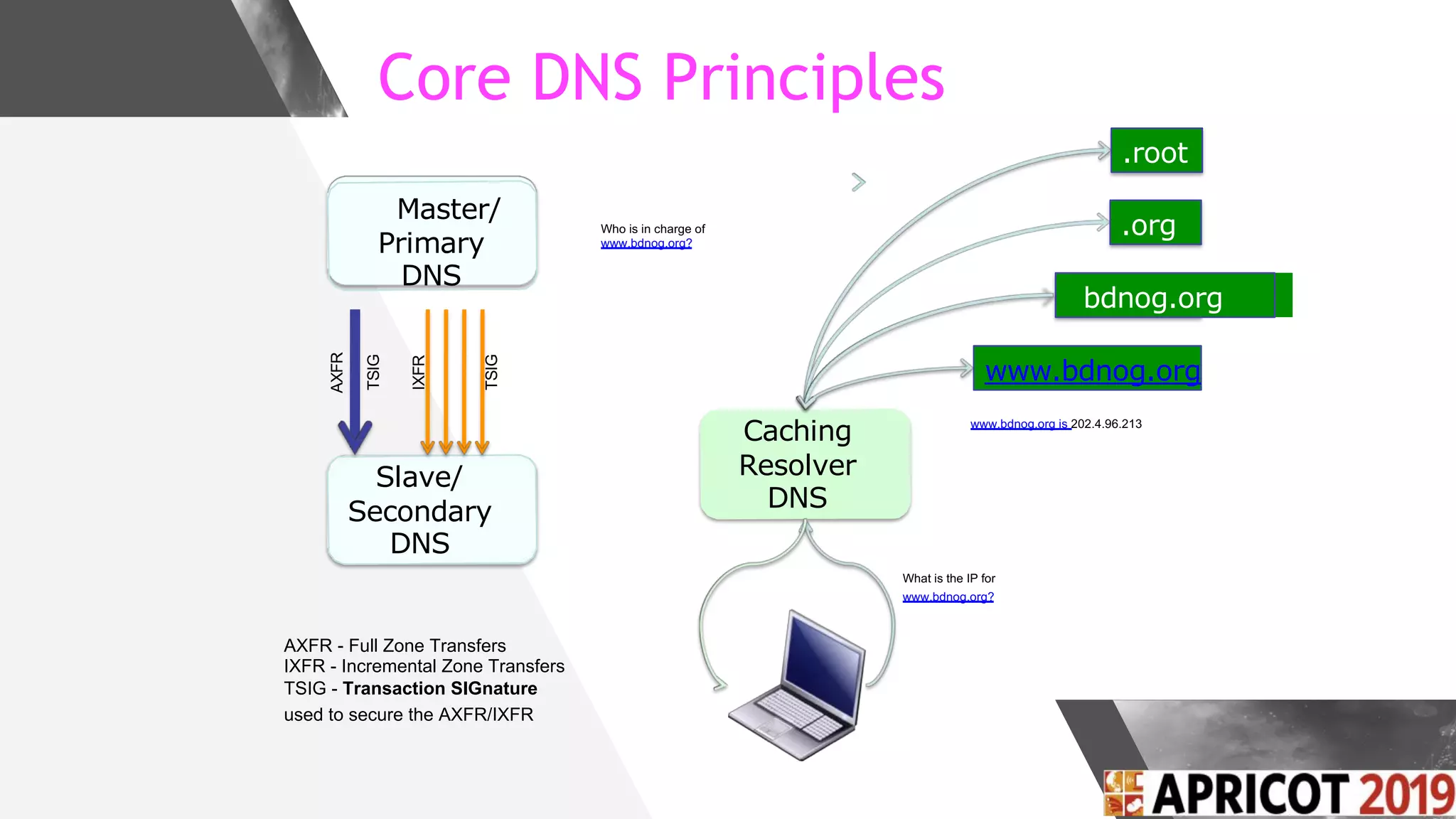
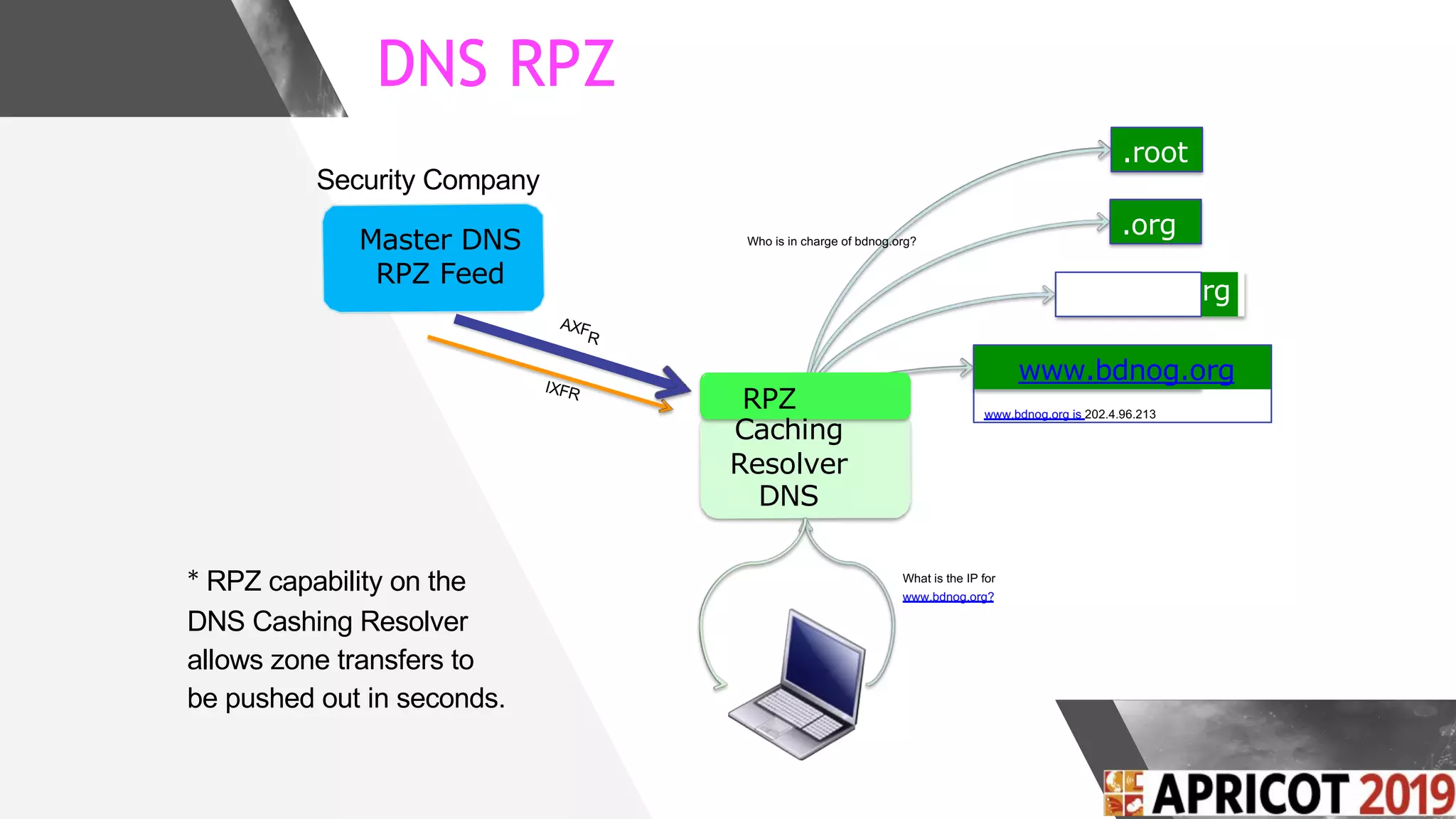
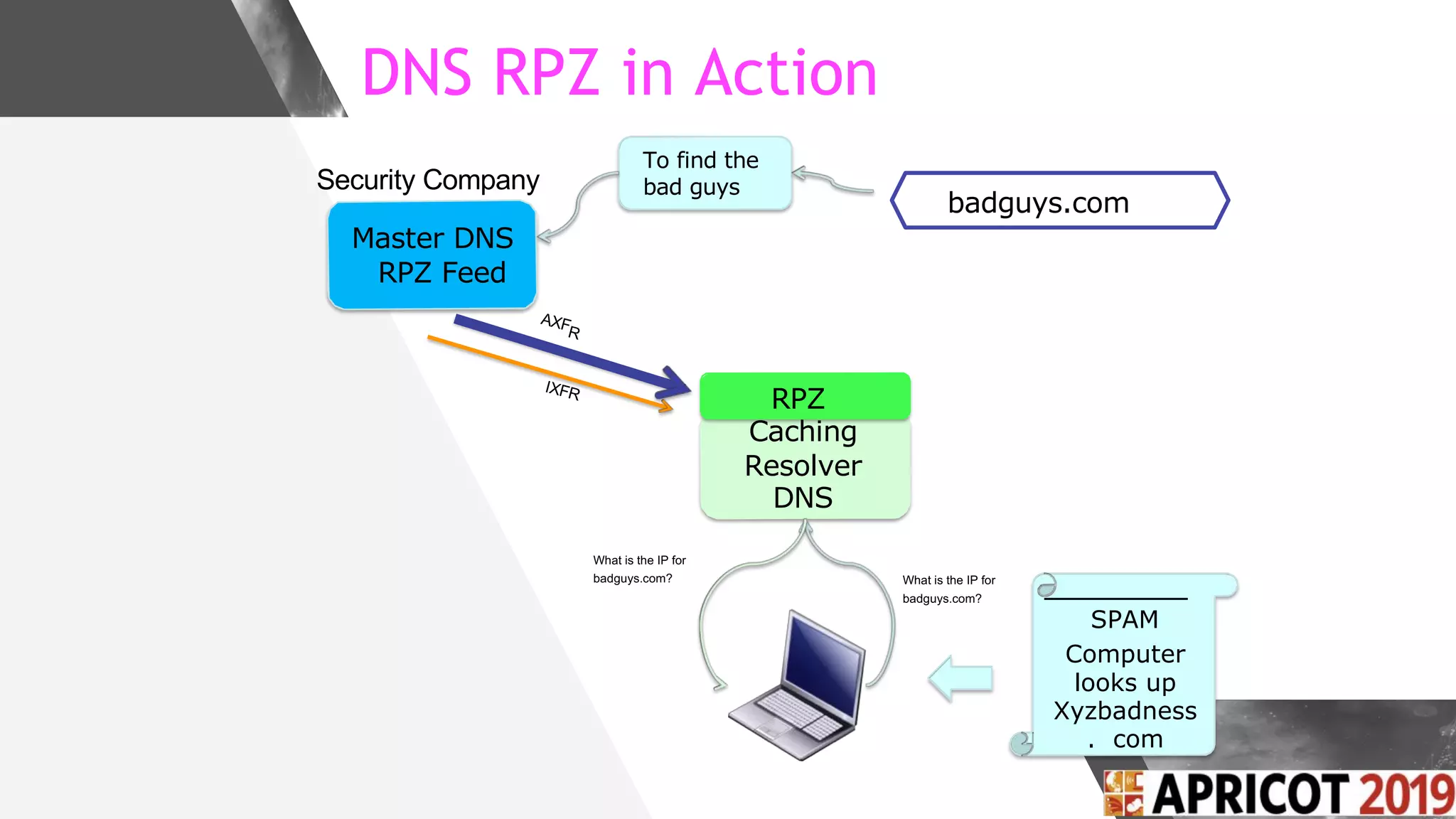
