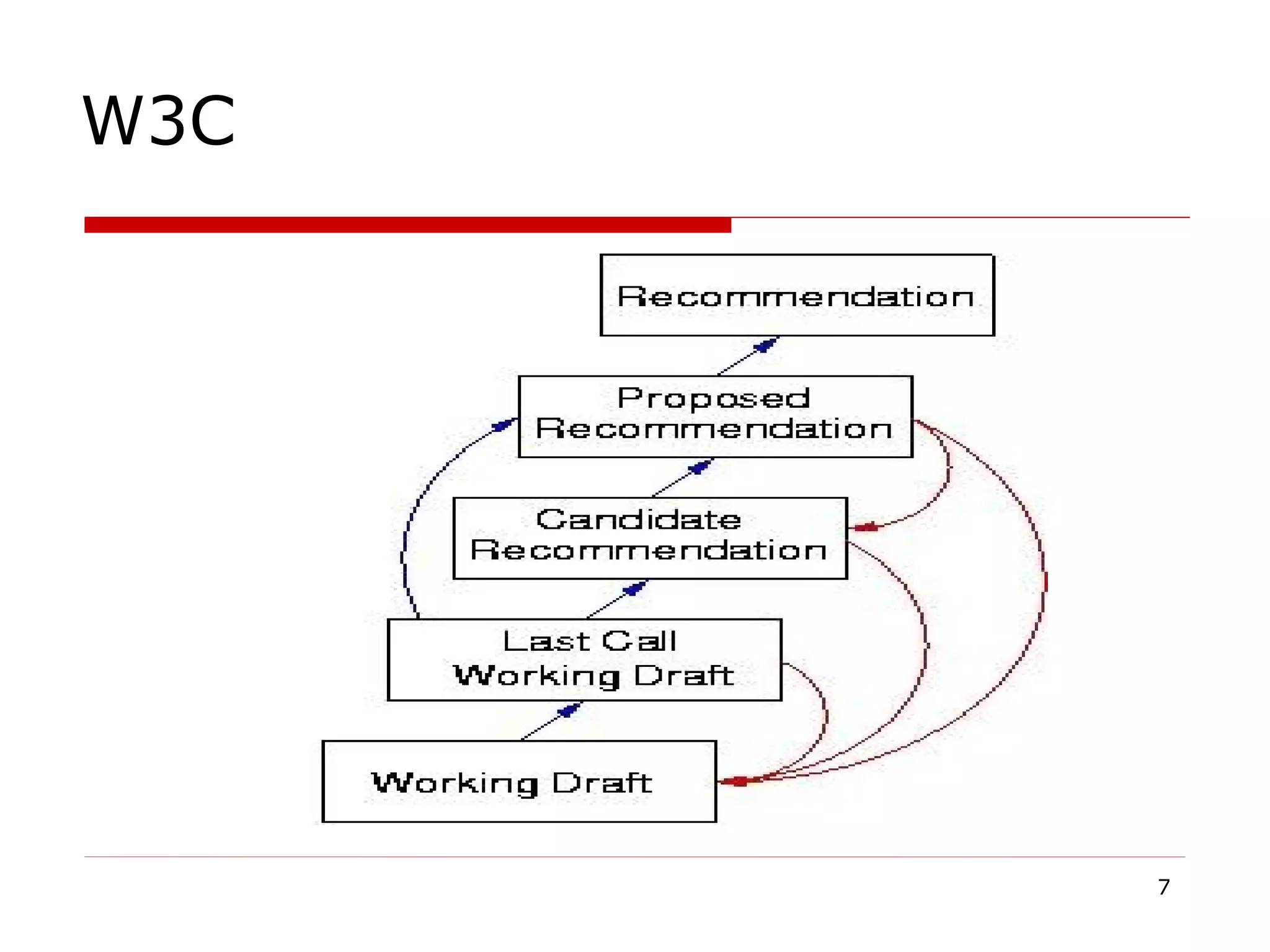
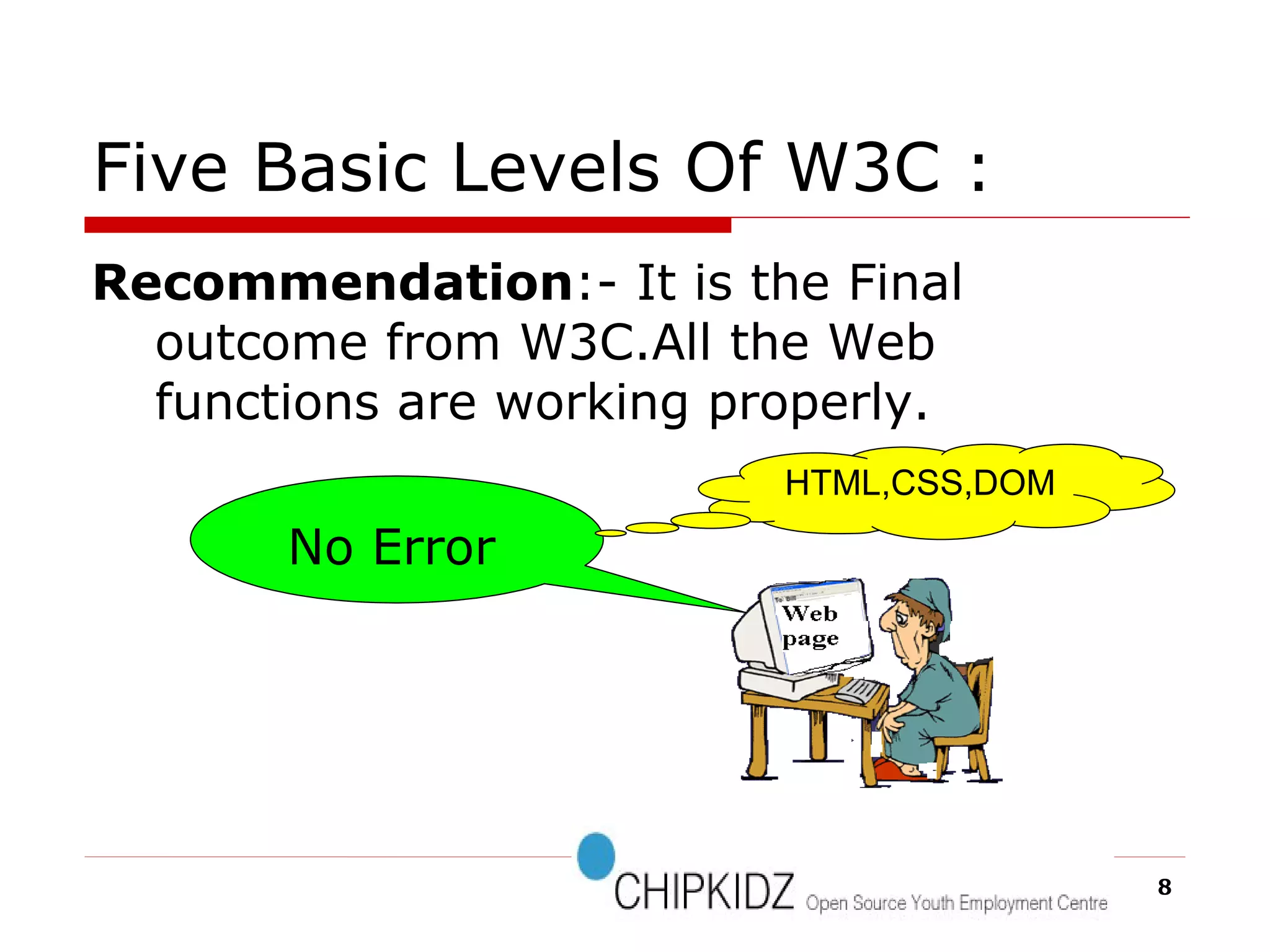
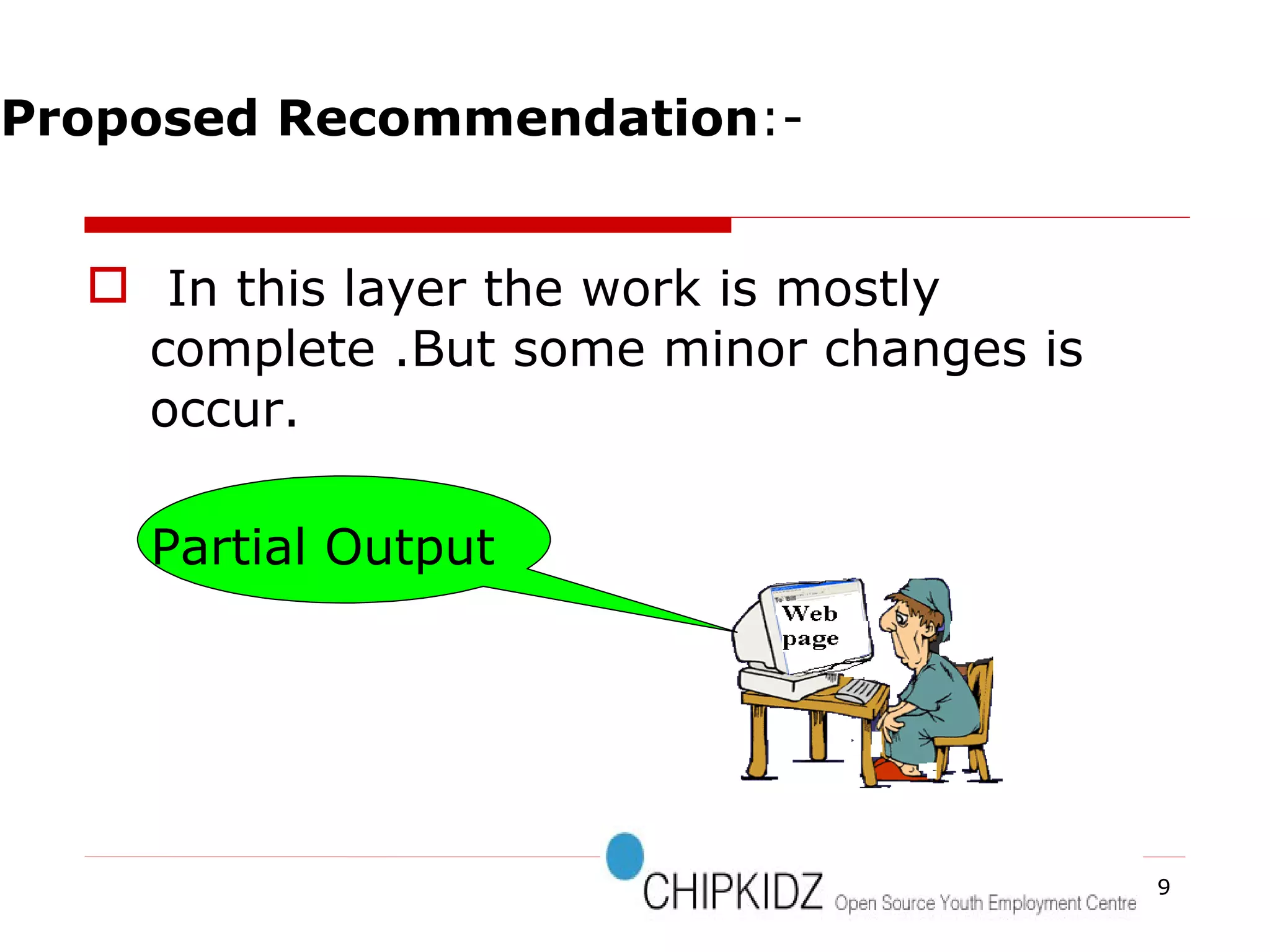
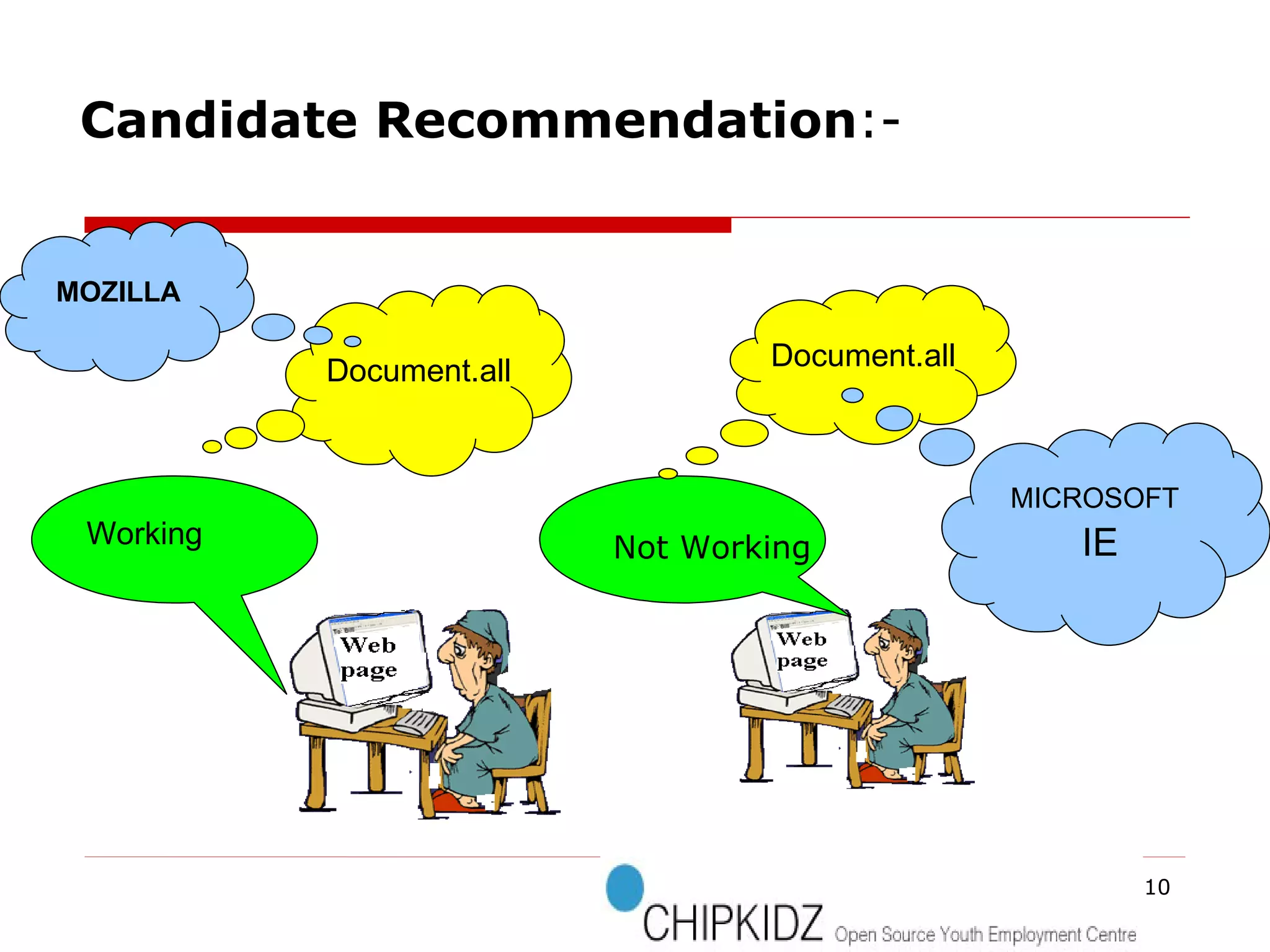
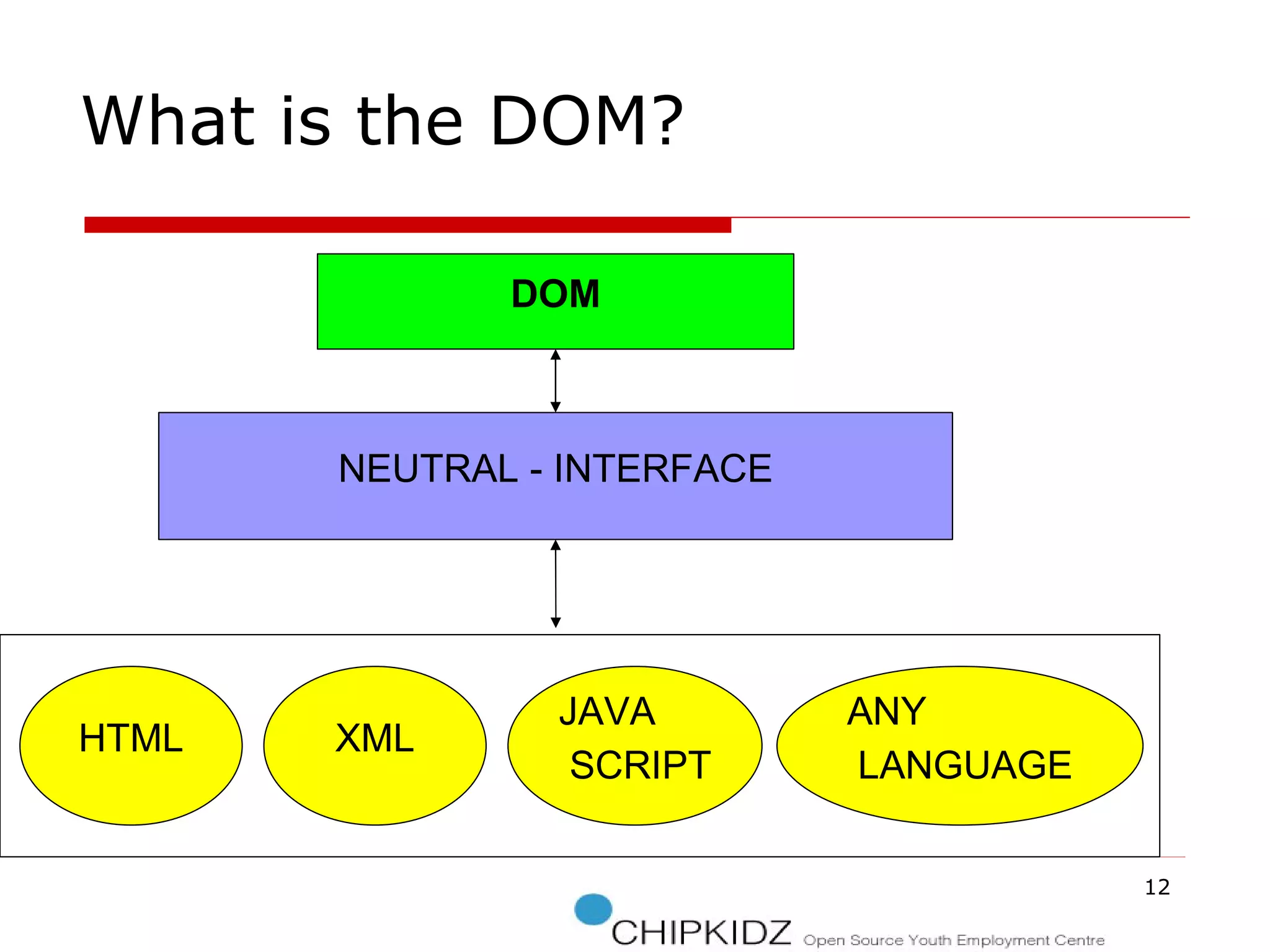
