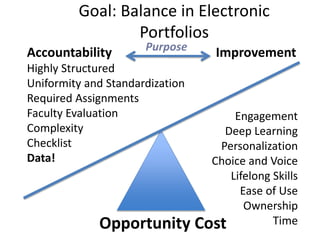
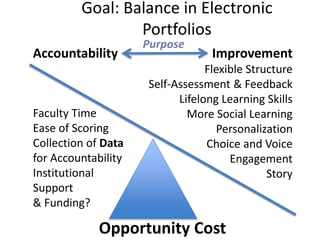
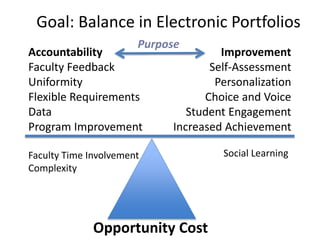
This document discusses balancing reflection and assessment in ePortfolios. It defines ePortfolios as both a process and product, noting they can serve learning/reflection purposes as well as assessment/accountability functions. The key is finding a balance between these two "faces" of ePortfolios to maximize student engagement and deep learning while also meeting institutional needs for assessment data. Tools and strategies are suggested for designing ePortfolios that integrate both reflection and assessment depending on the specific purpose. Motivation is also addressed, noting ePortfolios should support student autonomy, mastery, and sense of purpose to drive intrinsic rather than just extrinsic motivation.







![What is a Portfolio in Education?
A portfolio is a purposeful
collection of [academic] work that
exhibits the [learner/worker’s]
efforts, progress and
achievements in one or more
areas
[over time].
(Northwest Evaluation Association, 1990)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fresno2015-balancing-150823231920-lva1-app6891/85/Fresno2015-balancing-10-320.jpg)



































![Student Engagement!
CQ + PQ > IQ (Friedman, 2006)
[Curiosity + Passion > Intelligence]
Find voice and passions through
choice and personalization!
Portfolio as Story
Positive Digital Identity
Development - Branding
“Academic MySpace”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fresno2015-balancing-150823231920-lva1-app6891/85/Fresno2015-balancing-68-320.jpg)