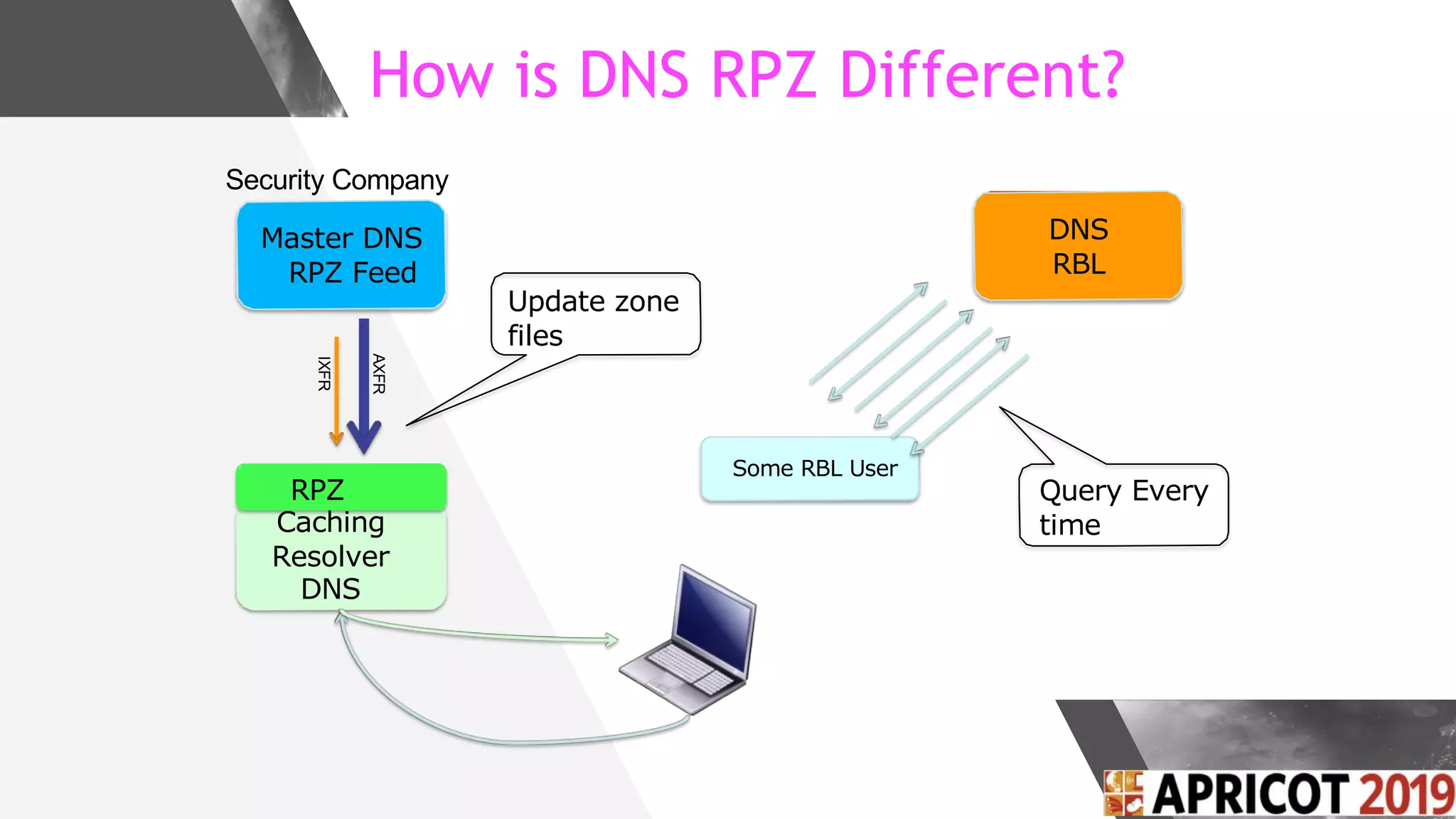
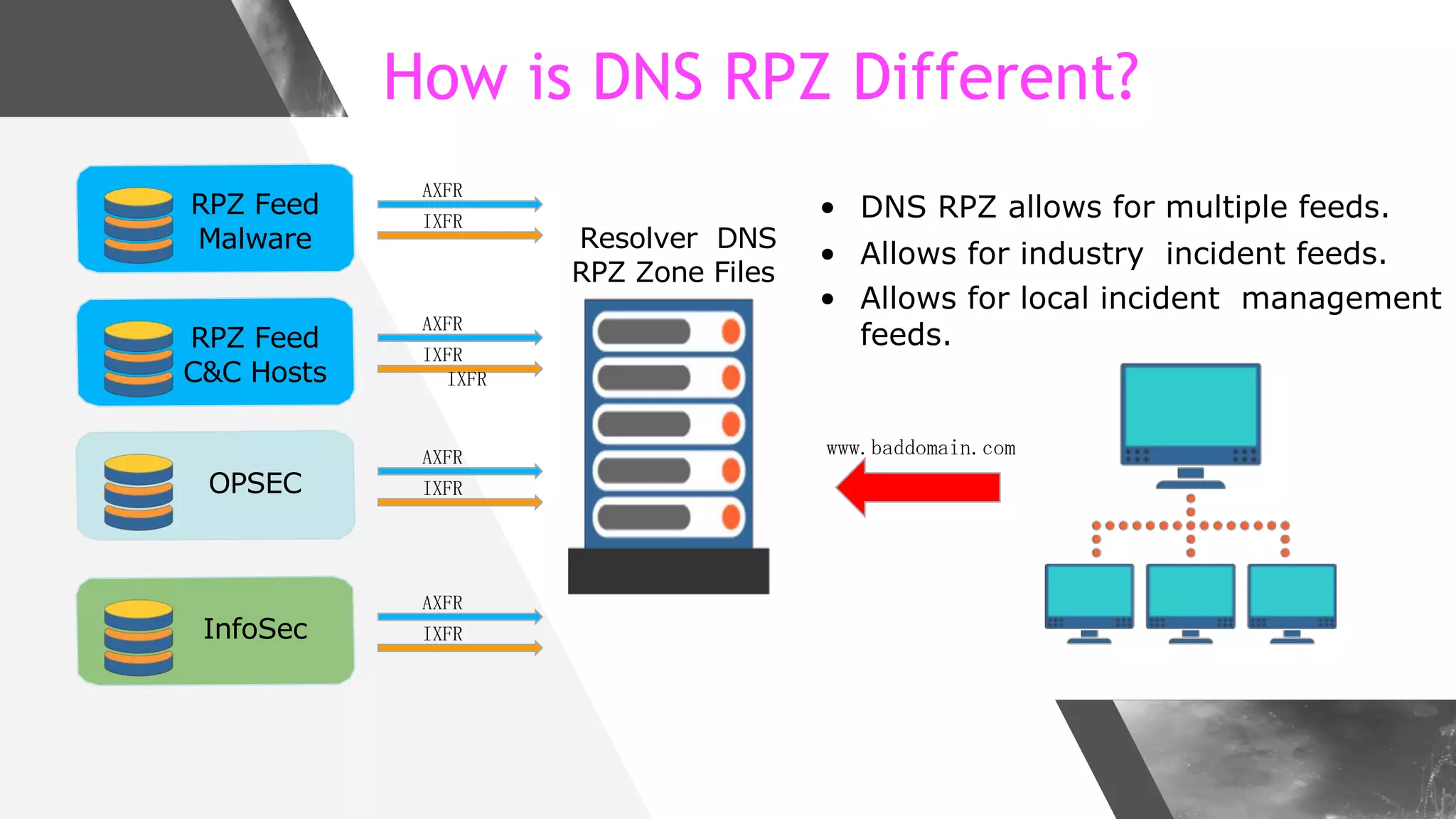
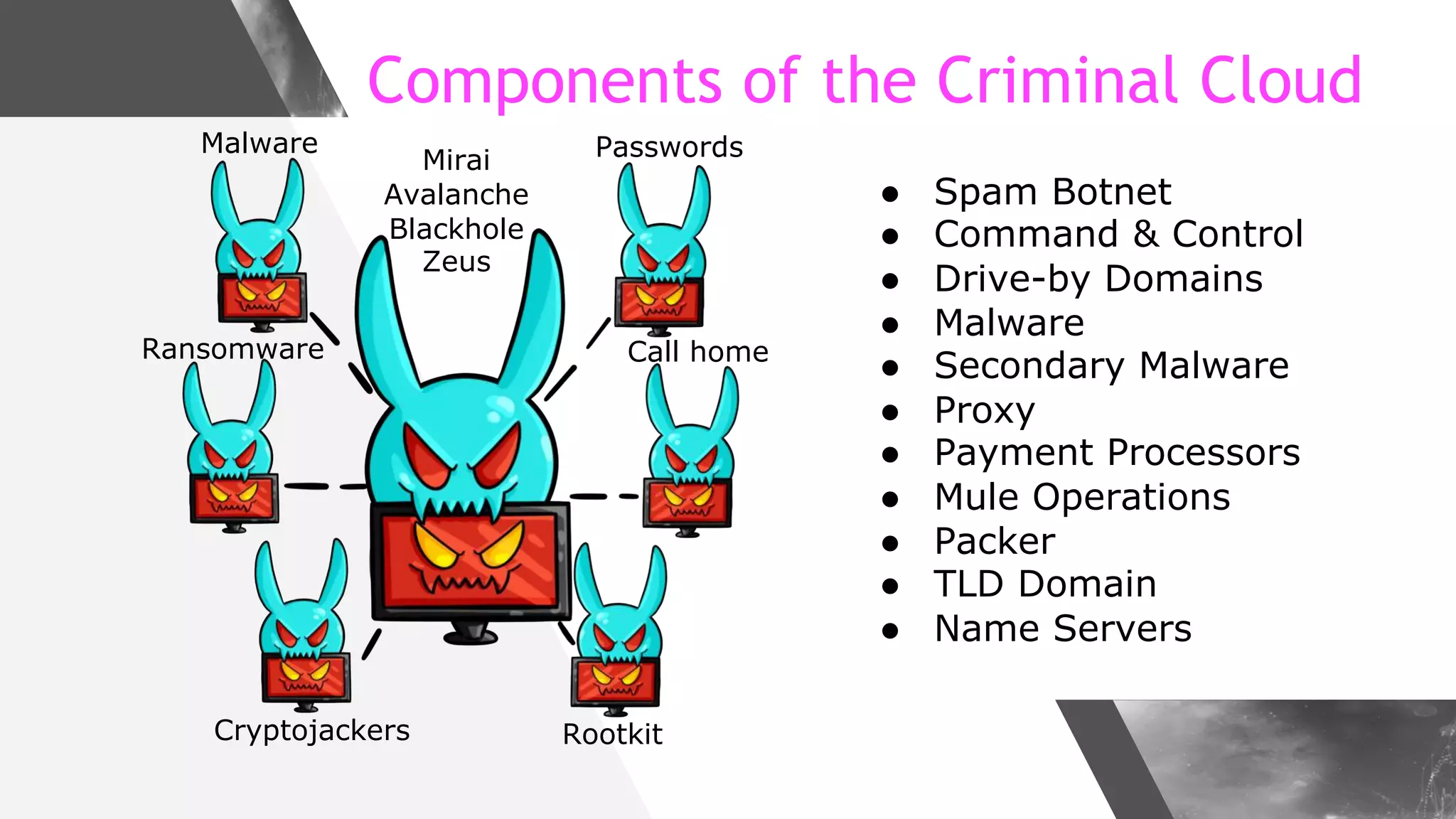