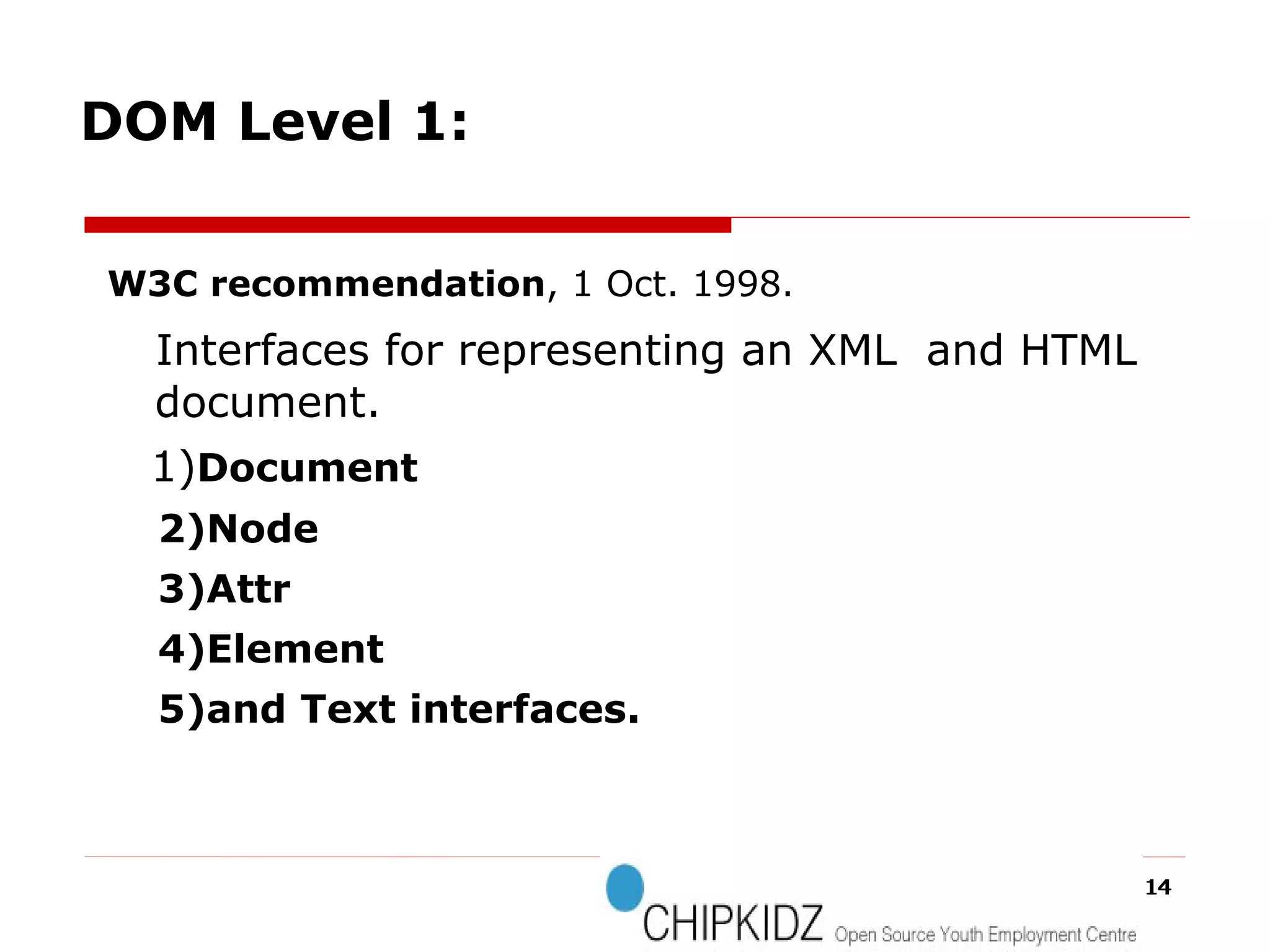
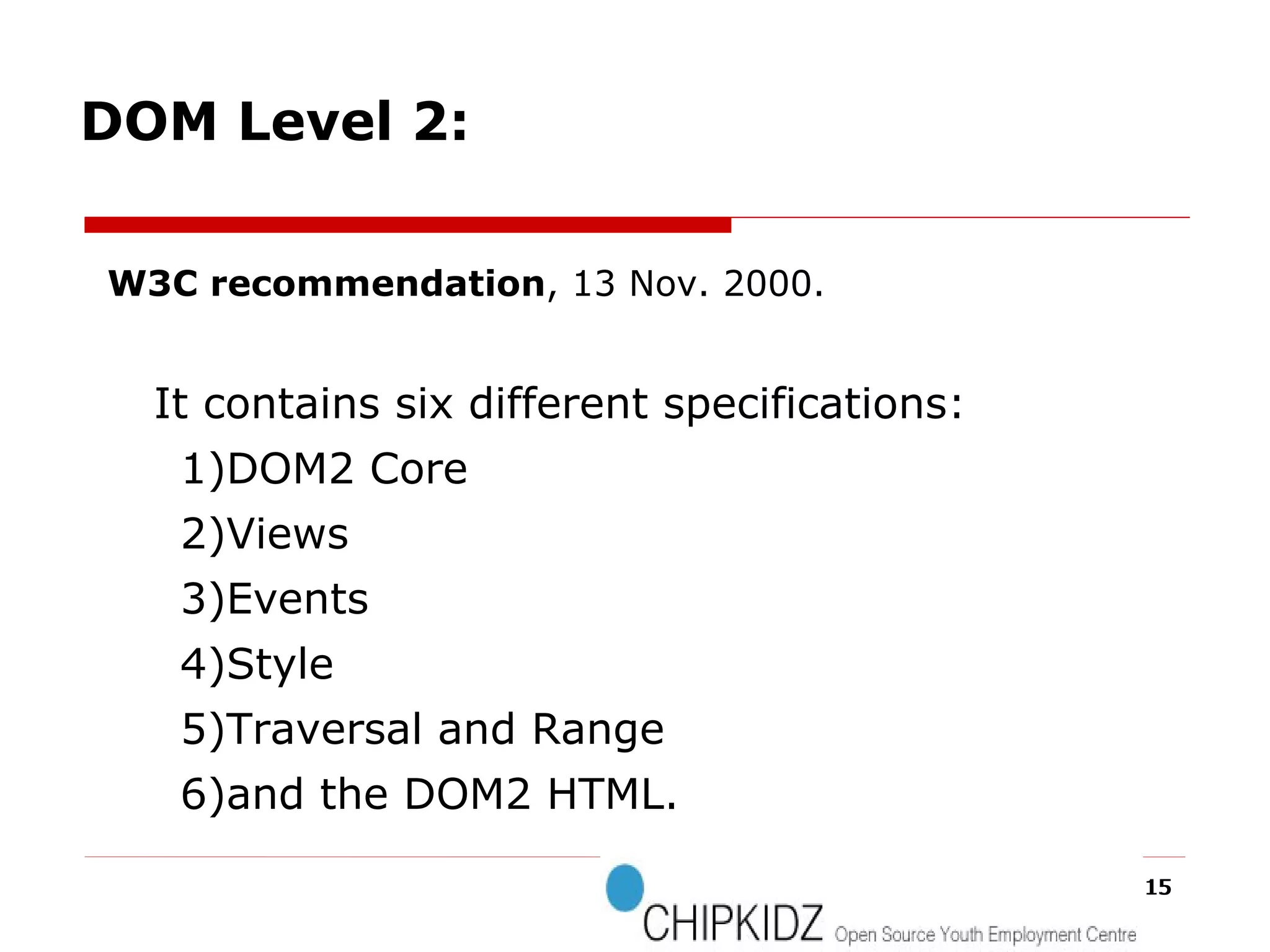
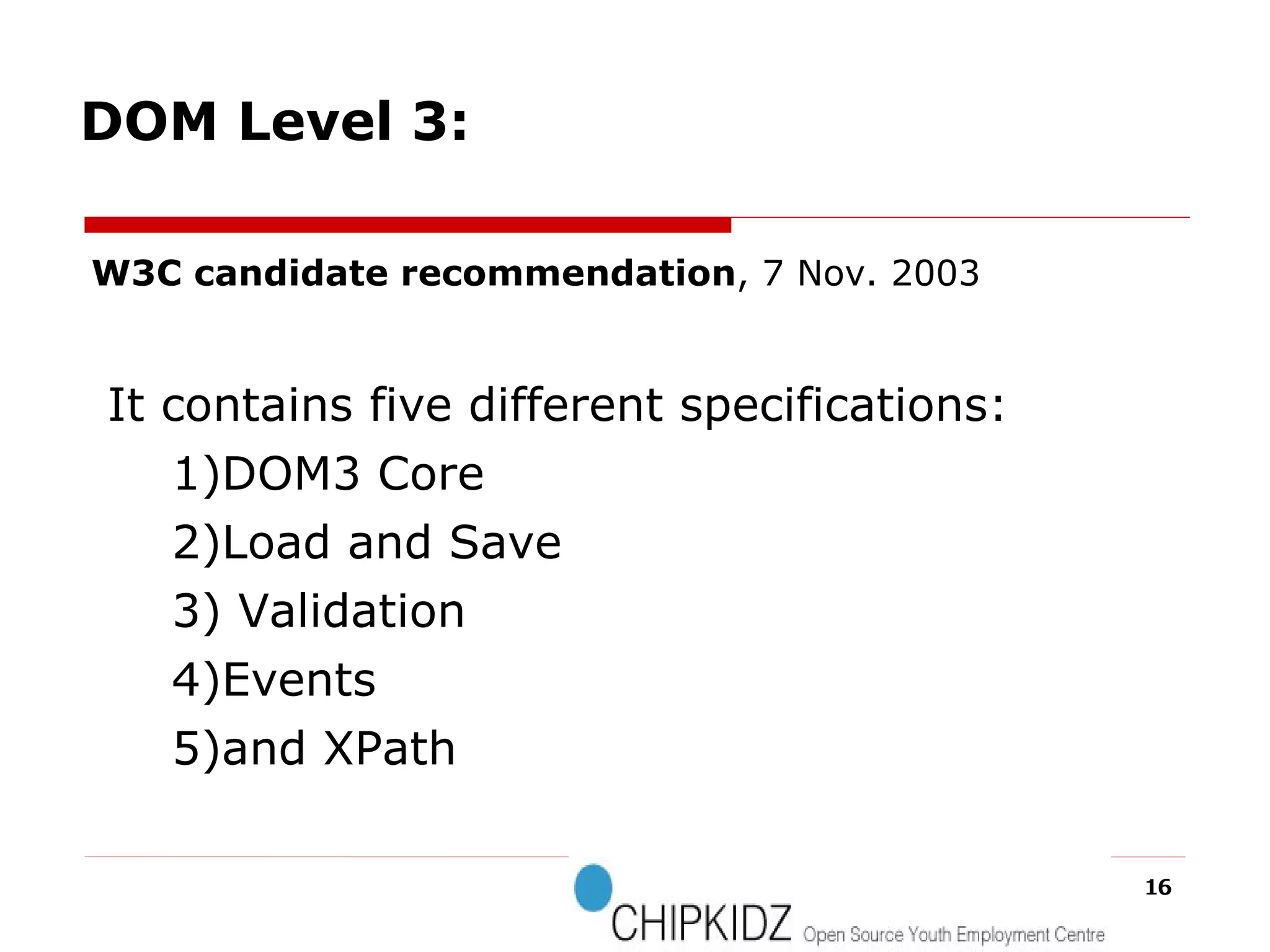
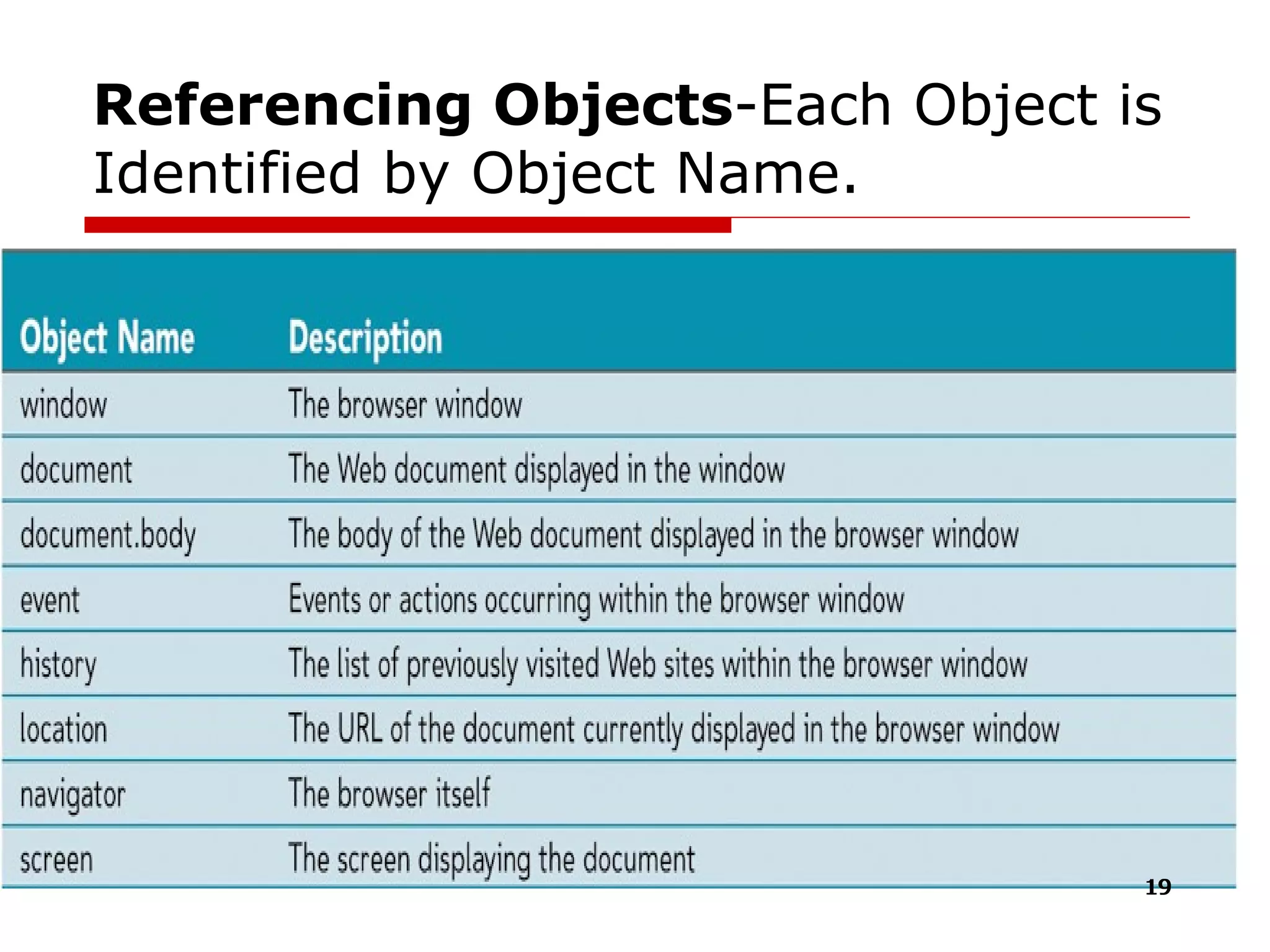
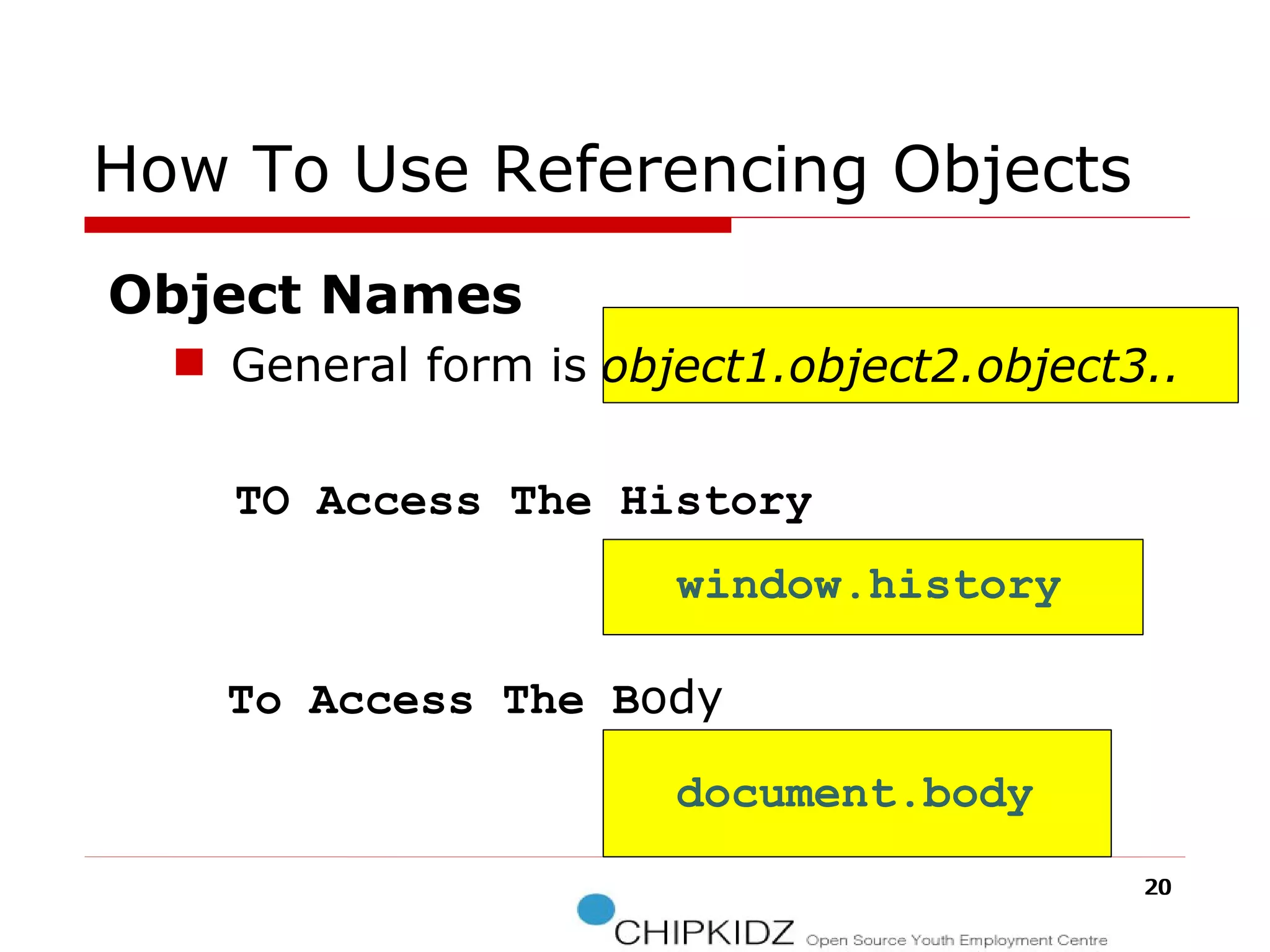
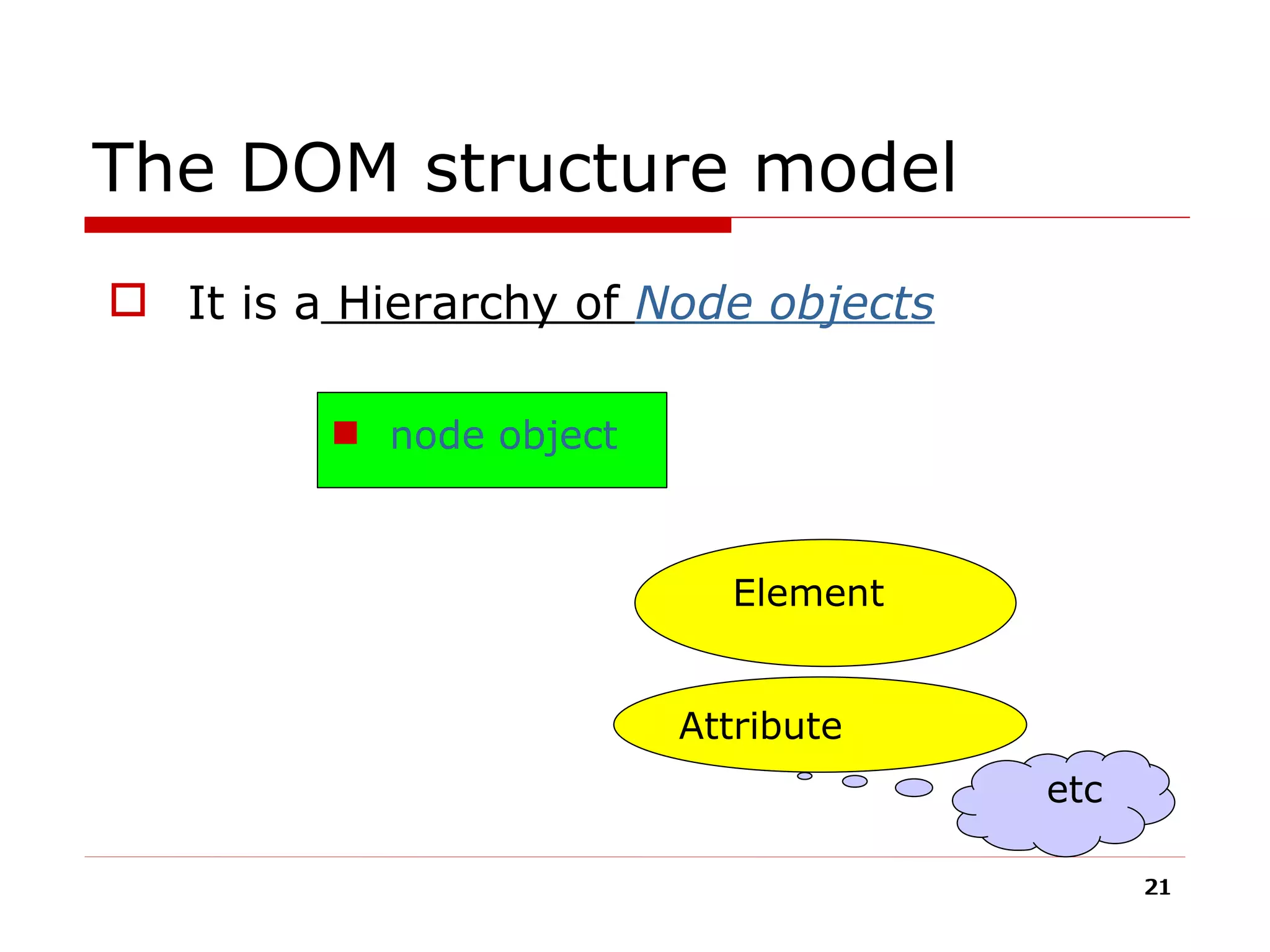
