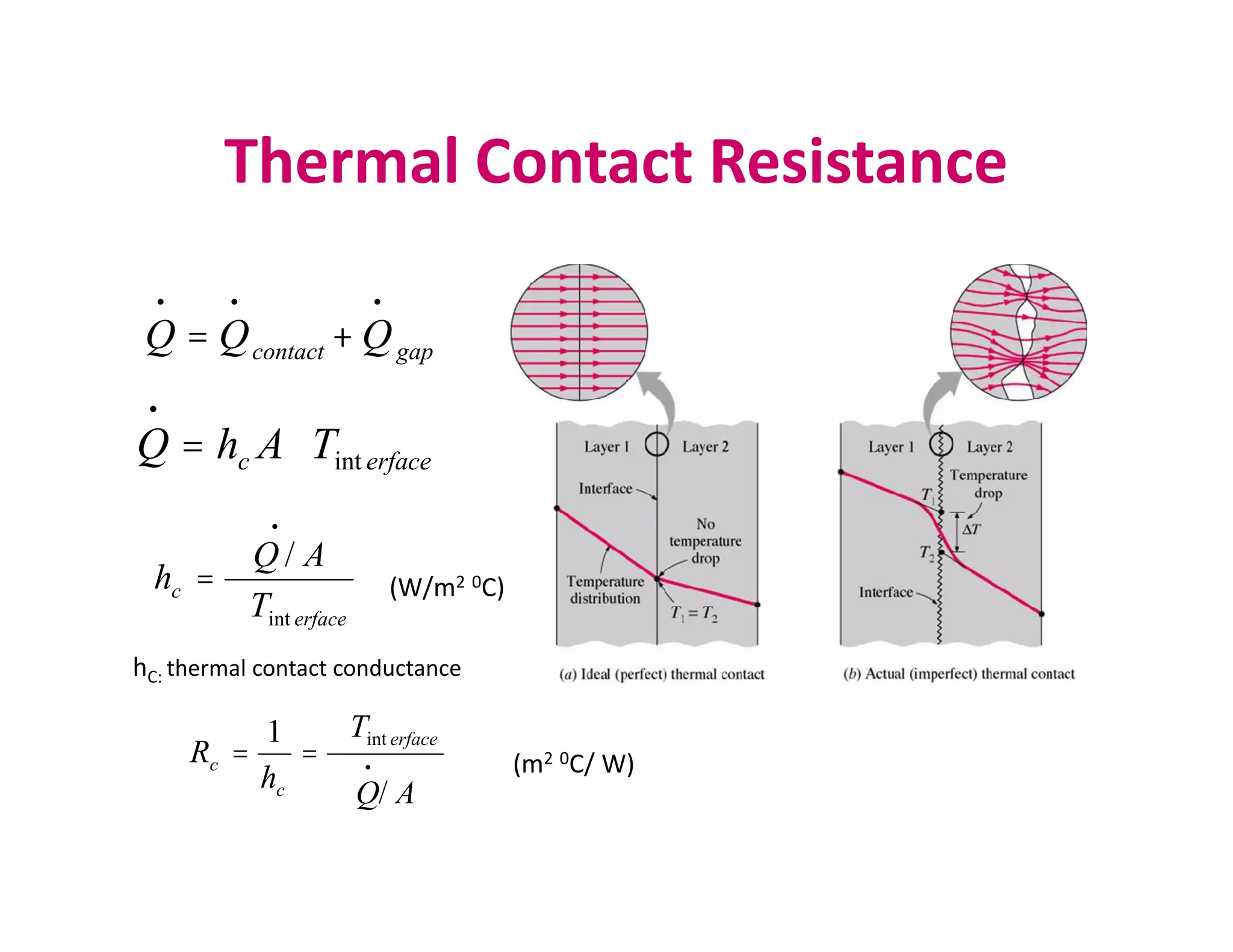
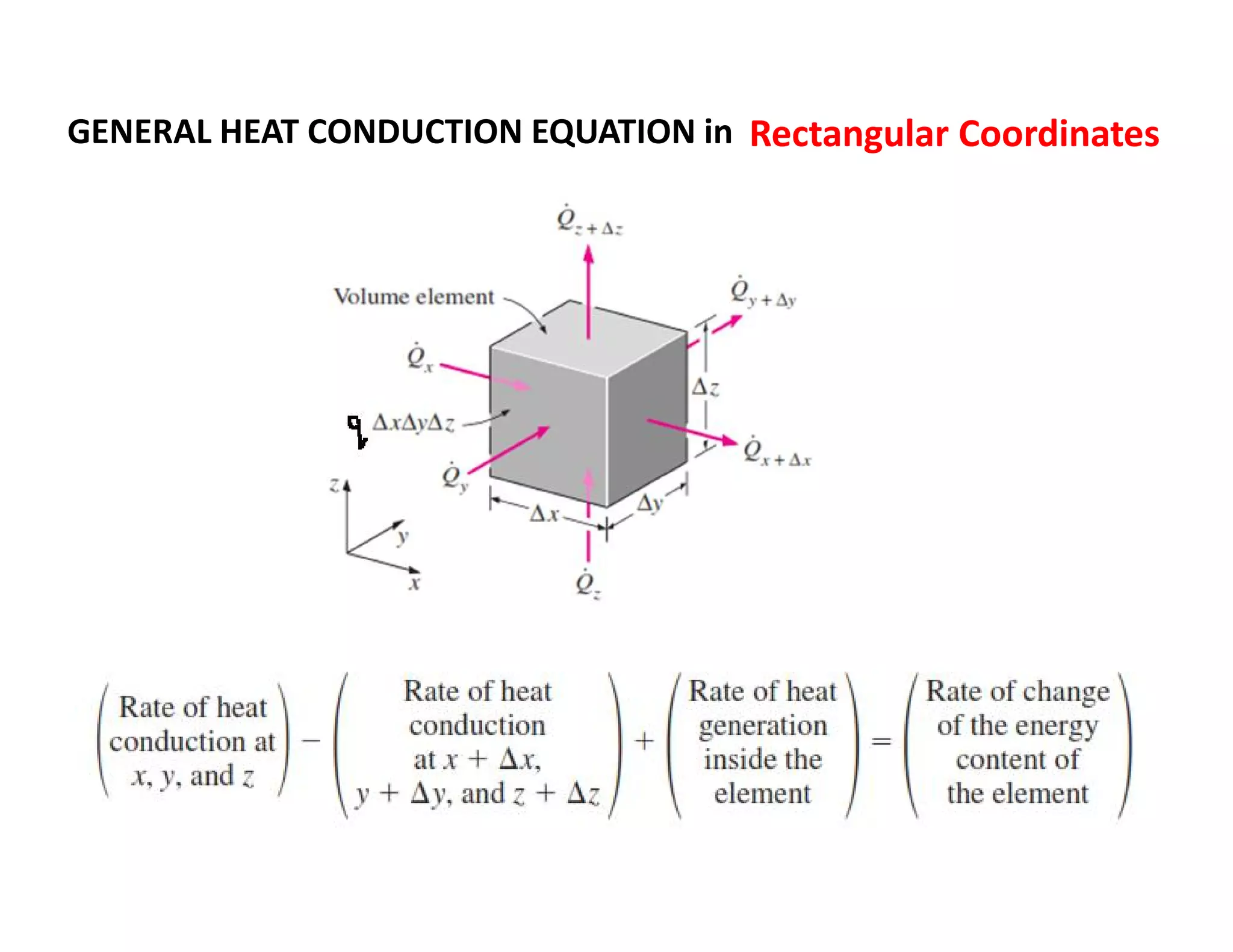
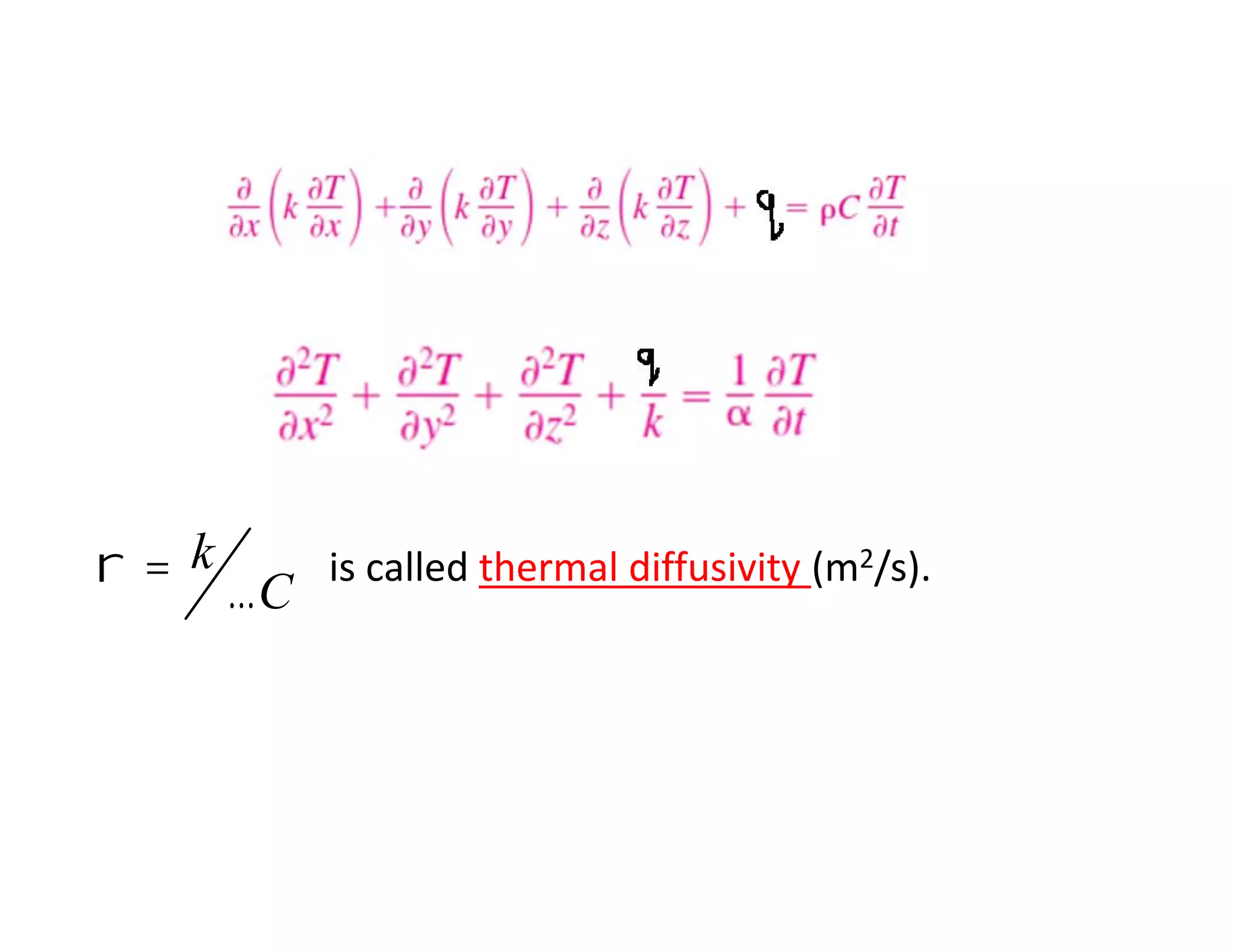