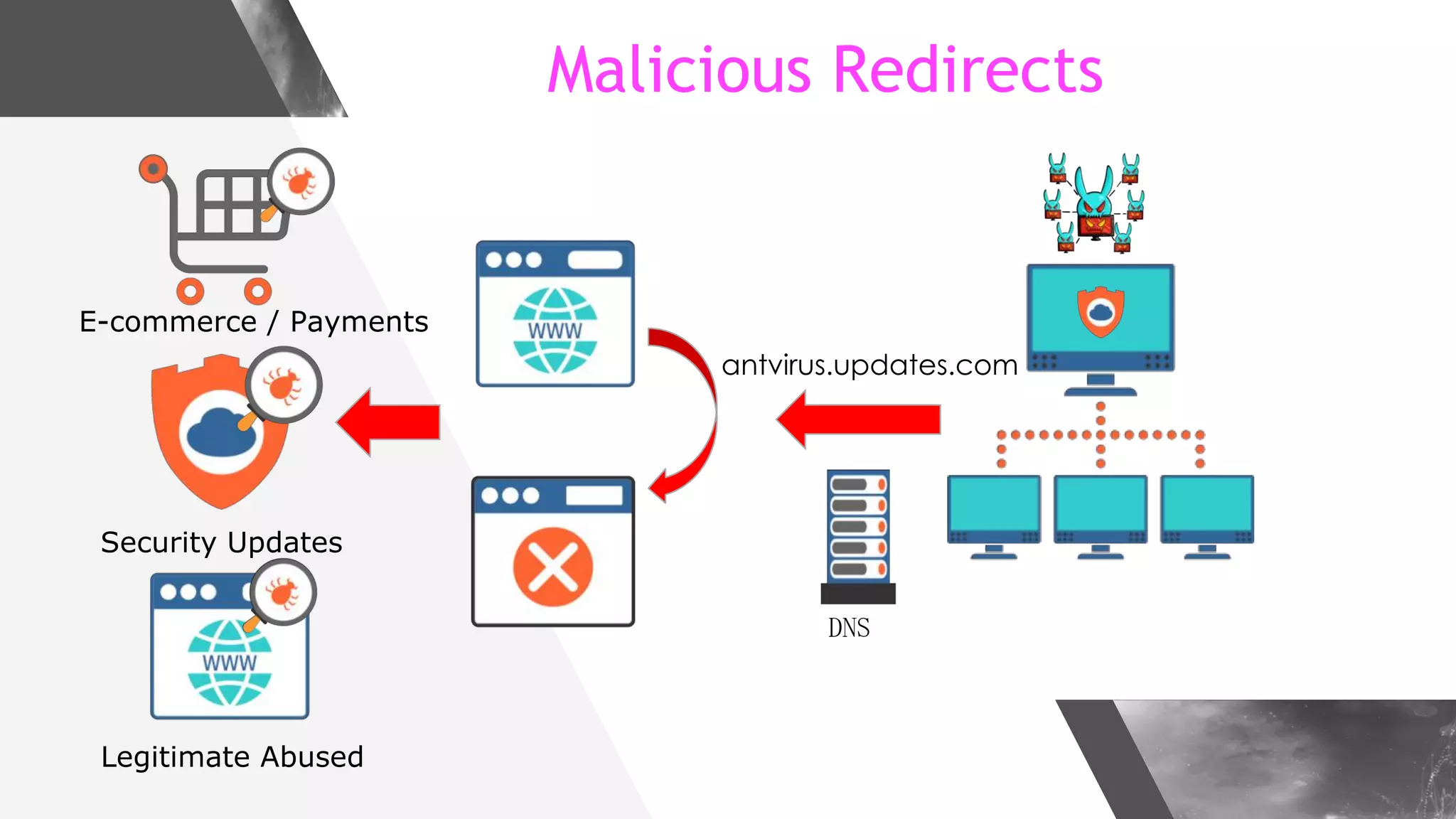
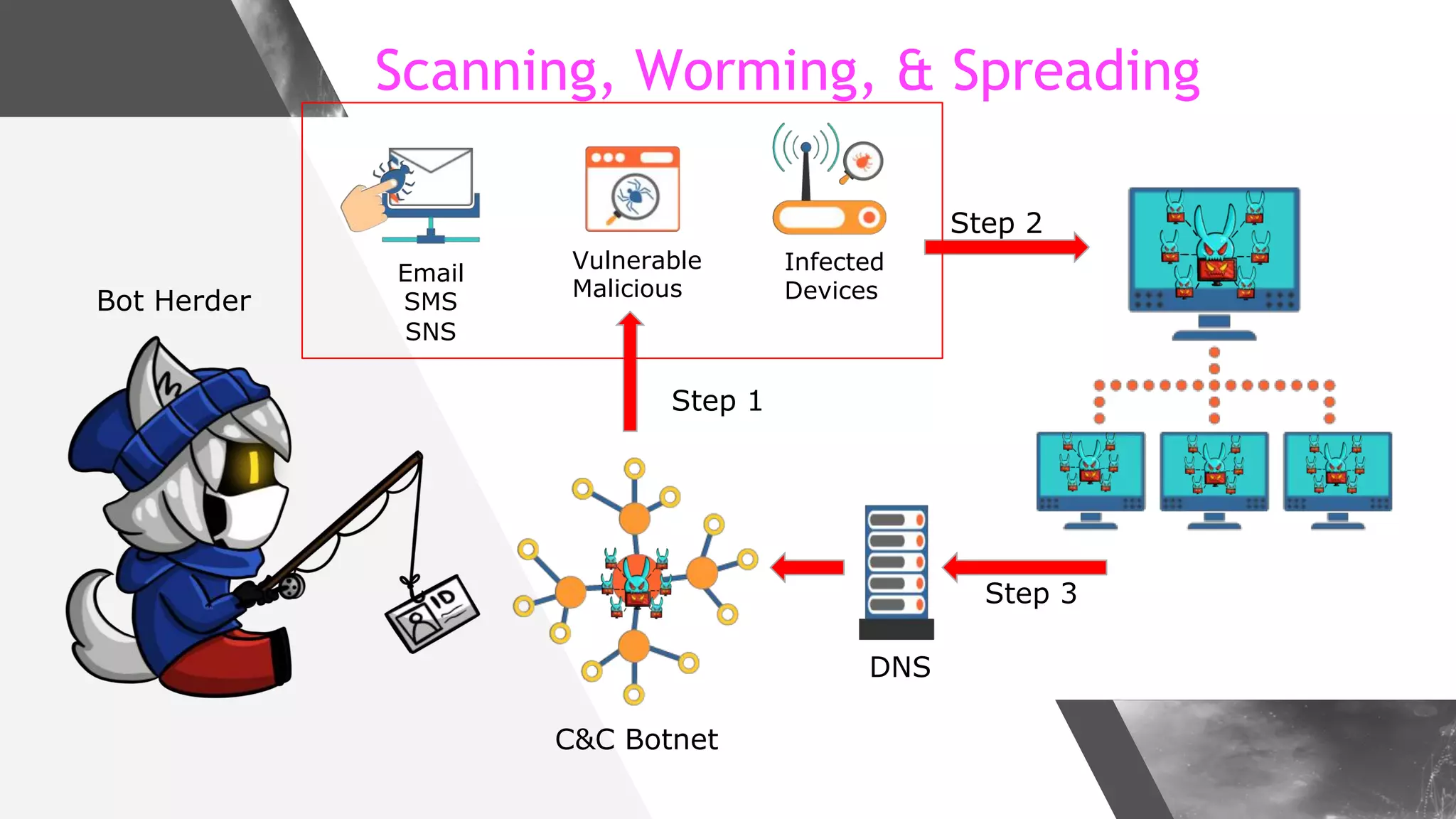
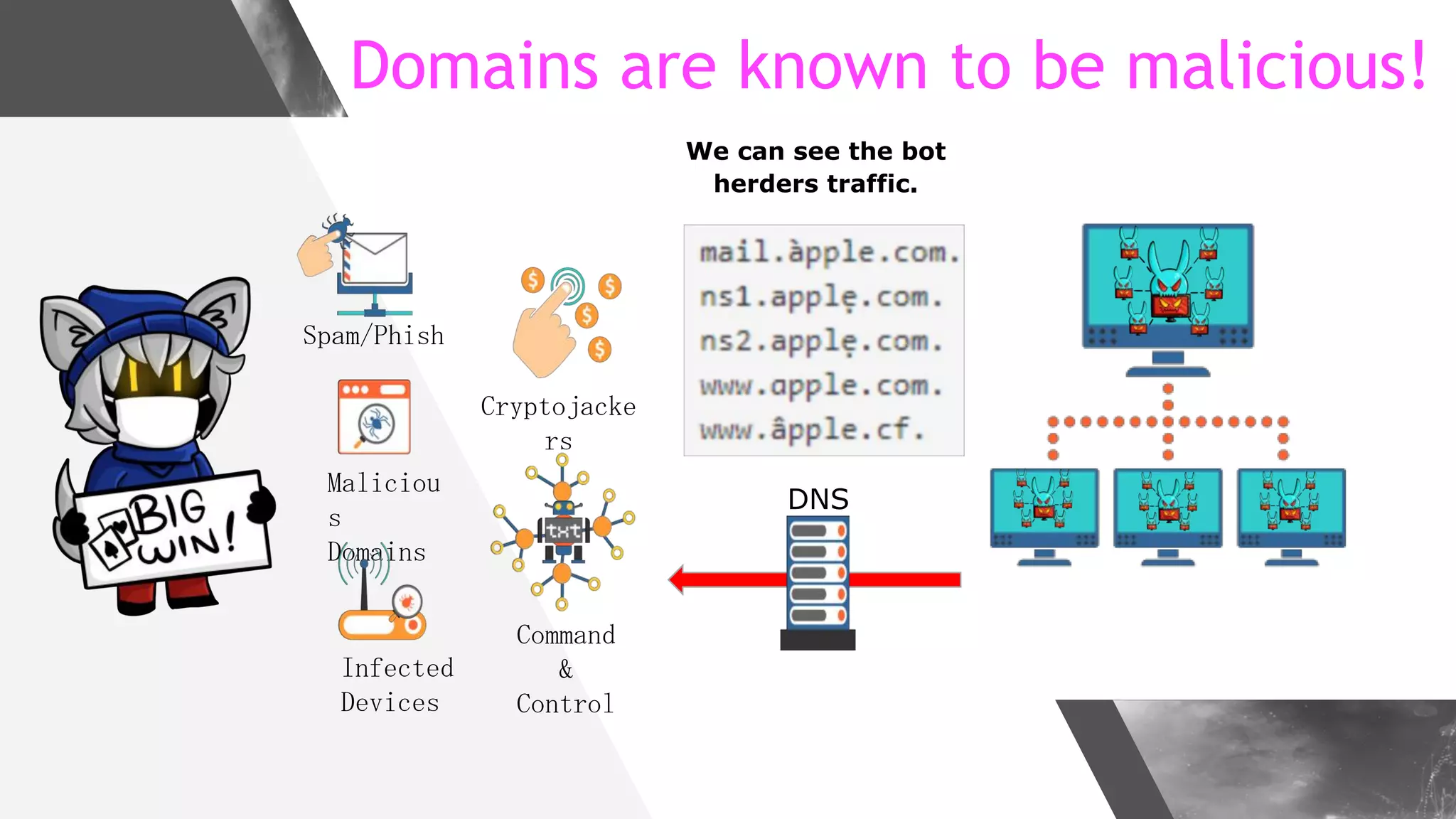
