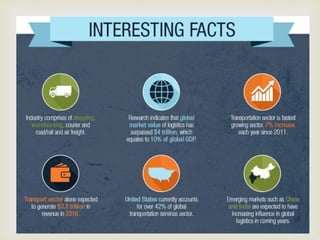
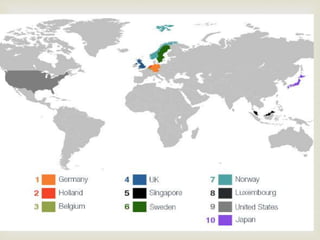
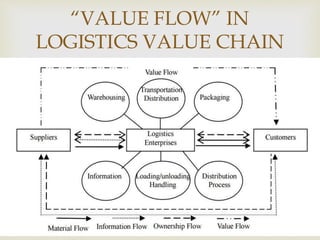
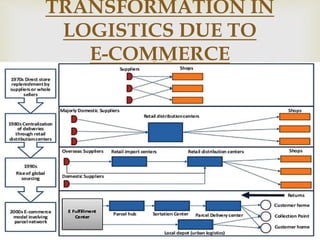
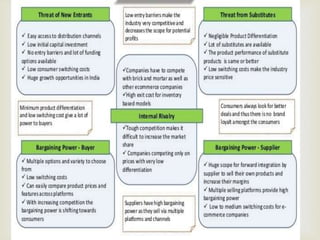
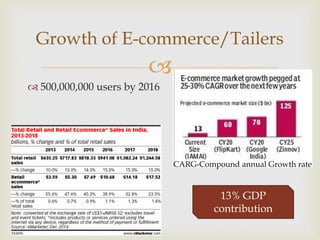
This document provides an overview of the logistics industry and Porter's Five Forces analysis. It discusses key domestic and international players like DHL, TNT, AFL, Exel, Kuehne & Nagel, and Schenker. Opportunities for growth in India include air cargo and the Delhi-Mumbai corridor project. Challenges are high costs due to delays and poor infrastructure. The future of e-commerce and initiatives like 'Make in India' are expected to drive growth in the logistics sector.