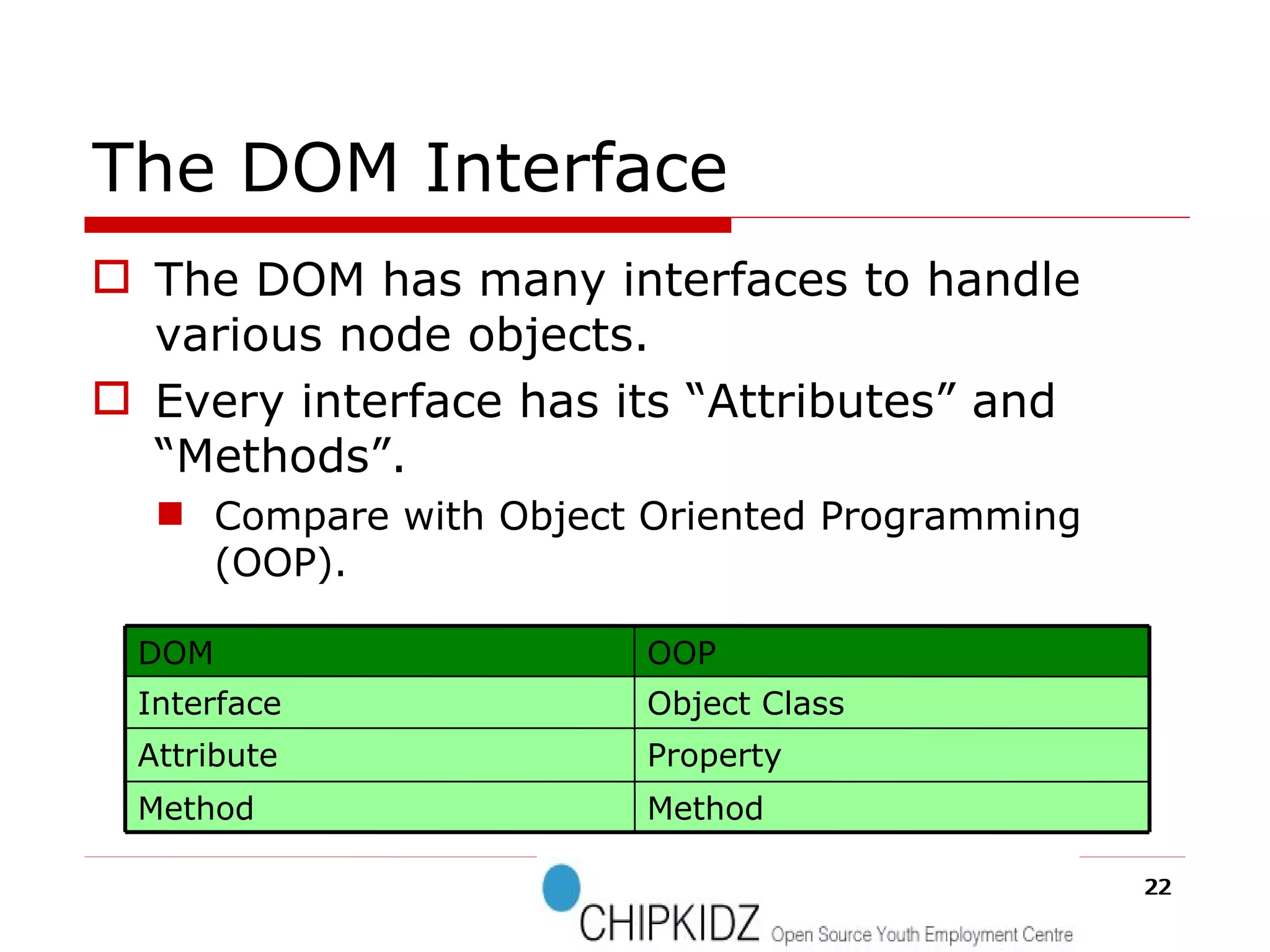
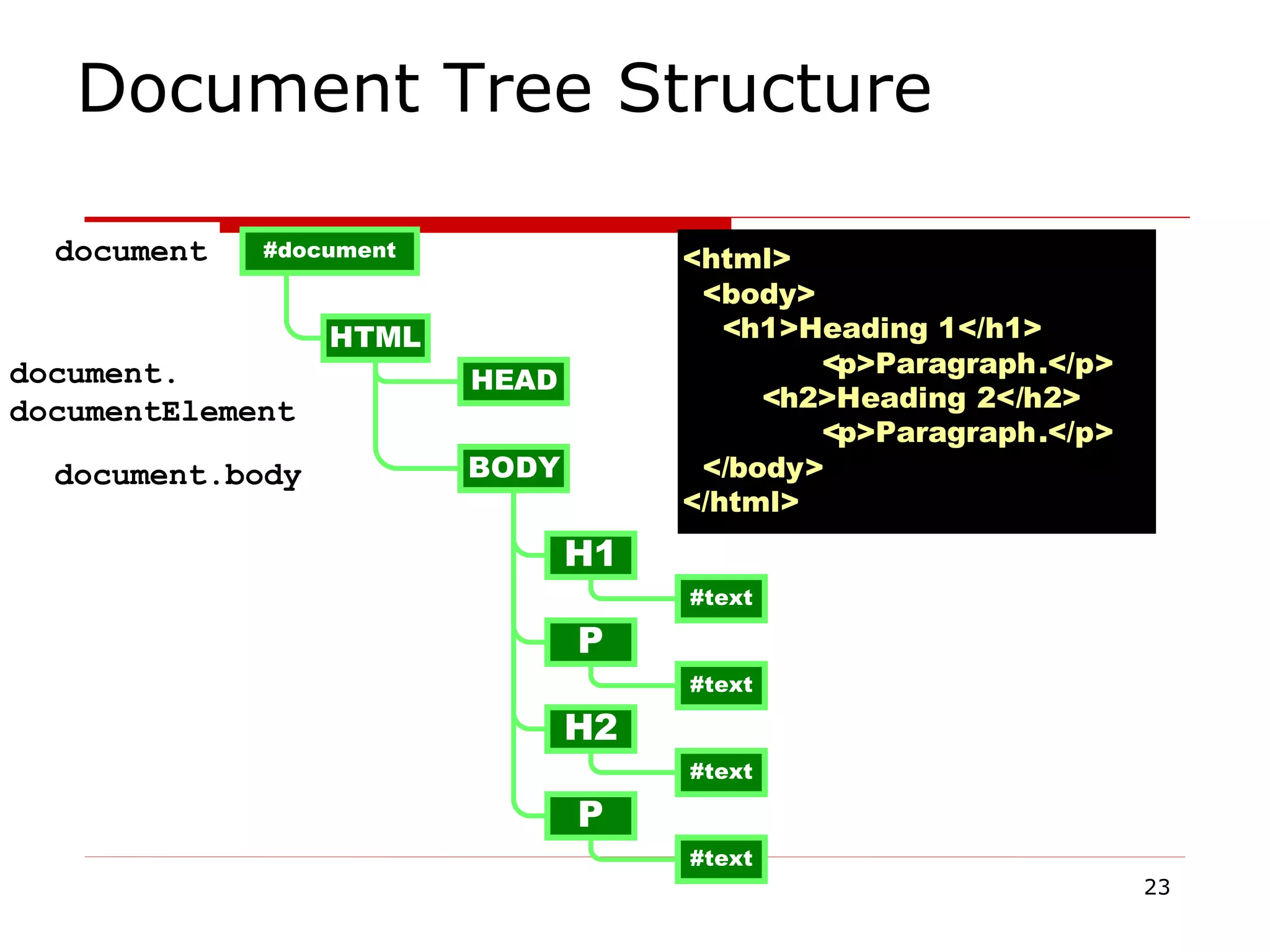
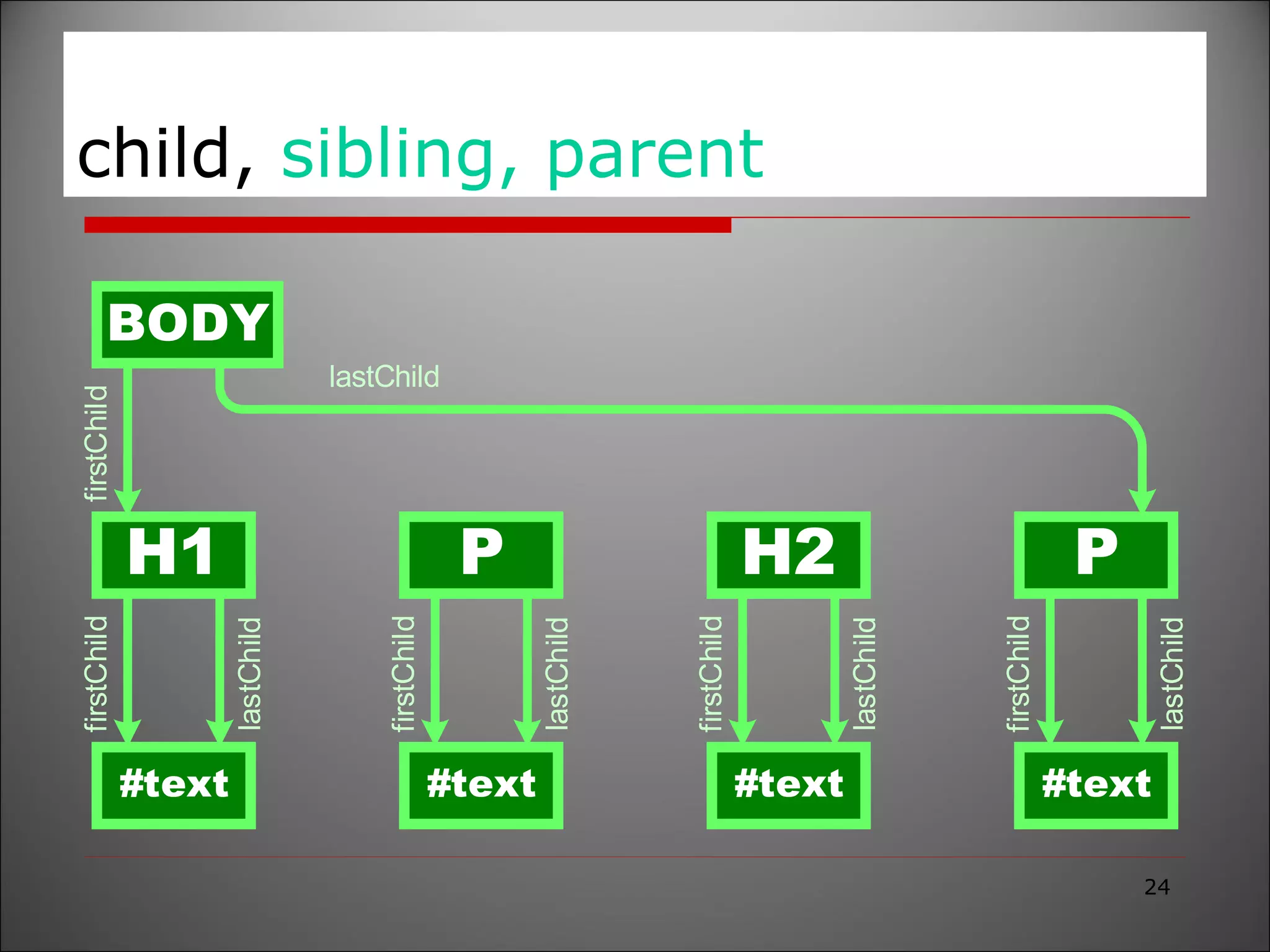
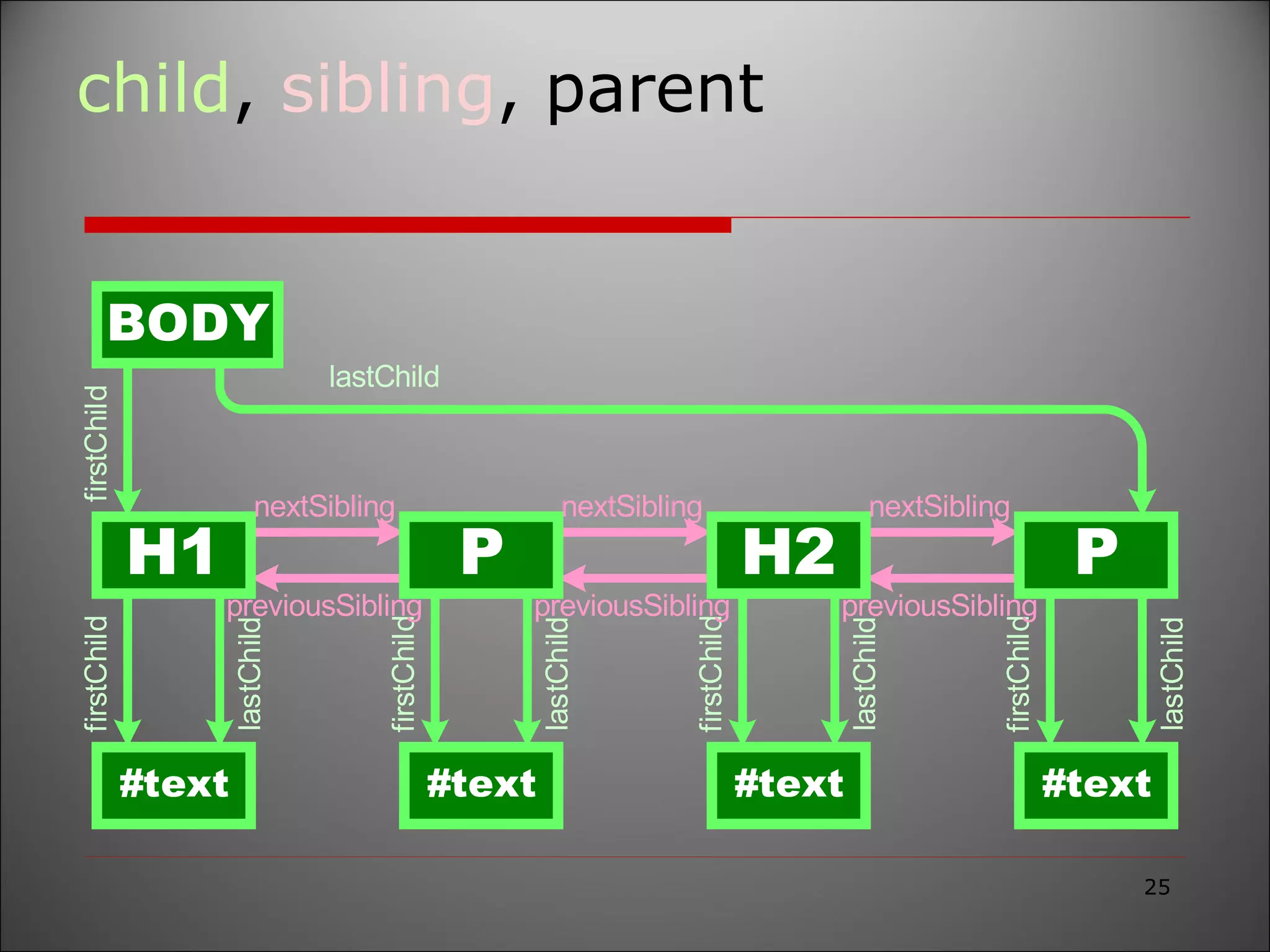
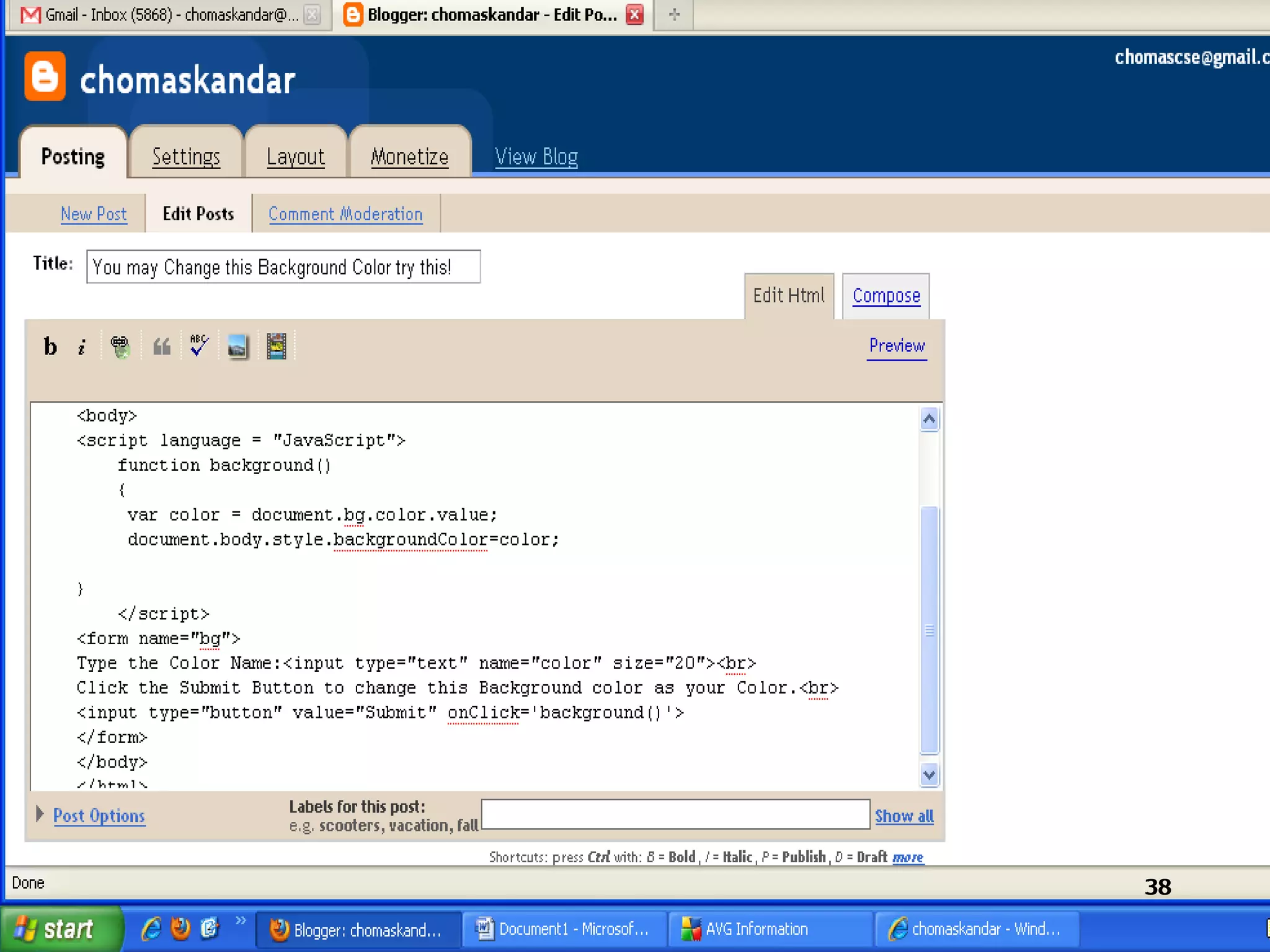