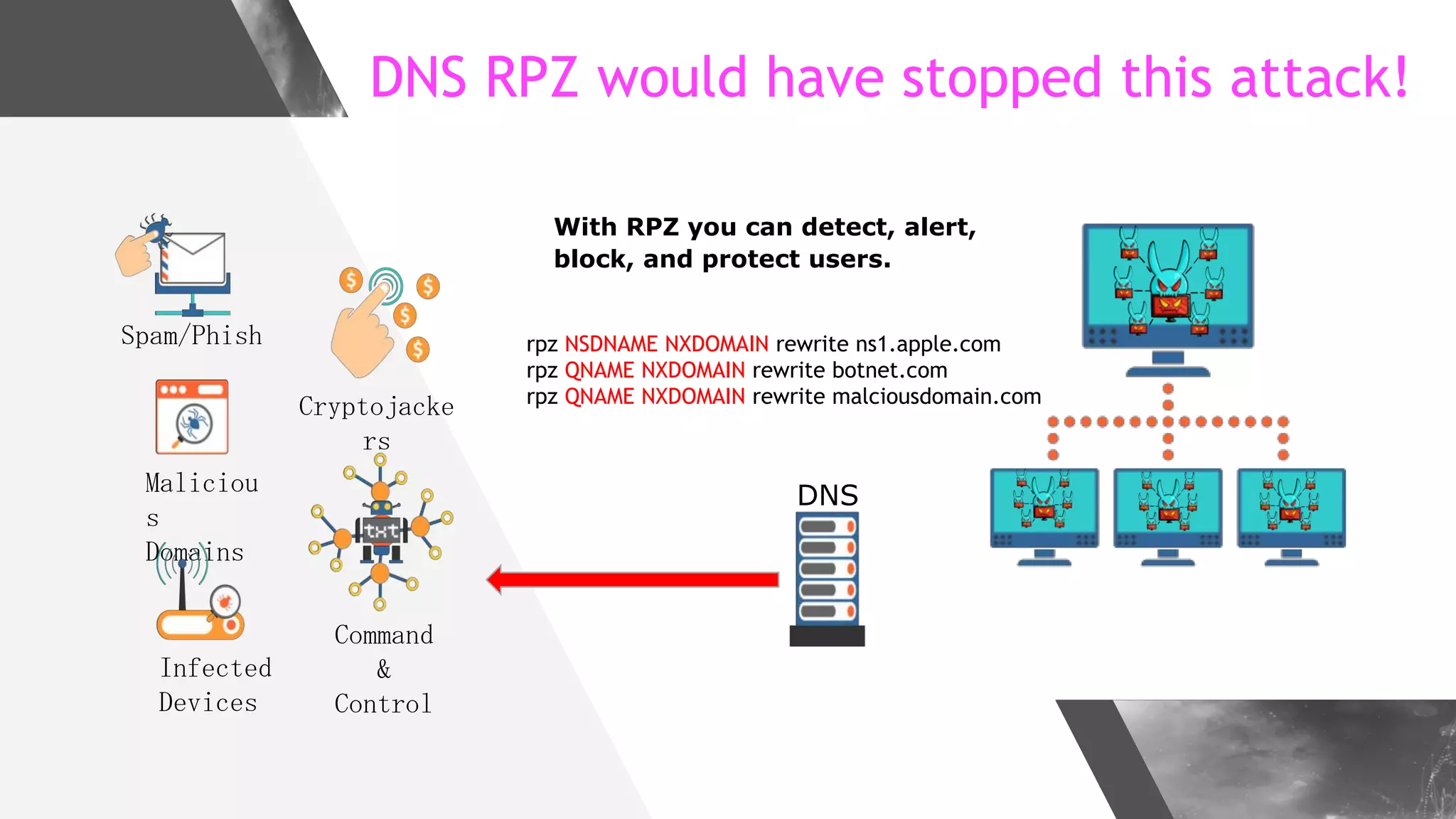
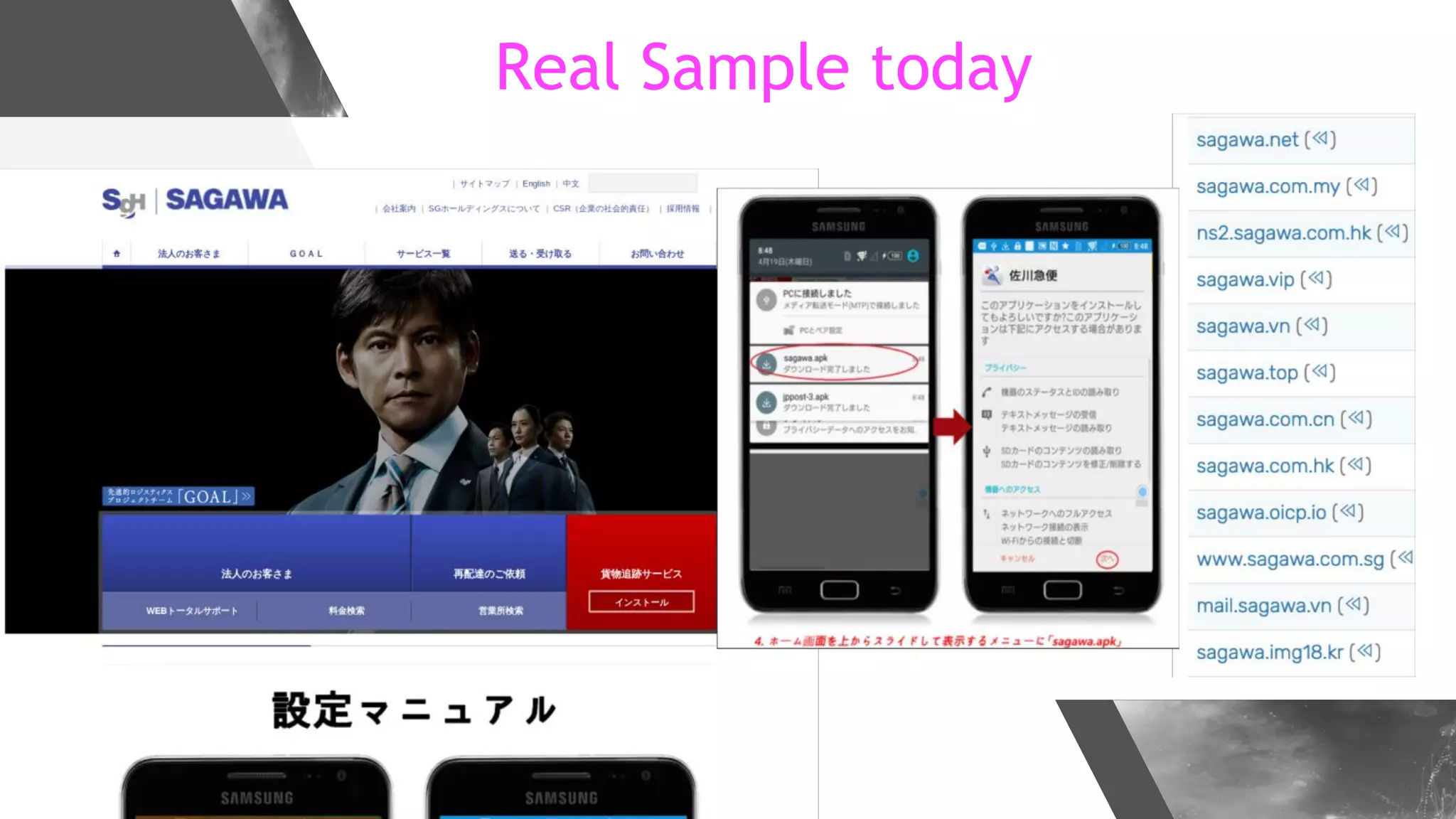
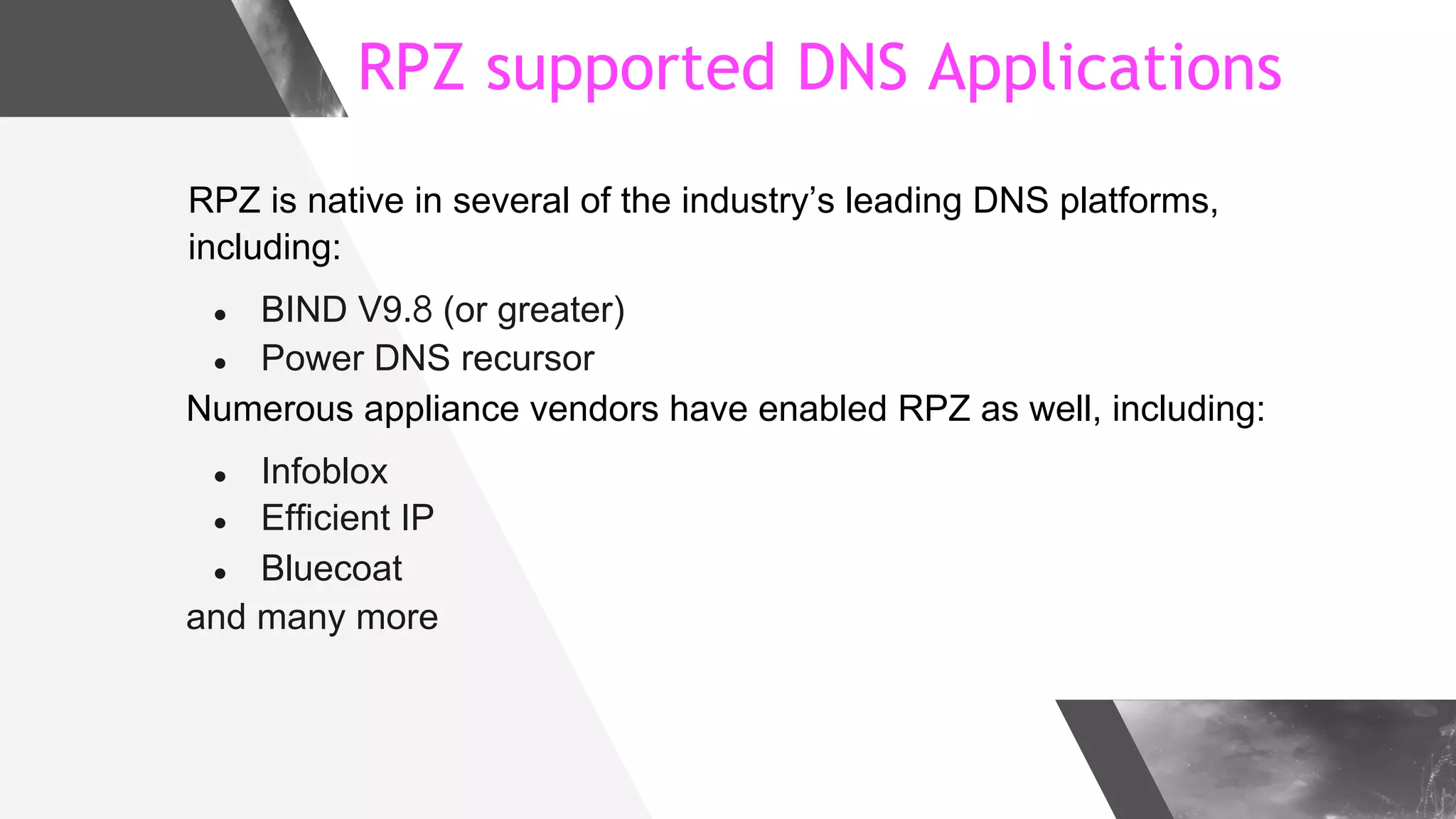