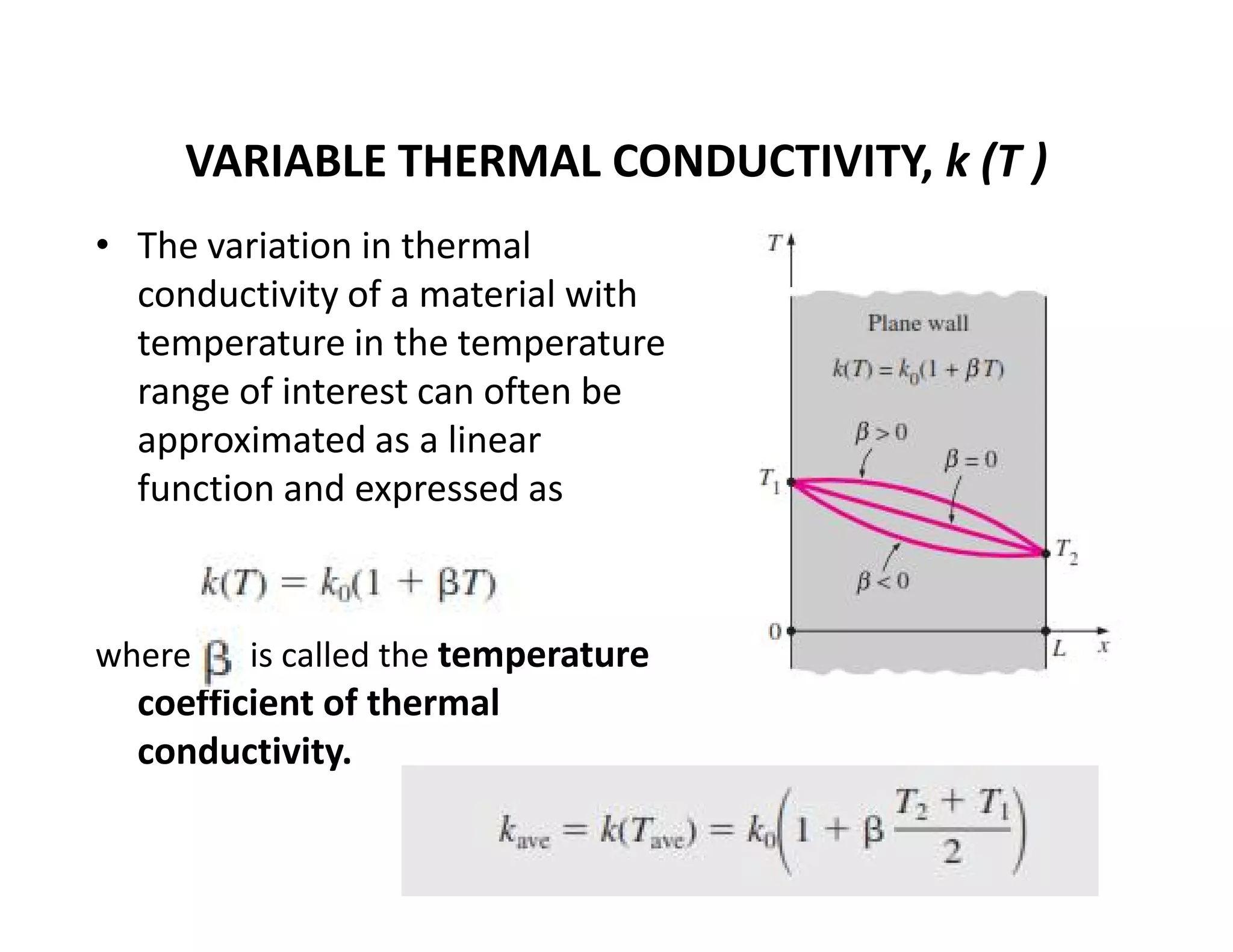
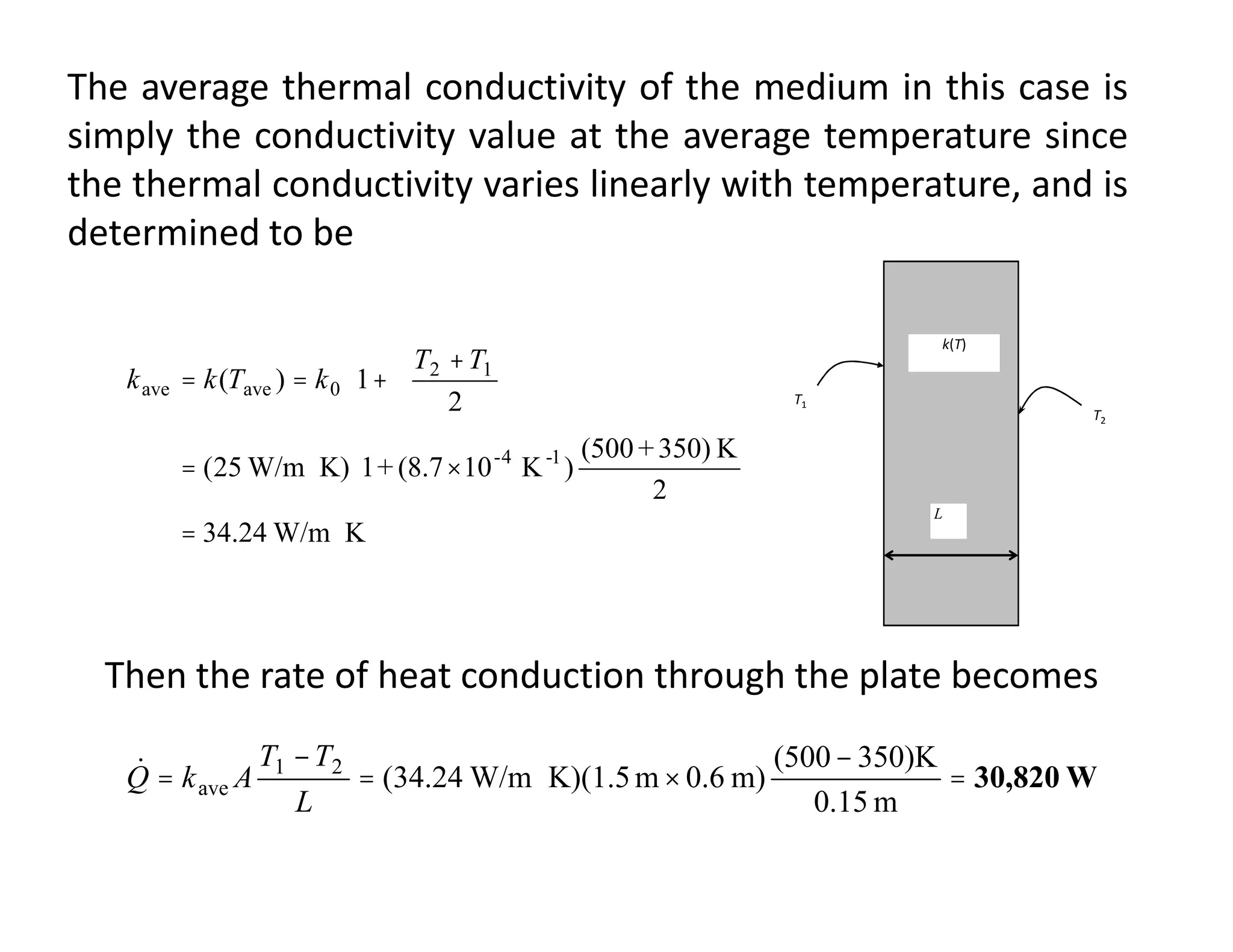