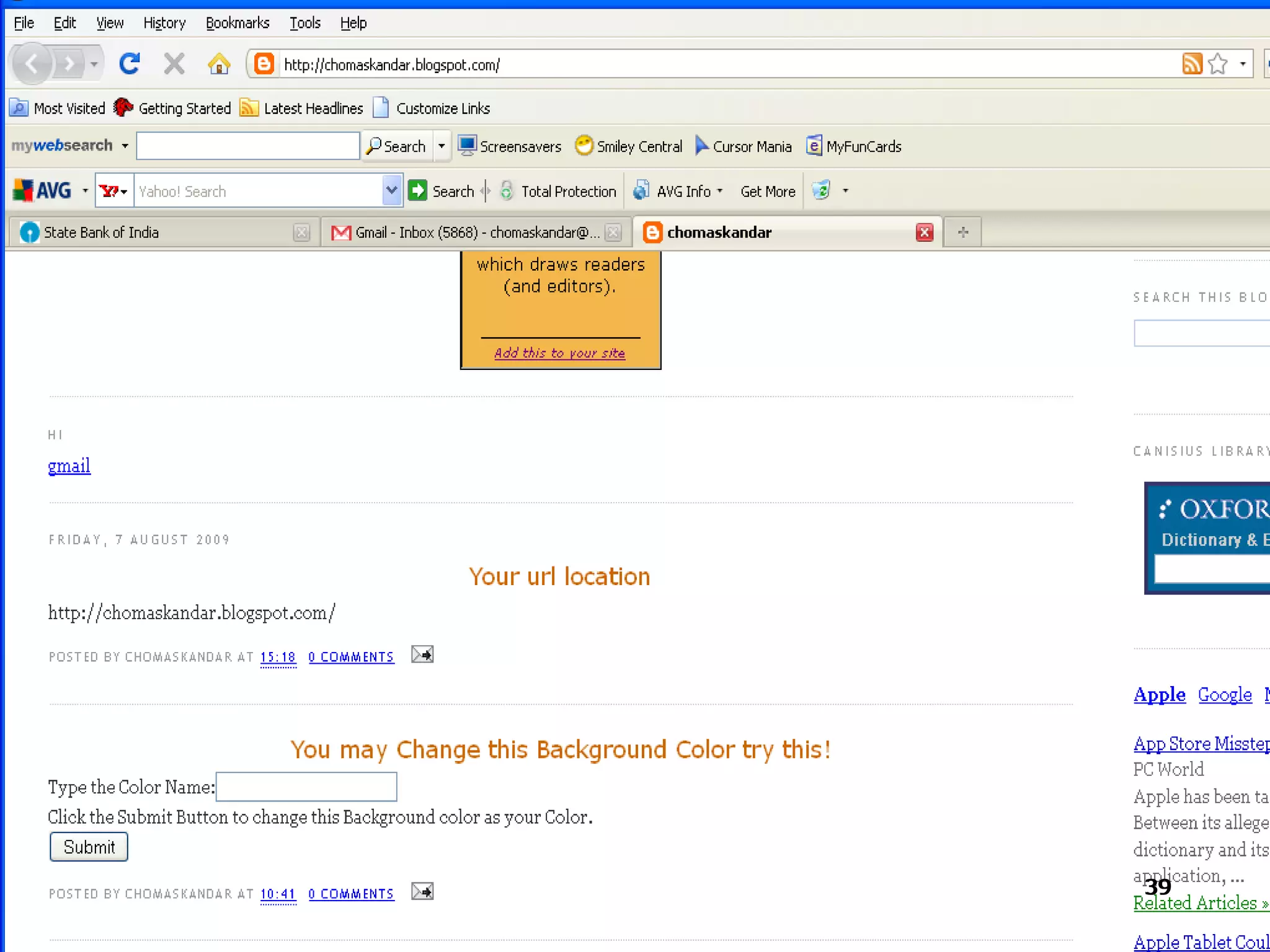
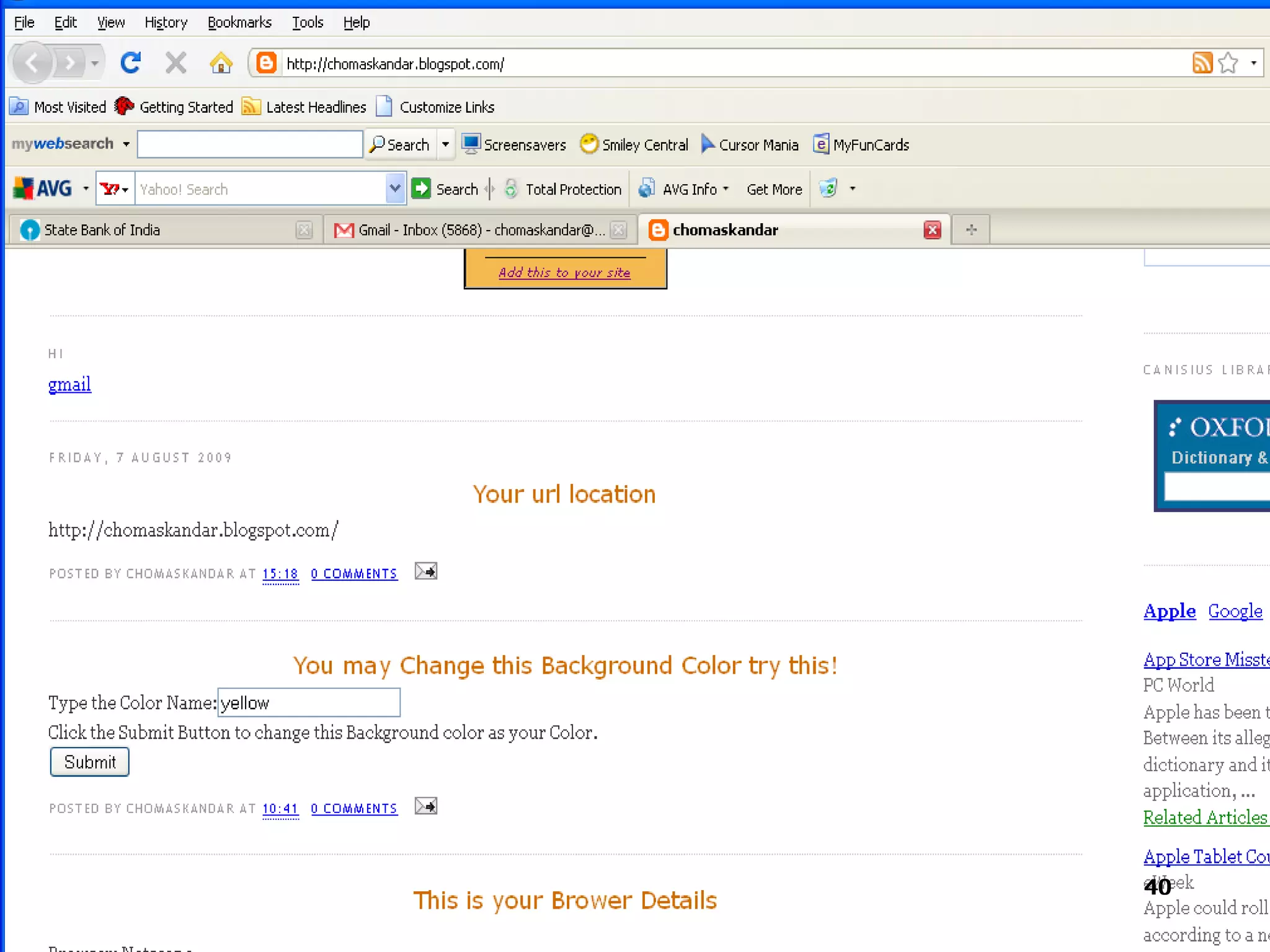
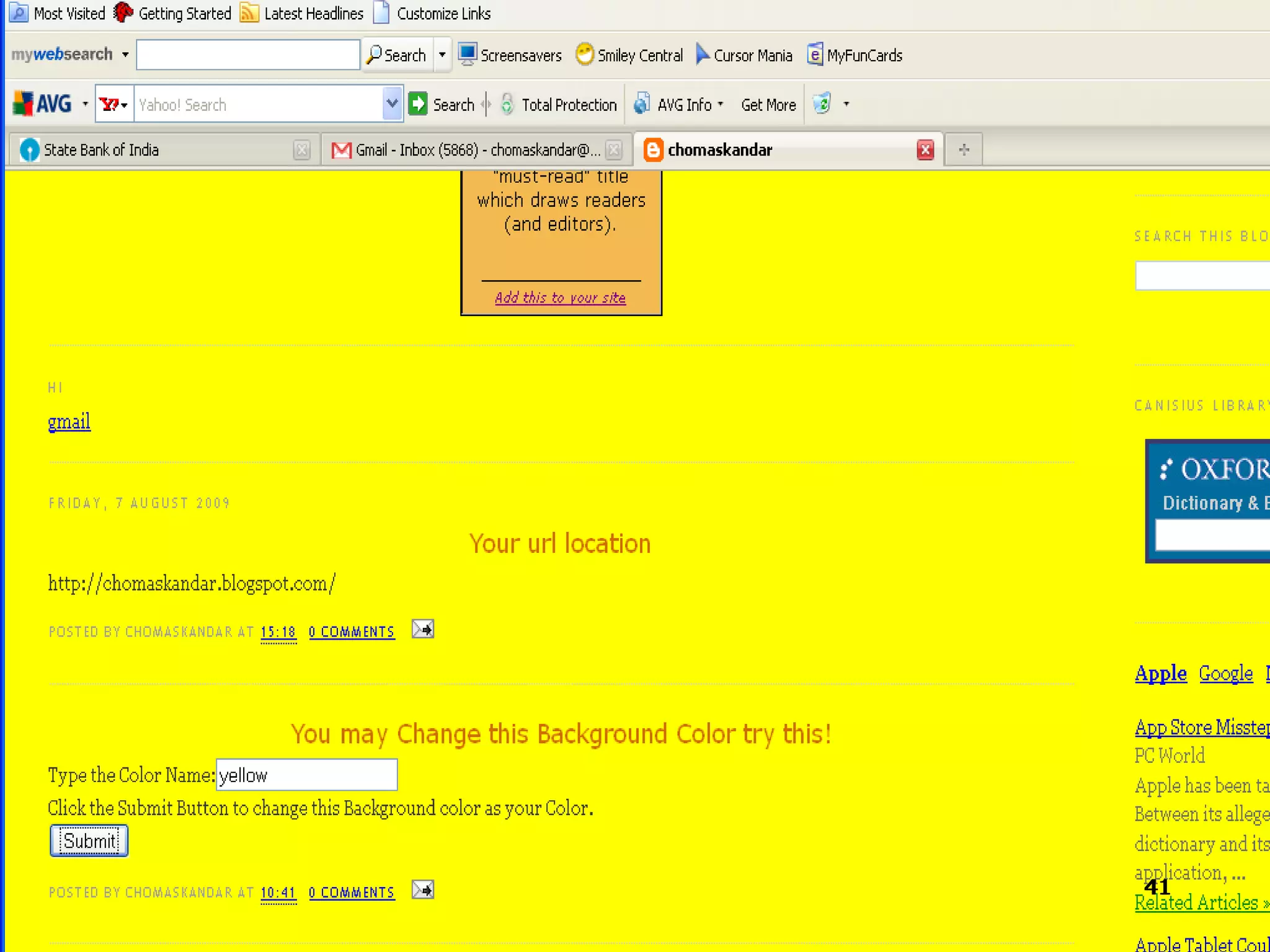
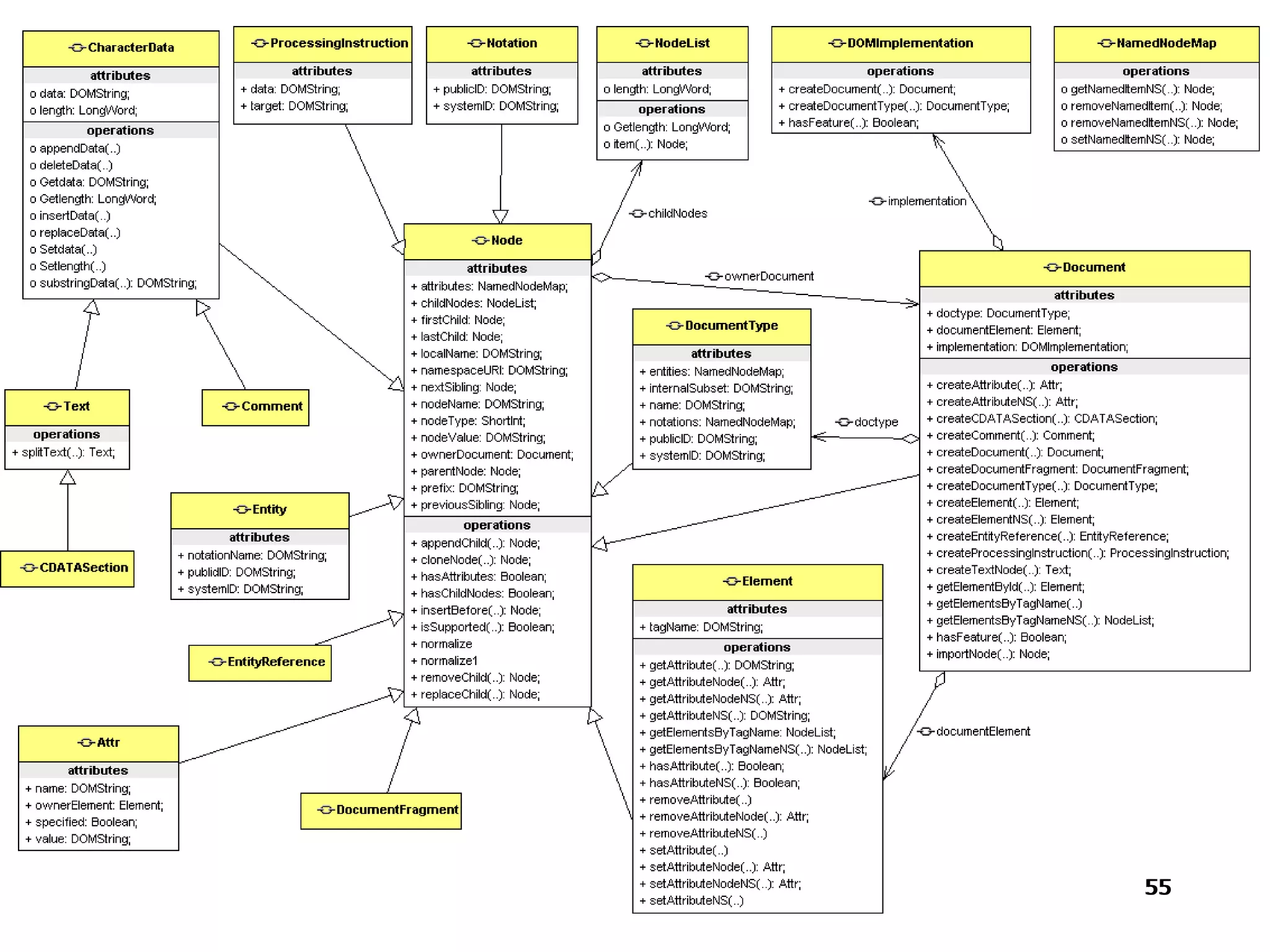
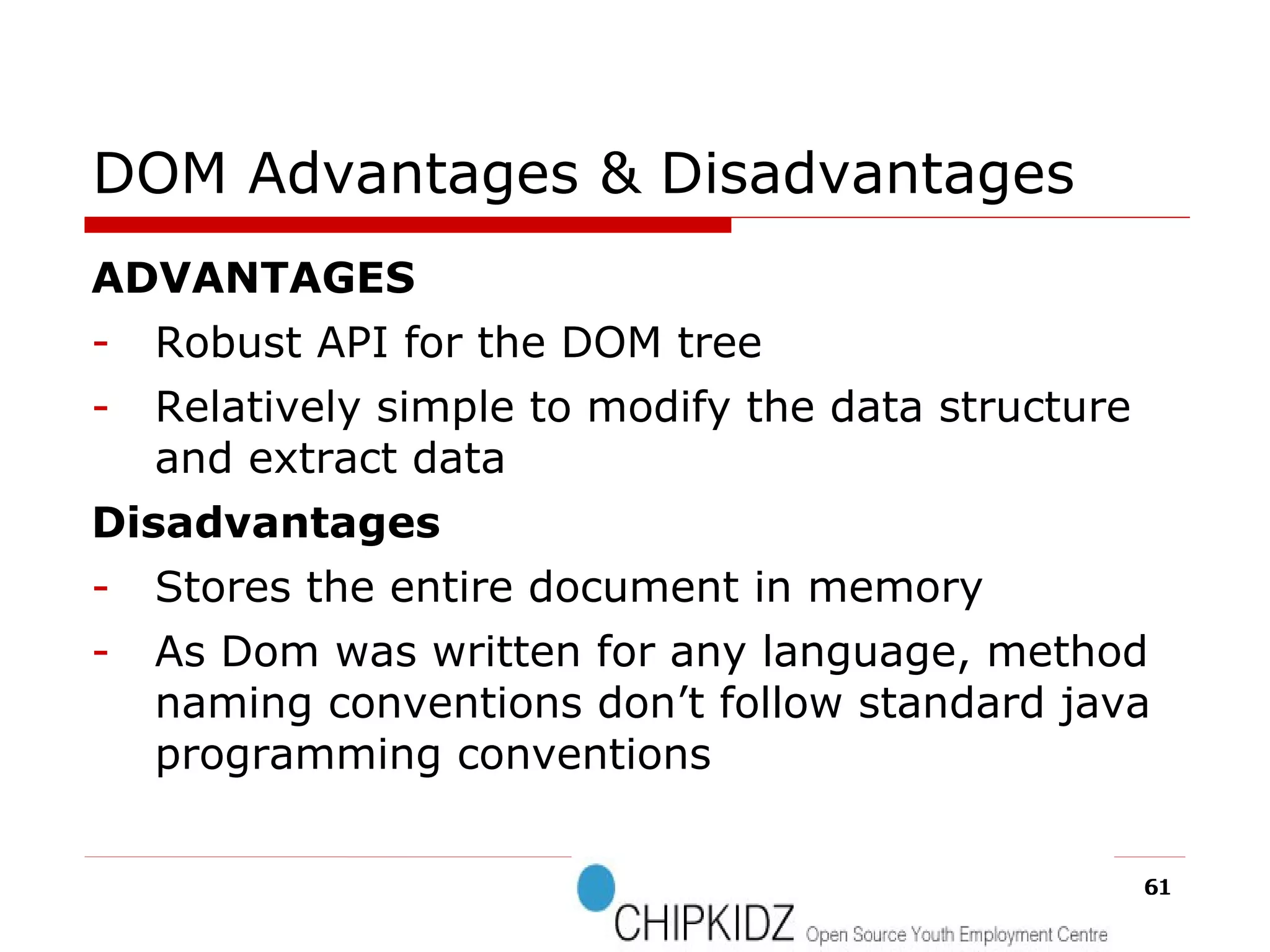