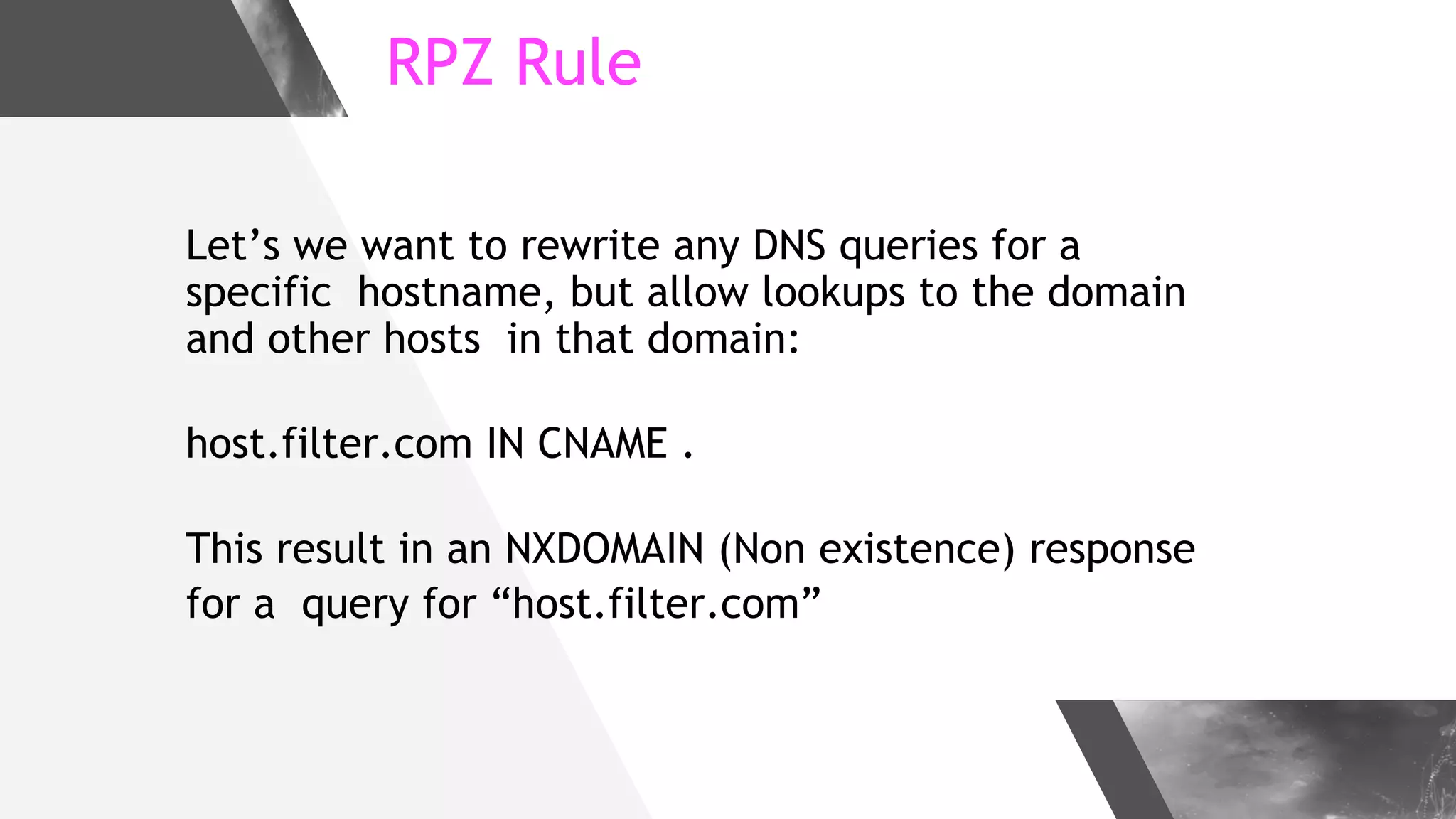
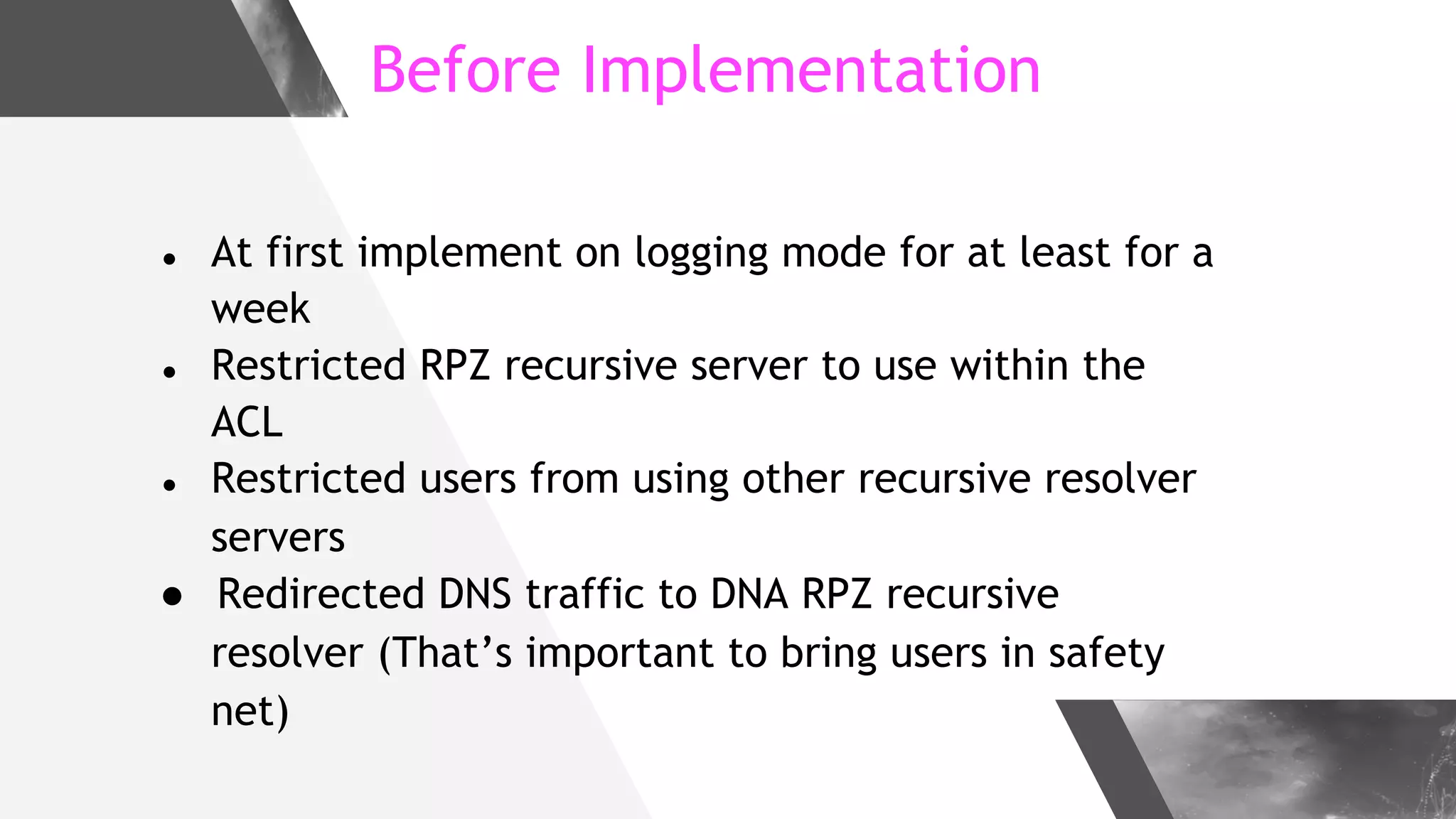