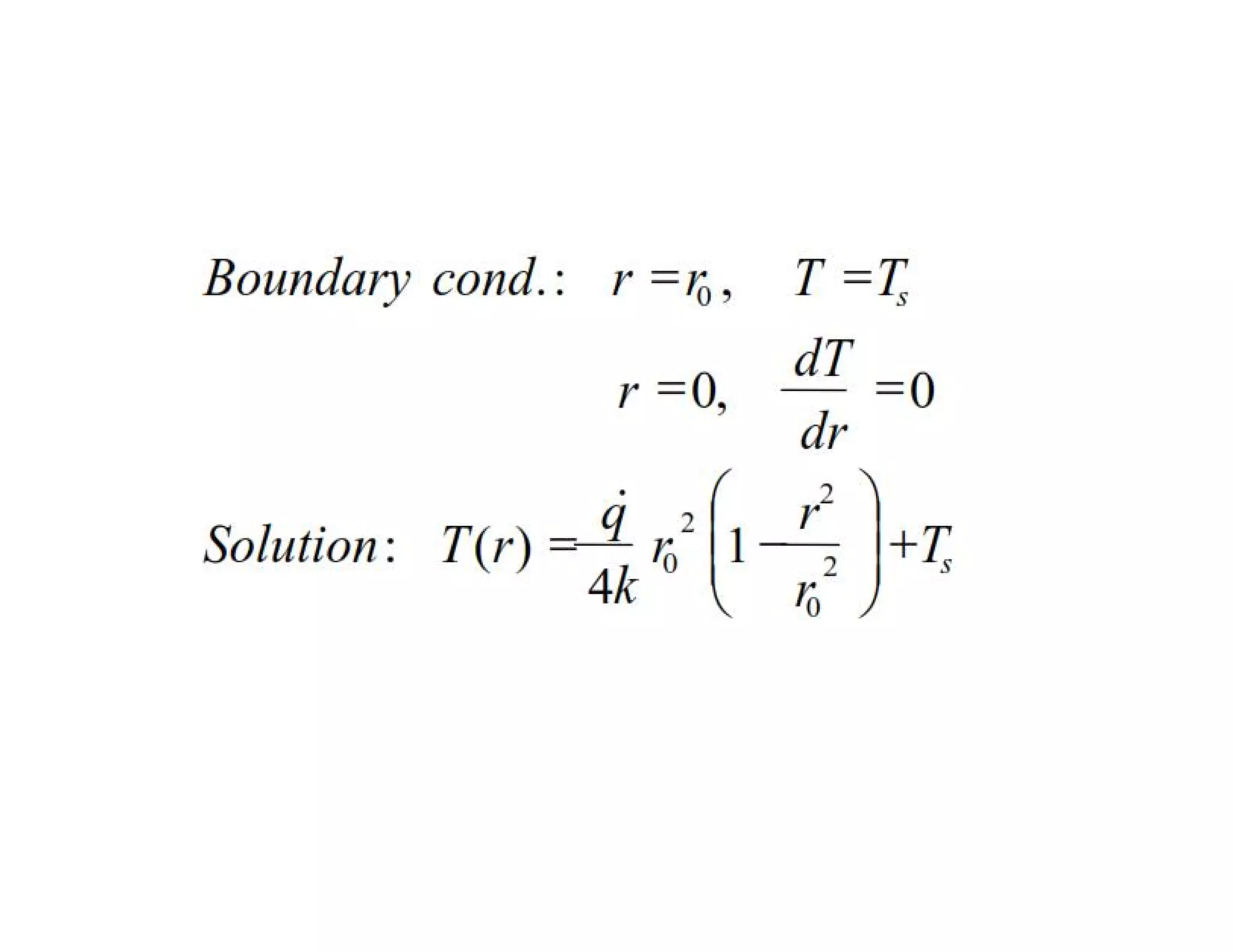Thermal contact resistance depends on surface roughness, material properties, temperature and pressure at the interface, and type of fluid trapped at the interface. The critical radius of insulation determines if insulation will help or hurt heat transfer. Internal heat generation in walls or cylinders means thermal resistance concept is not correct, and temperature will be non-linear.