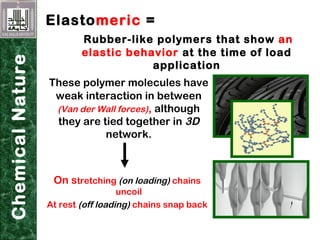
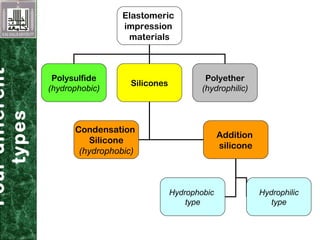
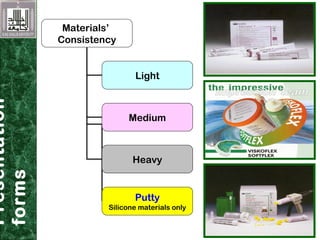
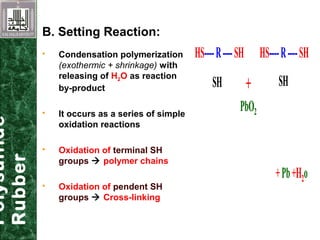
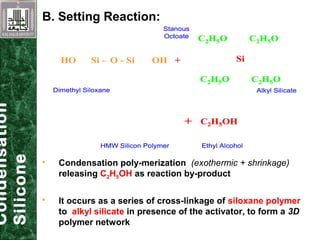
Elastomeric impression materials include polysulfide, condensation silicone, addition silicone, and polyether rubbers. They set via polymerization reactions, with setting times of 8-12 minutes on average. Polysulfide and condensation silicone set via condensation reactions producing water or alcohol as byproducts, while addition silicone and polyether set via addition reactions without byproducts. Polysulfide has the highest detail reproduction but all materials exhibit some polymerization shrinkage. Materials are available in light, medium, heavy or putty consistencies for use with stock or custom trays. Proper manipulation is required for accurate impressions.