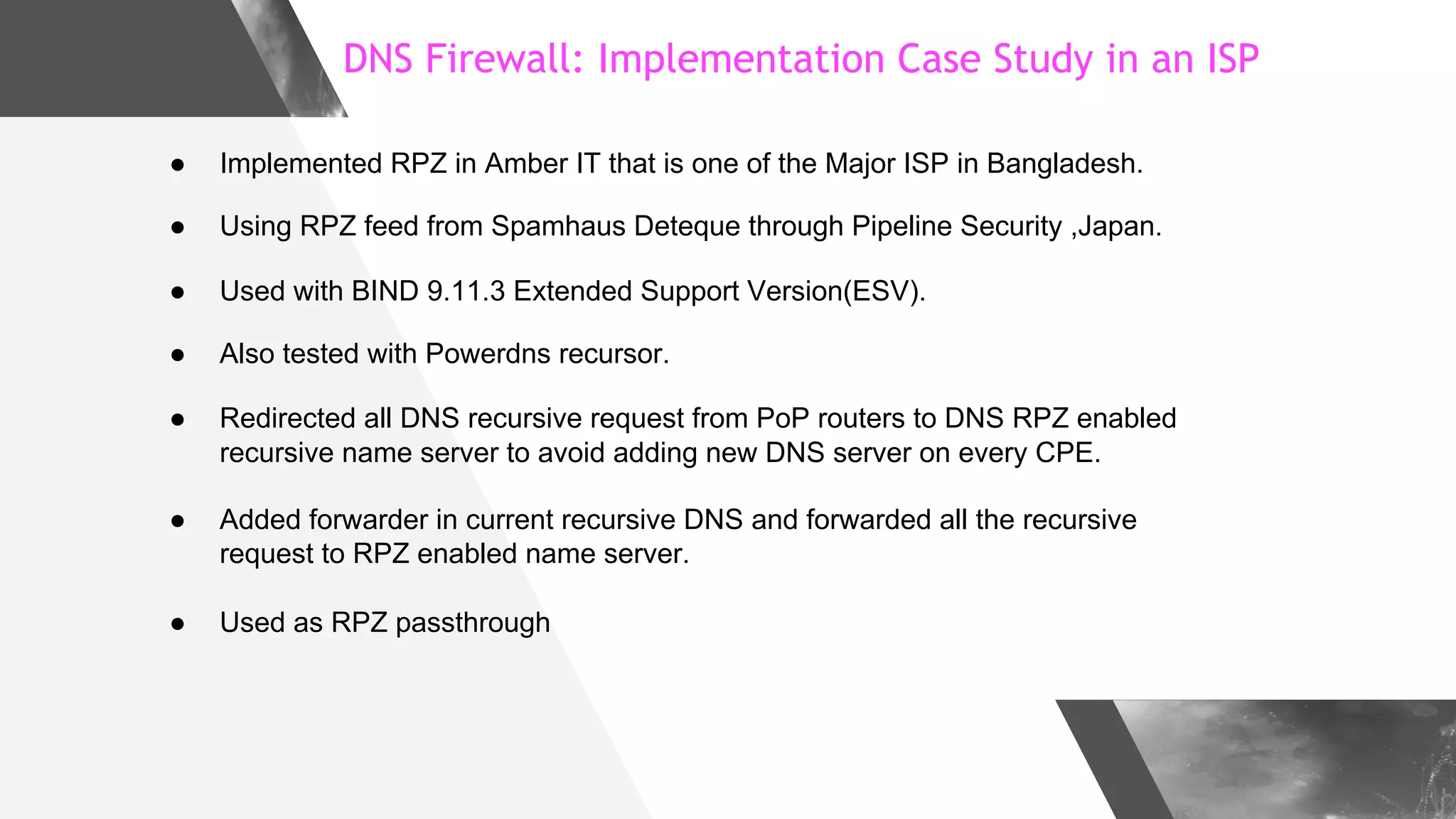
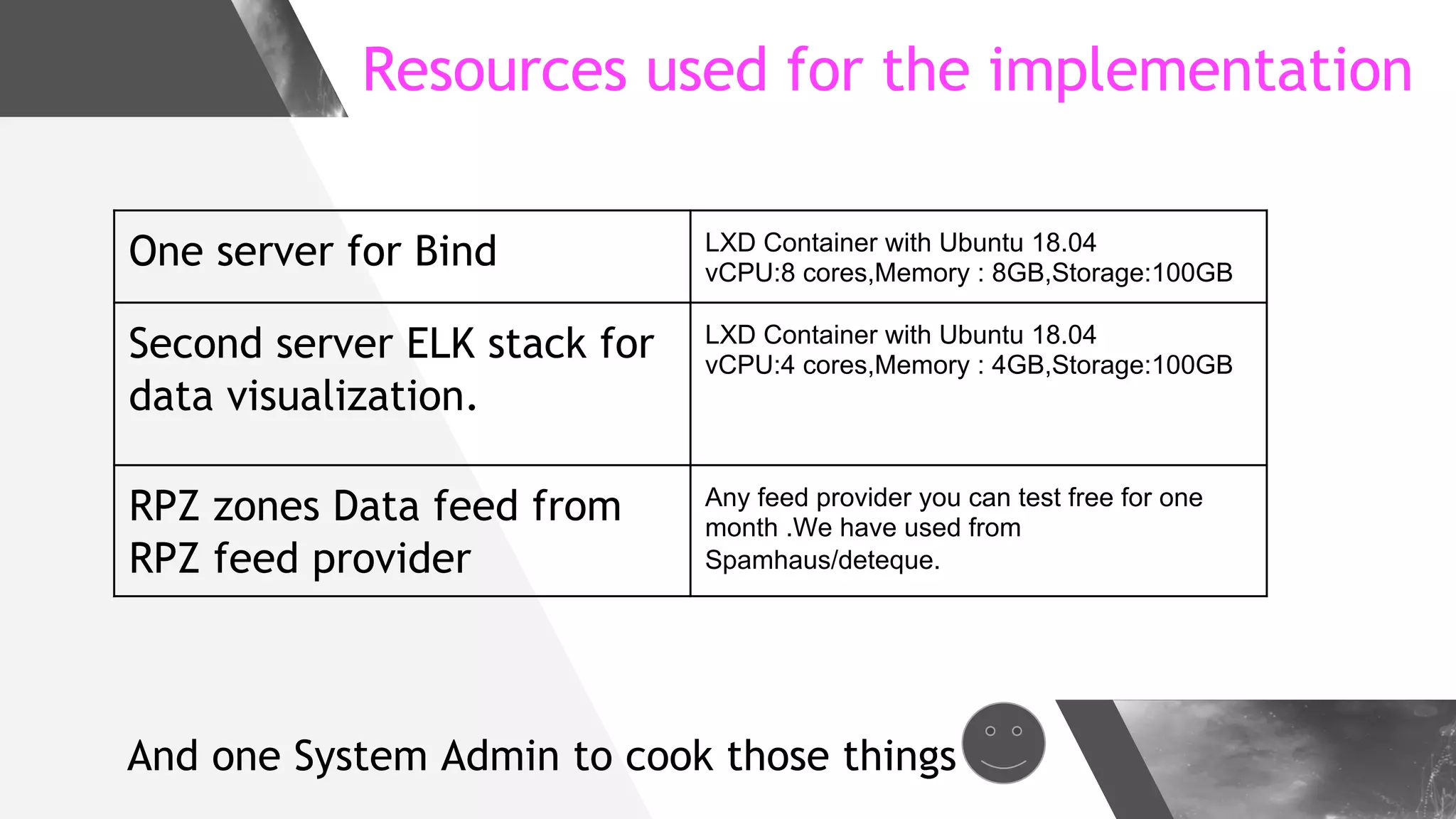
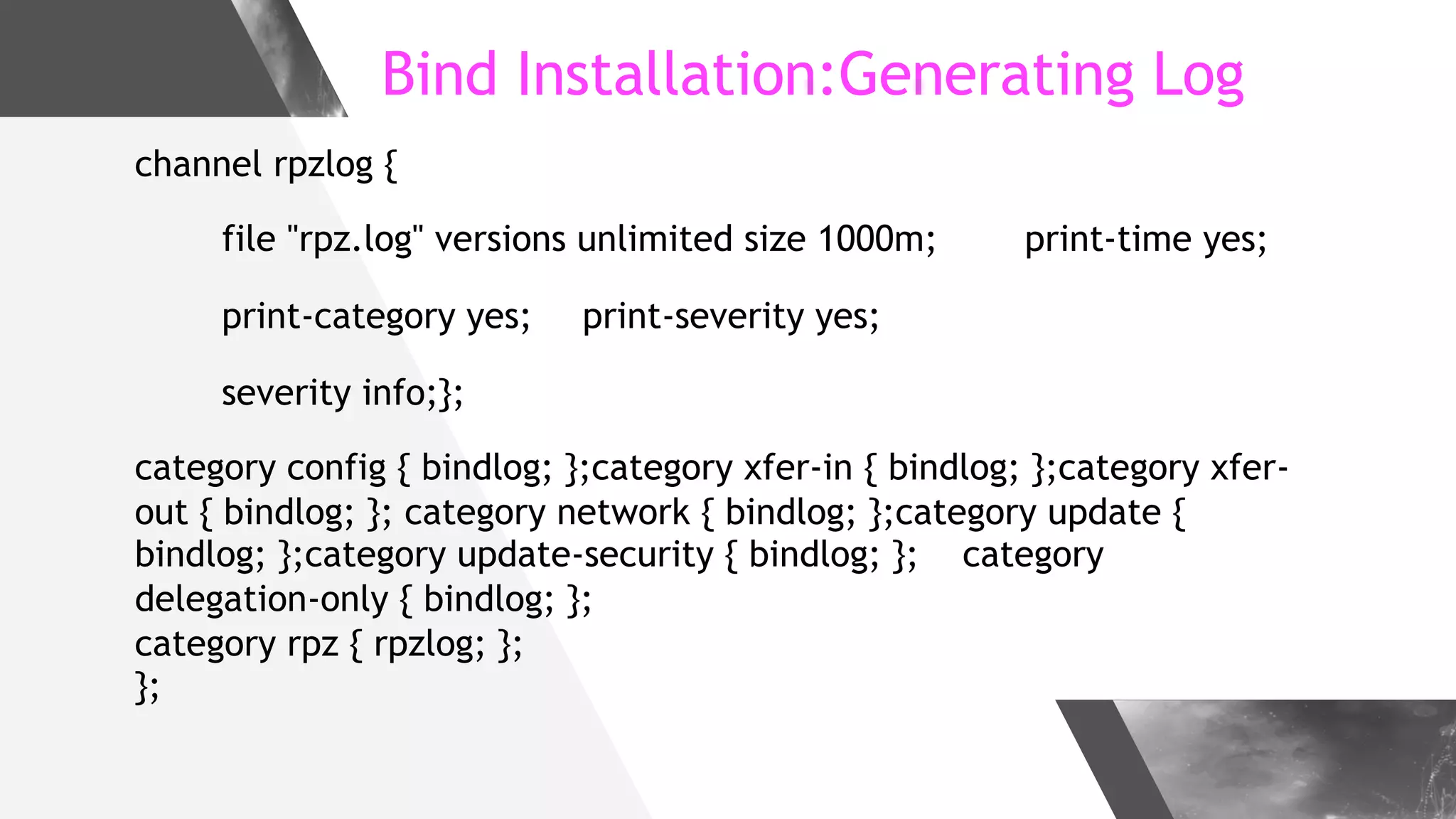