The document provides an overview of the Document Object Model (DOM), its recommendations by the W3C, and its structure, including interfaces and specifications from levels 1 to 3. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using DOM versus SAX for XML parsing, highlighting DOM's robust API and memory consumption issues. Additionally, the document contains examples of how to manipulate elements within the DOM using JavaScript.


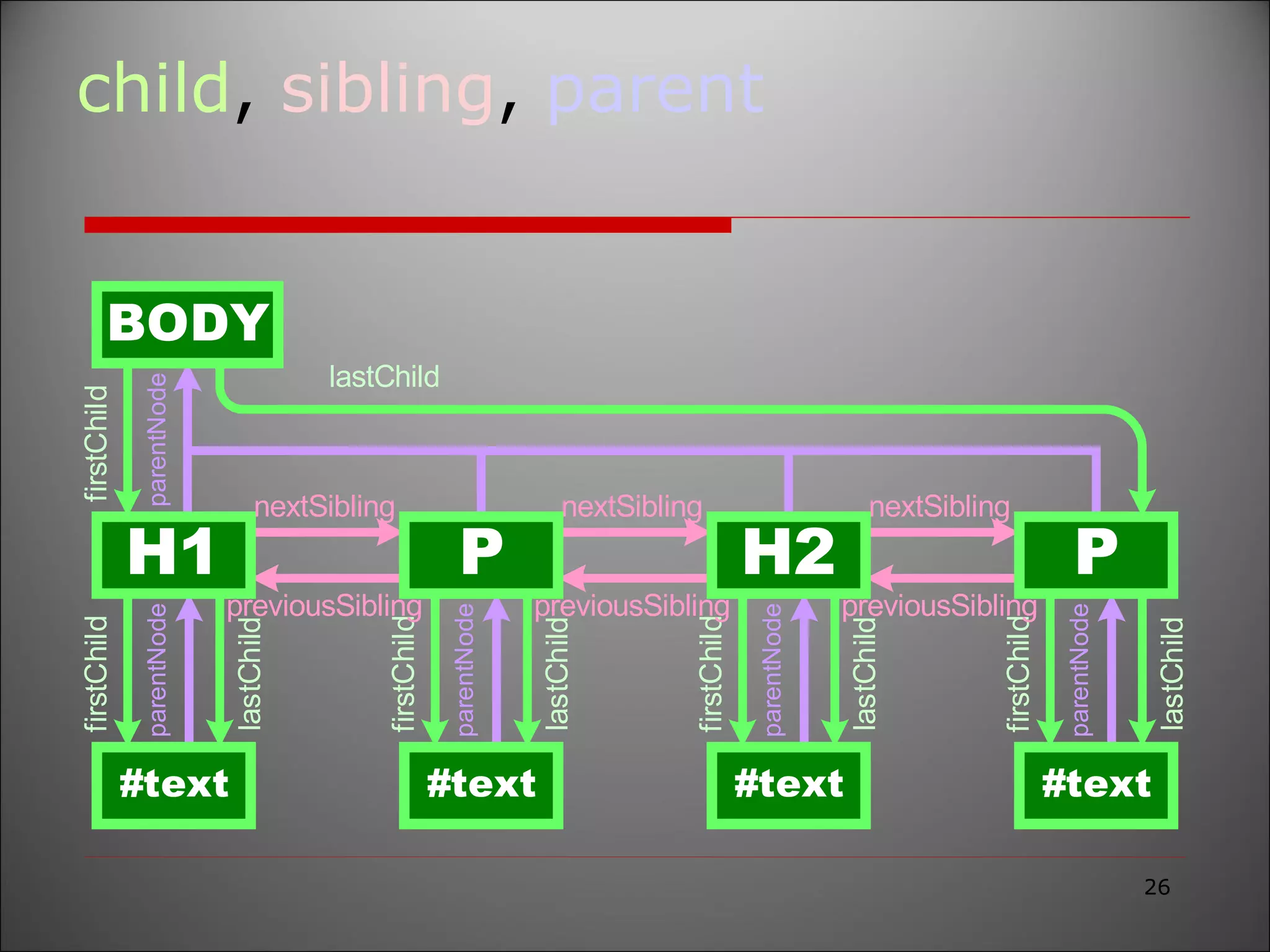
![document .firstChild .childNodes[0] .firstChild .parentNode .childNodes[1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documentobjectmodel-090907013239-phpapp02/75/Document-Object-Model-30-2048.jpg)















![[email_address] For more Information http://web2sharing.wordpress.com For any Queries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/documentobjectmodel-090907013239-phpapp02/75/Document-Object-Model-72-2048.jpg)
