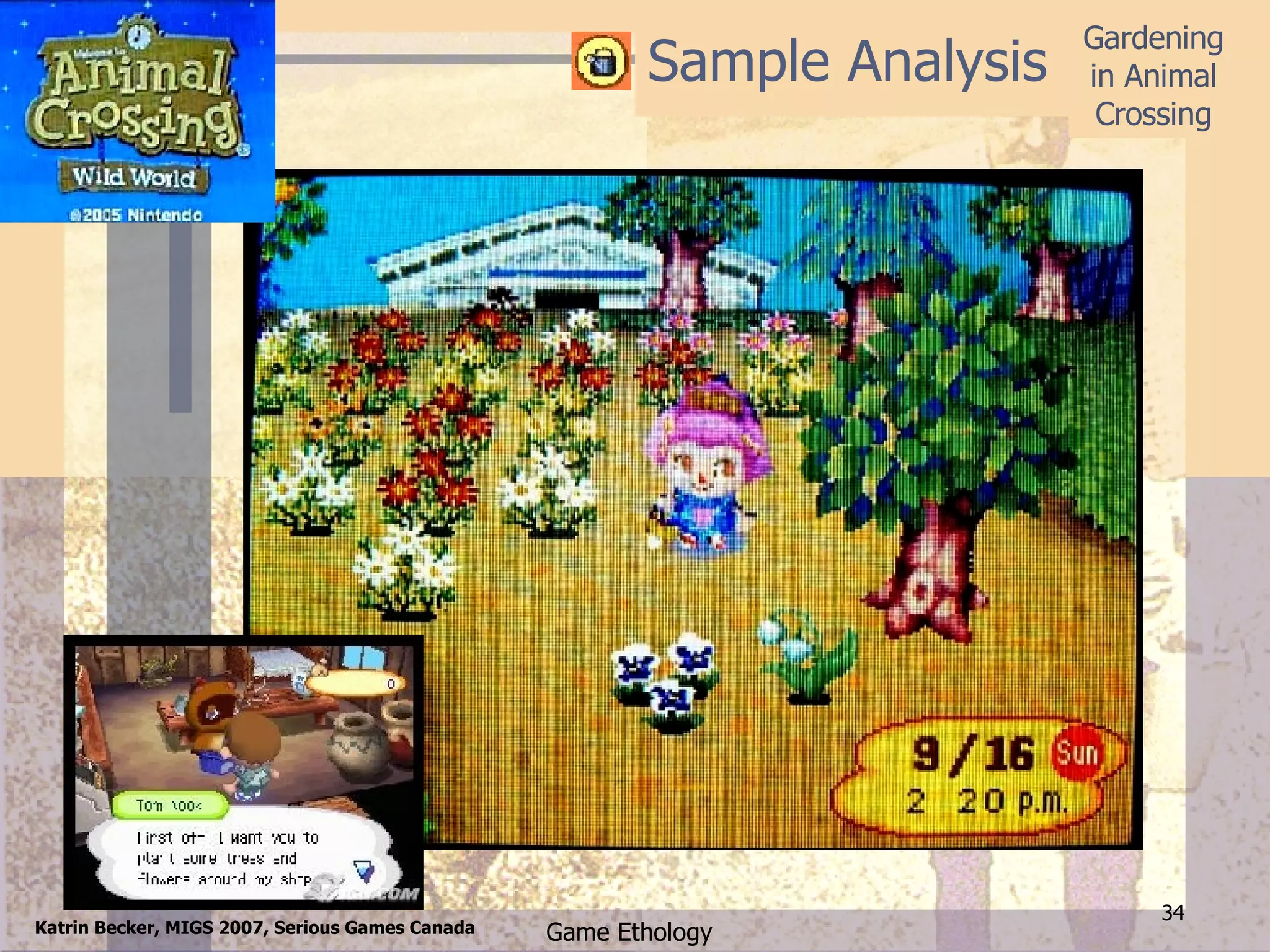
The document proposes applying concepts from ethology, the study of animal behavior, to analyze game design and player behavior in games. It outlines an approach called "game ethology" which involves observing and categorizing player behaviors, interactions, and progression over time to better understand game mechanics and design. The approach is demonstrated through an analysis of the gardening activities in the game Animal Crossing, examining behaviors, development over time, similarities to other games, and how the mechanics support the game's goals.