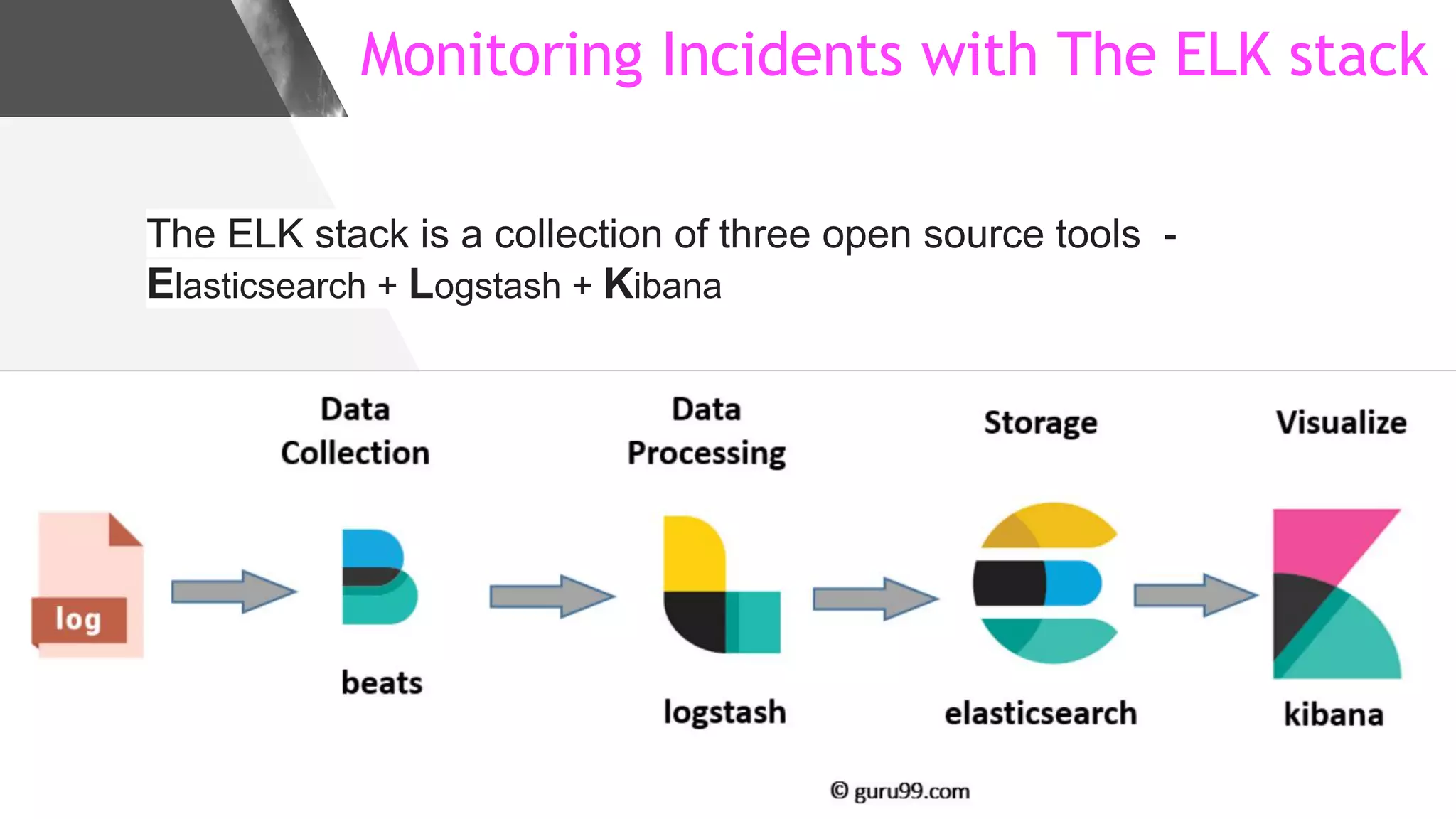
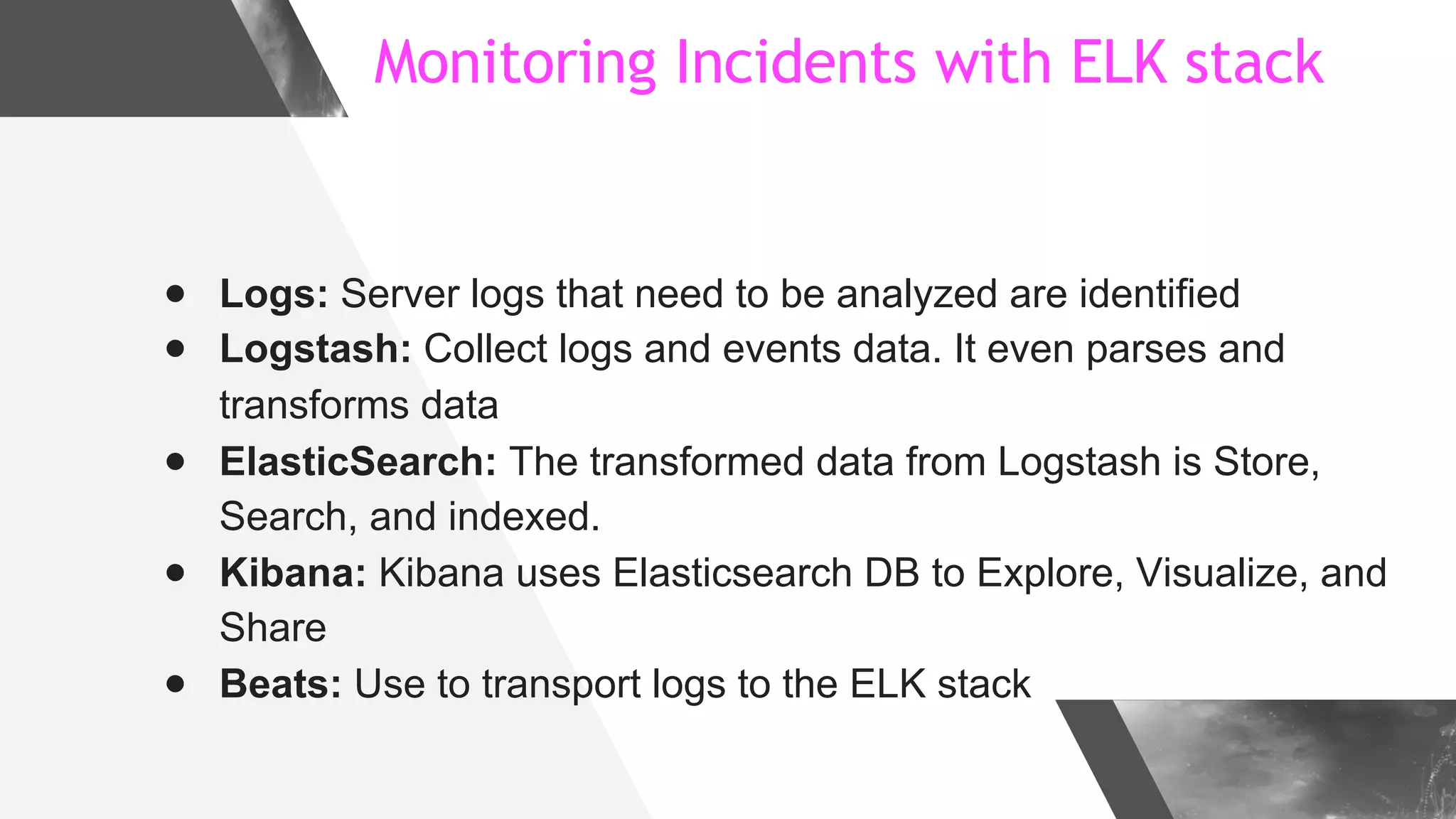
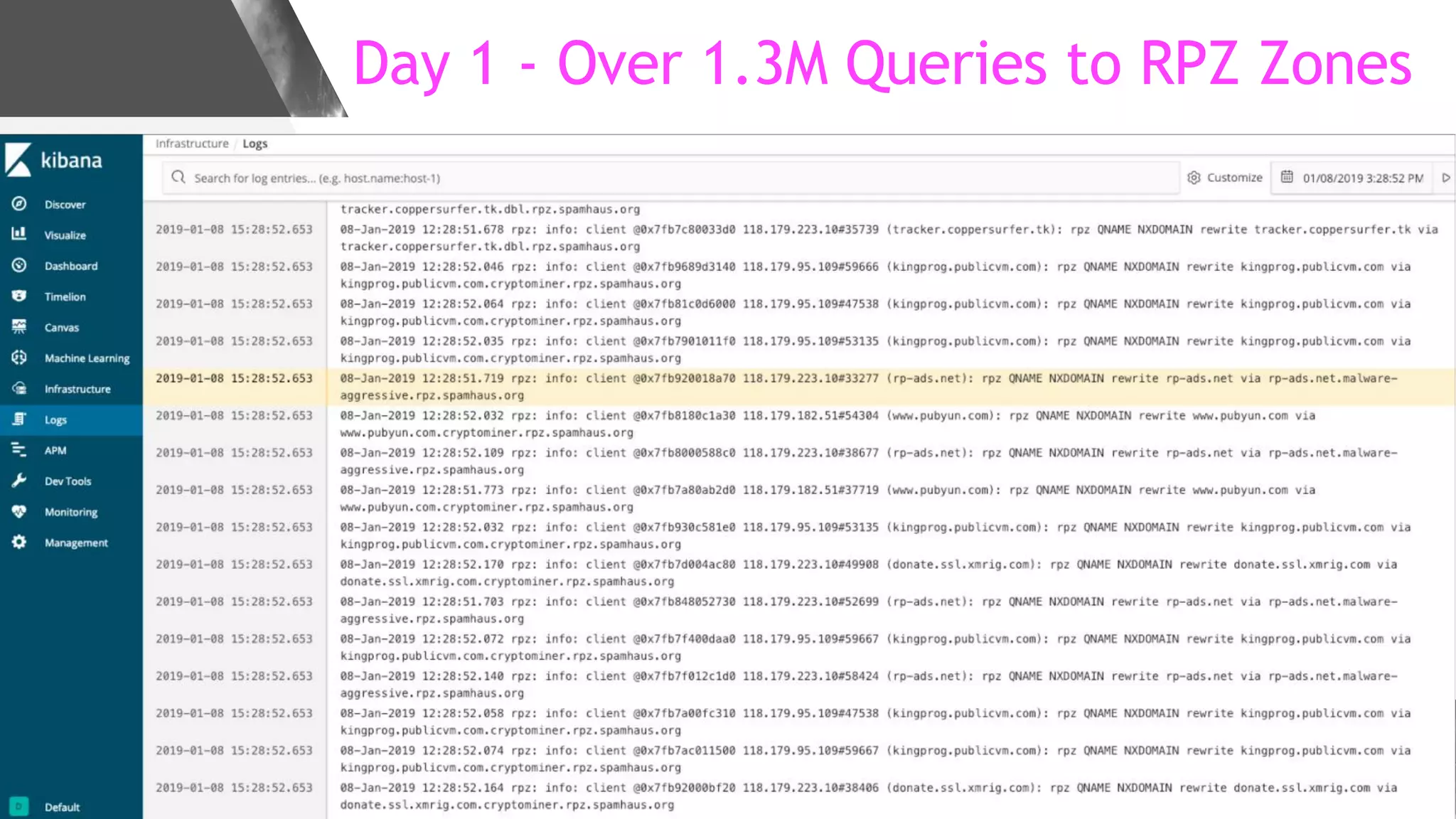
