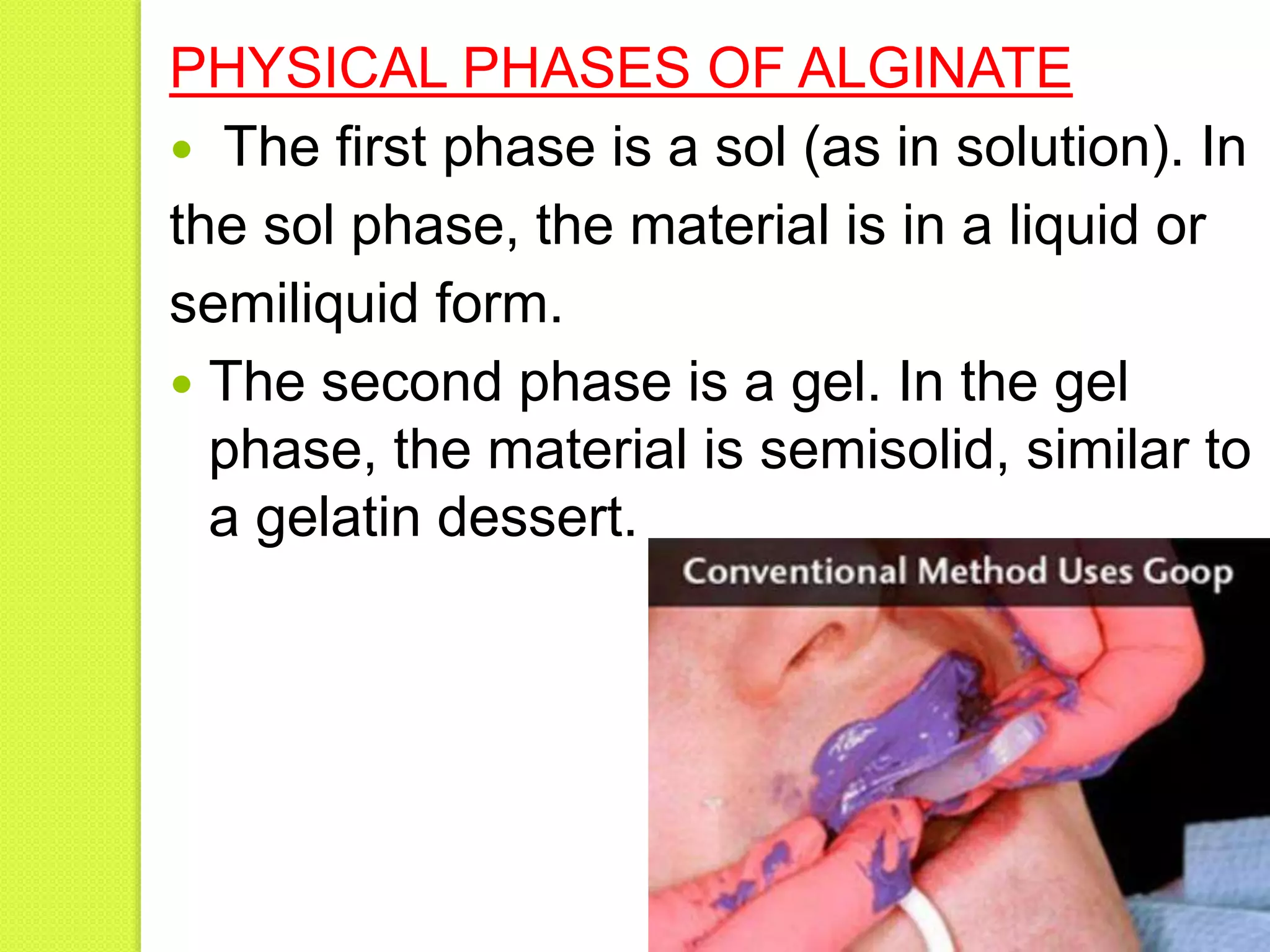
This document discusses hydrocolloids, which are gelatin particles suspended in water. There are two main types used for dental impressions: agar and alginate. Agar is a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed that is widely used for cast duplication. It can be reused but has low tear strength. Alginate is derived from seaweed and sets via a chemical reaction between soluble alginate and calcium sulfate to form insoluble calcium alginate. Alginate makes accurate impressions but cannot be reused or corrected. Both materials are inexpensive and easy to use but have limitations such as dimensional instability and low strength.