![Learning in Serious Games Learning is still usually how we win the game (or get to the end). About knowledge, skills, attitudes Some exceptions? psDoom [ http://psdoom.sourceforge.net/ ] utility Some are about action or prompting action: Example: FreeRice [ http:// www.freerice.com / ] Drill / quiz / contest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/game-ethology-2-1196262414746653-3/75/Game-Ethology-2-11-2048.jpg)

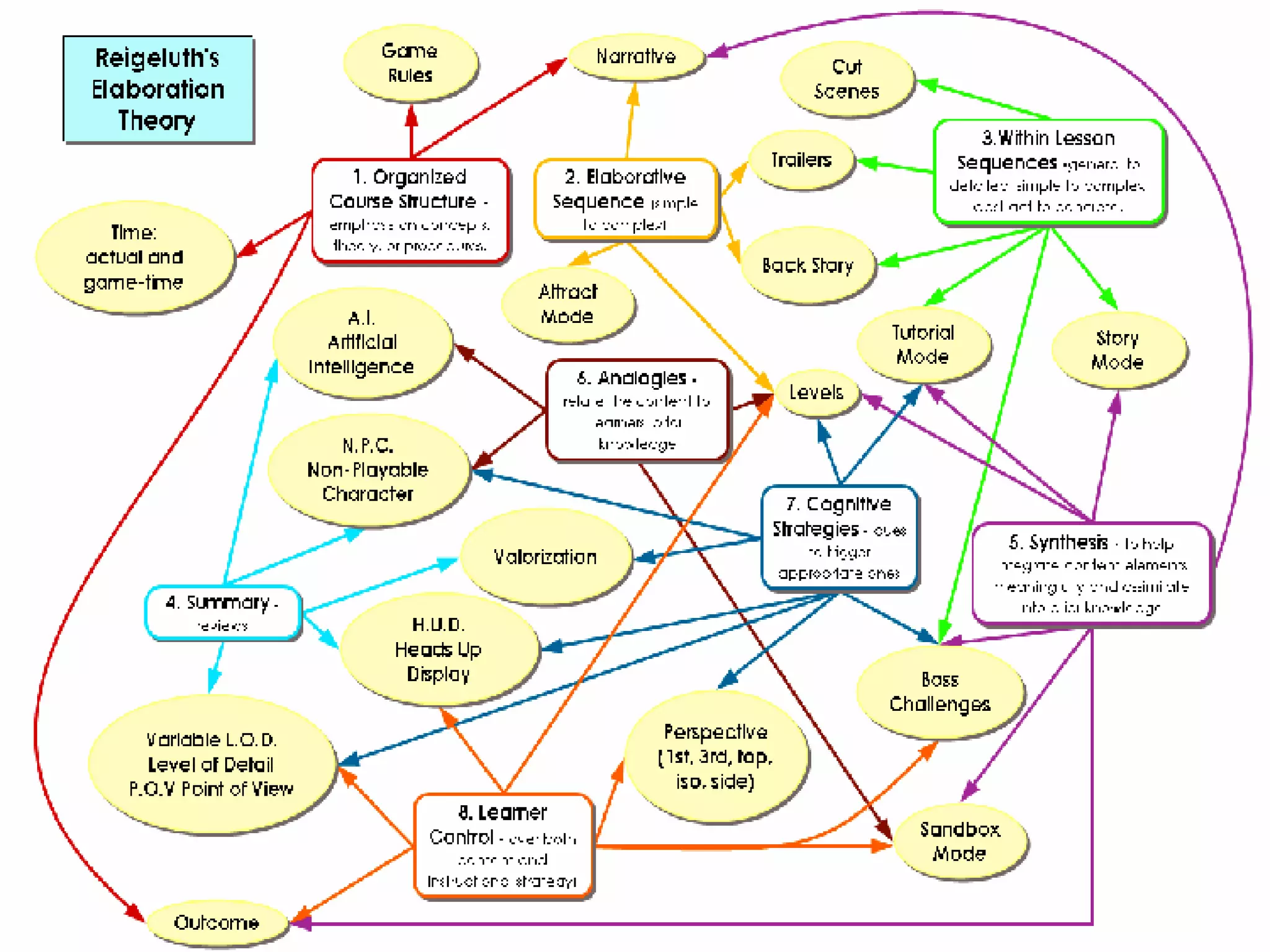


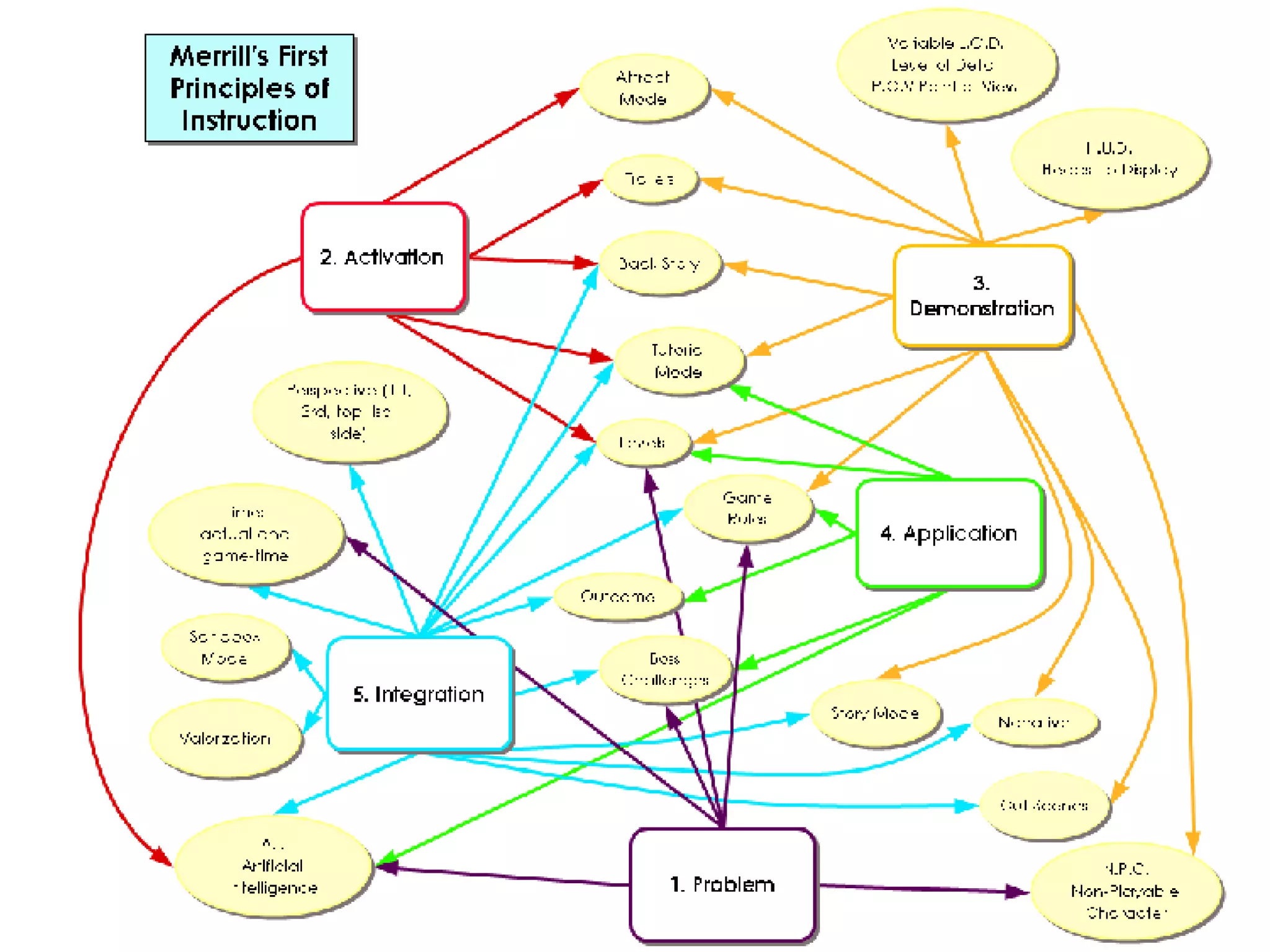










![Game Ethology Causation (interaction) . [How does it work?] What are the stimuli that elicit the response, and how has it been modified by recent interaction? Development (flow) : [How does it develop?] How does the behaviour change over the life of the game, and what early experiences are necessary for the behaviour to be shown? Evolution : [How it ‘evolve’?] How does the behaviour compare with similar behaviour in related games, and how might it have arisen through the process of evolution? Function (purpose) : [What is it for?] How does the behaviour impact on the game’s chances of success (survival) and sequels?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/game-ethology-2-1196262414746653-3/75/Game-Ethology-2-28-2048.jpg)