Endo.practical
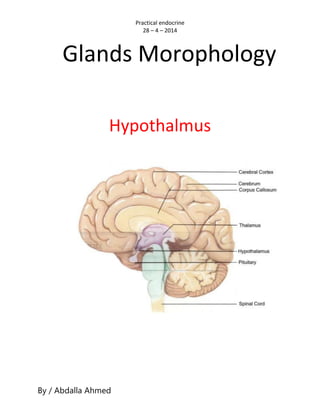
- 1. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Glands Morophology Hypothalmus
- 2. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed
- 3. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Thyroid gland
- 4. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Parathyroid gland Adrenal gland
- 5. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Pancreas Hormone Assay Test • Many hormones can be measured (Assayed) in the blood to give an indication of metabolic process and conditions, or “hormone imbalance” • Hormone assays are blood test – a few millimeters of blood from vein is requrid . • Hormone test is give a concentration of specific hormone in the blood stream .
- 6. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed • These results are compared to a reference range of “normal” values, obtained testing well people without symptoms . • The specific hormone level may be therefore be low, normal or high. • Each of these results needs to be carefully interpreted by a doctor who understands the complex interaction in endocrine system . A high or low level may not indicate disease, and similarly, a normal test does not always exclude abnormality . The most common hormone test is: Thyroid function tests: • Thyroid function test (TFT) are a biochemical measure of the amount of thyroid hormones { Thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3) } which can be directly measured, both in their total blood Concentration in the blood stream, to determine whether the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive . • The most commonly performed test is the Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), an indicate measure of thyroid hormone levels. • The secration of TSH is regulated by thyroid hormone levels. - Thus a high TSH usually means that Thyroid hormone levels are low - TSH is trying to stimulate the underactive Thyroid gland. - Low TSH usually means that high thyroid hormone levels from an overactive gland are suppressing TSH production .
- 7. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Female Infertility Test: Female hormonal testing is recommended when irregularities are identified in menstrual cycle or physical examination. These including estrogen and progesterone levels, FSH and LH levels, Inhibin, Testosterone and other androgens, thyroid tests, and Prolactin levels. • The results of these hormonal tests help determine the best course of treatment for each individual patient. Radioimmunoassay • Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is a very sensitive in vitro assay technique used to measure concentrations of antigens (for example, hormone levels in the blood) by use of antibodies. As such, it can be seen as the inverse of a radiobinding assay, which quantifies an antibody by use of corresponding antigens.
- 8. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed • Although the RIA technique is extremely sensitive and extremely specific, requiring specialized equipment, it remains among the least expensive methods to perform such measurements. • It requires special precautions and licensing, since radioactive substances are used. • It used usually for the measurement of Blood TSH, LH,FSH and Growth Hormones . ELISA • The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a test that uses antibodies and color change to identify a substance. • ELISA is a popular format of biochemistry assay that uses a solid- phase enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a substance, usually an antigen, in a liquid sample or wet sample. • The ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine and plant pathology, as well as a quality-control check in various industries. Types of ELISA : Indirect ELISA Sandwich ELISA Competitive ELISA Multiple and portable ELISA Hormone Assay Techniques ELISA :
- 9. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed
- 10. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed
- 11. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed ELISA PLATE ELISA Reader
- 12. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Estrous Detection Estrus Cycle •It is the reproductive cycle of female animal other than primates. It has 4 phases: 1. Proestrus. 2. Estrus. 3. Metesrus. 4. Diestrus. 5. Anestrus. Proestrus • One or several Follicles of the ovary start to grow. Their number is species specific . • Typically this phase can last as little as one day or as long as three weeks. depending on the species. • Under the Influence of estrogen the lining In the uterus (endometrium) starts to develop. • Some animals may experience vaginal secretions that could be bloody. • The female is not yet sexually Receptive.
- 13. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Estrus : • Estrus refers to the phase when the female is Sexually receptive ("in heat”). • Under regulation by gonadotropic hormones, ovarian follicles mature, and estrogen secretions exert their biggest influence. • The female then exhibits sexually receptive behavior, a situation that may be signaled by visible physiologic changes. • Ovulation may occur spontaneously in some species. Metestrus : • This is phase is characterized by the activity of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. • The signs of estrogen stimulation subside and the corpus luteum starts to form. • The uterine lining begins to appear . Diestrus : In the absence of pregnancy the diestrus phase (also termed pseudo- pregnancy) terminates with the regression of the corpus luteum. The lining in the uterus is not shed, but is reorganized for the next cycle.
- 14. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Anestrus : • Anestrus refers to the phase when the sexual cycle rests. • This is typically a seasonal event and controlled light exposure through the pineal gland that releases melatonin . • Melatonin may repress stimulation of reproduction in long-day breeders and stimulate reproduction in short-day breeders. • Melatonin is thought to act by regulating the hypothalamic pulse activity of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone. • Anestrus is induced by time of year, pregnancy, lactation, significant illness, Chronic energy deficit and possibly age. Estrus Detection l-Personal observtltion . •2 times dally for 30 min. )in the morning & In the evening) is essential Sings of heat : • Physical mounting, or "standing heat," occurs within the first 12-18 hours after the onset of heat(cow) • Roughened tail-head; if a cow has been ridden by other animals, the half on her tall-head could be standing up or completely missing • Dirty streaks and marks on lower hips, sides, or shoulders, In wet Weather or areas, the forefeet of rider animals may leave muddy traces on the sides and hips of cows in heat. • Nervousness and restlessness • Grouping together; animals coming into heat will usually congregate in small groups (three to five animals)
- 15. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed • Swollen vulva; reddening (bright cherry pink), and mucus discharge as an indicator for estrus • Bloody discharge at the end of estrus usually indicates a missed heat; observe this animal for return to heat in 18-24 days . 2- Records 3-Closed circus television (Video Cameras) 4-Temperature Measurement • There is a drop in temp. 1- 2 days before estrus then it rise again 5-Pedometer •This device is used along with a computer to determine how far an animal has walked. • Animals in heat are usually restless and may walk long distances searching for bulls. 6- Heat mount detectors (KAMAR). • These are devices loaded with dye attached above the cow's tail head. • They are sensitive to pressure and are activated when one animal mounts another. (dis adv.: may not be suitable because herd management conditions occasionally may result in false readings, complete loss of the device and missed heat periods).
- 16. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed 8-Mesarment of vaginal resistance (probe): • Falling in vaginal electric resistance during estrus (inflammation) 9- Teaser animal (mount (lipido) without conception ) • Treated males (estrogen) • (Young bulls-treated steers (testosterone) • treated females ( Estrogen) • Vasectomized male. Vaginal Smear : • Aim : • Vaginal smears may be taken to provide information on estrous cyclicity at various intervals. • Ovulation occurs at approximately midnight after the pro-oestrous stage, when the females become receptive to the male. • The classic stages of the rat oestrous cycle can be designated as estrous (E), metestrous (M), di-estrous (D) and pro-estrous (P).
- 17. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Estrous :
- 18. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Metestrus :
- 19. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Pro-estrus :
- 20. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Di-estrus:
- 21. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Semen Evaluation semen Collection: • Semen was collected from all animals at a frequency • Frequency of semen collection - Bull Buffalo. twice a day, 2 days per week. -Ram, Buck 3-4 times a day for several weeks -Stallion: one ejaculate every 2-3 days • Collection of semen was carried out by using artificial vagina. • Anestrous female was used as Teaser. •Semen evaluation : • Immediately after collection, the ejaculates were transferred to the laboratory and were placed in the incubator adjusted at 37 0 c. • All surfaces with which the semen get in contact were kept warmed at 37 0 c. • Semen quality was measured by: volume of the ejaculate, individual sperm motility, sperm cell concentration, alive and abnormal sperm percent and biochemical analysis: I- Physical evaluation: Volume of the ejaculate: it is measured to the nearest 0.1 ml Using a graduated collection cup.
- 22. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Evolution of sperm density : Scales Gross appearance Approximate sperm concentration ( 10 sperm / ml ) 0 Clear to cloudy 0 to 200 1 Cloudy to milky 200 to 400 2 Milky 400 to 800 3 Thick milky 800 to 1200 4 creamy 1200 to 1800 5 Thick creamy 1800+ II- Microscopic evaluation: Mass motility : A tiny drop of Semen sample was placed on clean, dry, warm slide and examined microscopically using thermostatically controlled hot stage adjusted at 38-40 C . • Mass of activity of spermatozoa was Scored (0 - 5) according to the Intensity of the movement as follows: 0= no sperm movement 1= slight tail undulation without forward motion 2= slow tail undulation with slow ot stop and start forward motion 3: forward progression at a moderate Speed 4= rapid forward progression 5= very rapid progression In which cells are difficult to follow visually
- 23. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Alive and abnormal sperm percent : • Duplicate smears from each freshly collected ejaculate were stained with Eosin-Nigrosin stain to determine alive (unstained) and morphologically abnormal sperm percent. • A total of 200 sperm cell in were examined randomly, 100 in each of two smears. • Sperm cell abnormalities were classified into major sperm defects (are those that have been correlated to impaired fertility) and minor sperm defects (are those that seem to be of minor importance . Sperm concentration : Sperm-cell concentration per ml was measured by counting the number of spermatozoa present on both sides of a Neubauer improved haemocytometer after the semen had been diluted 1:100 in formalin and then multiplying by dilution factor.
- 24. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Normal Bull sperms : Sperms Abnormality:
- 25. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Two tails – bent tail – coiled tail - Folded tail with pyriform head
- 26. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Pregnancy Diagnosis 4. Detection of the fetus and fetal membranes: a. By rectal examination ( large animal) b. abdominal palpation (small animal e.g. rabbit ,cat ,dog) c. Ultrasonography: rapid, accurate, determination of fetal gender Ultrasonography : Picture from lecture
- 27. Practical endocrine 28 – 4 – 2014 By / Abdalla Ahmed Abdominal palpation : Rectal palpation :