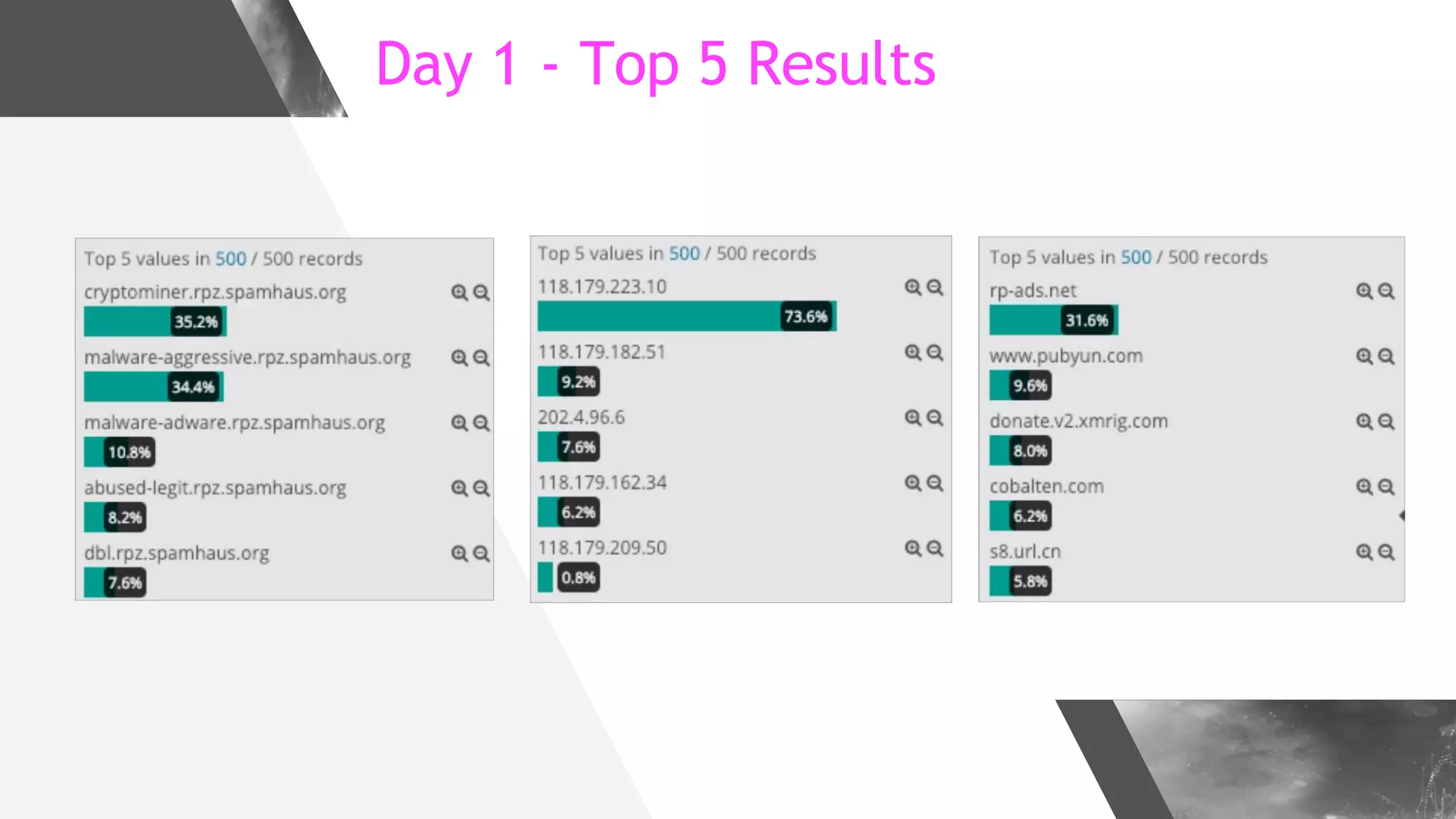
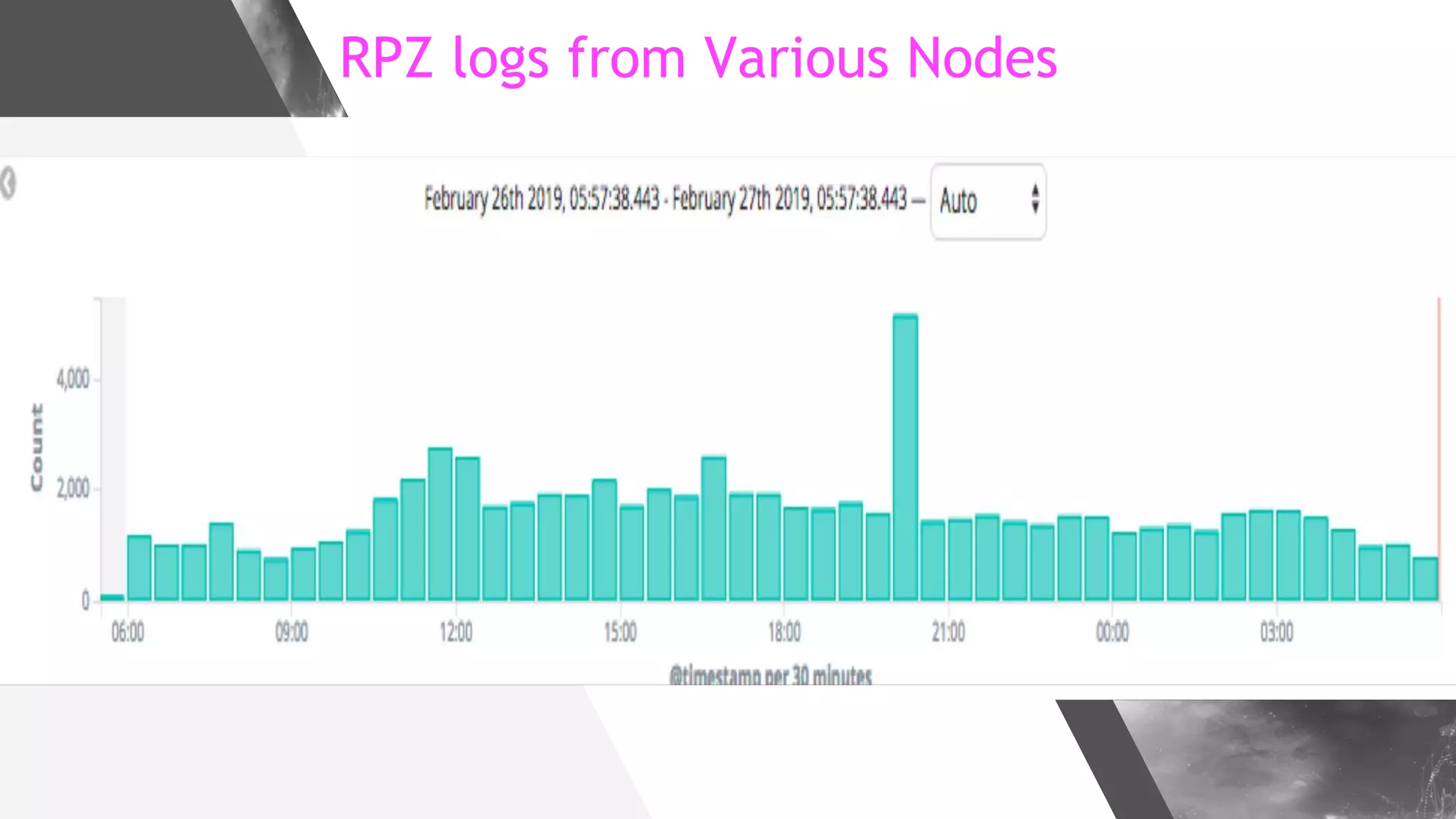
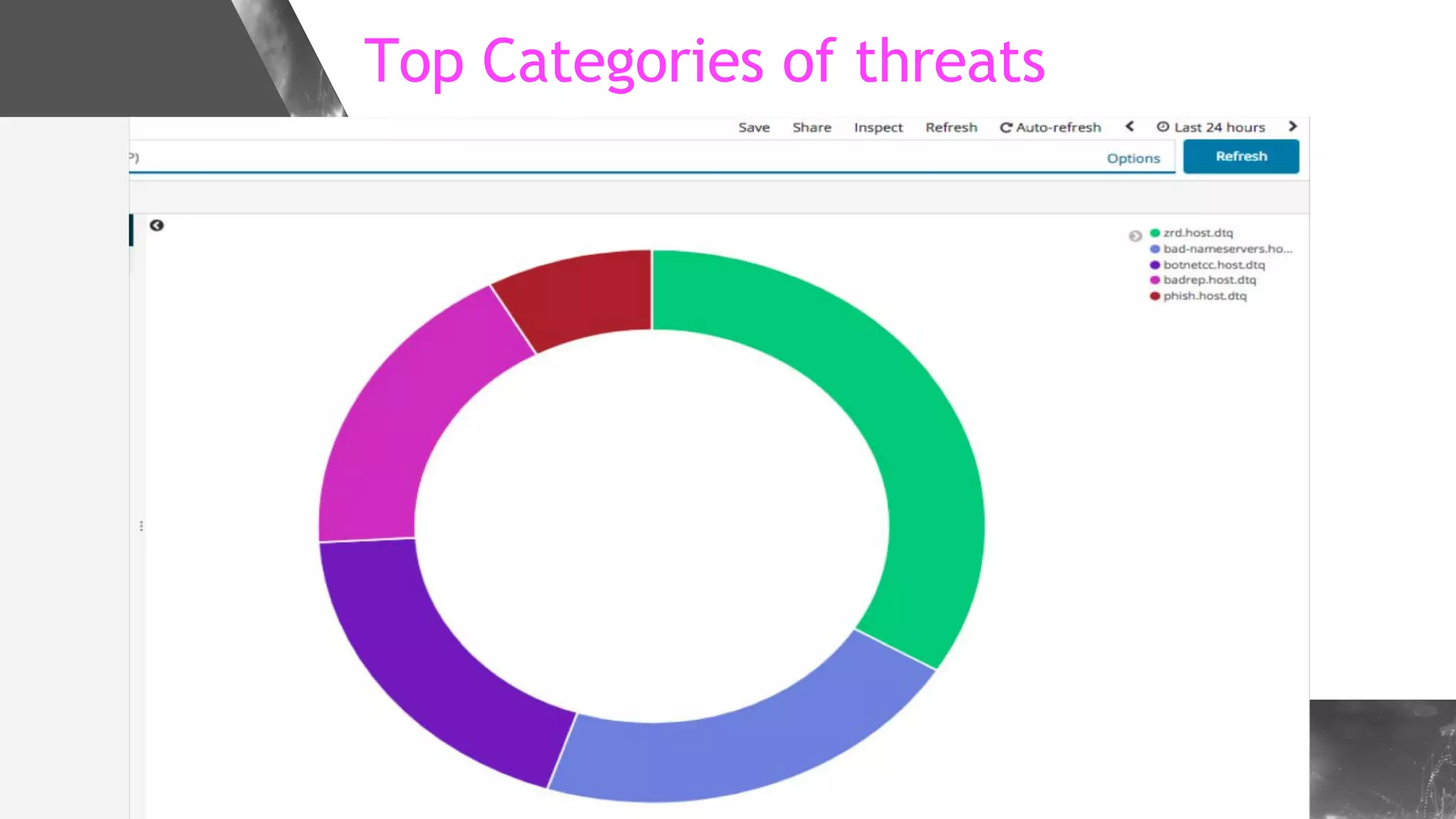
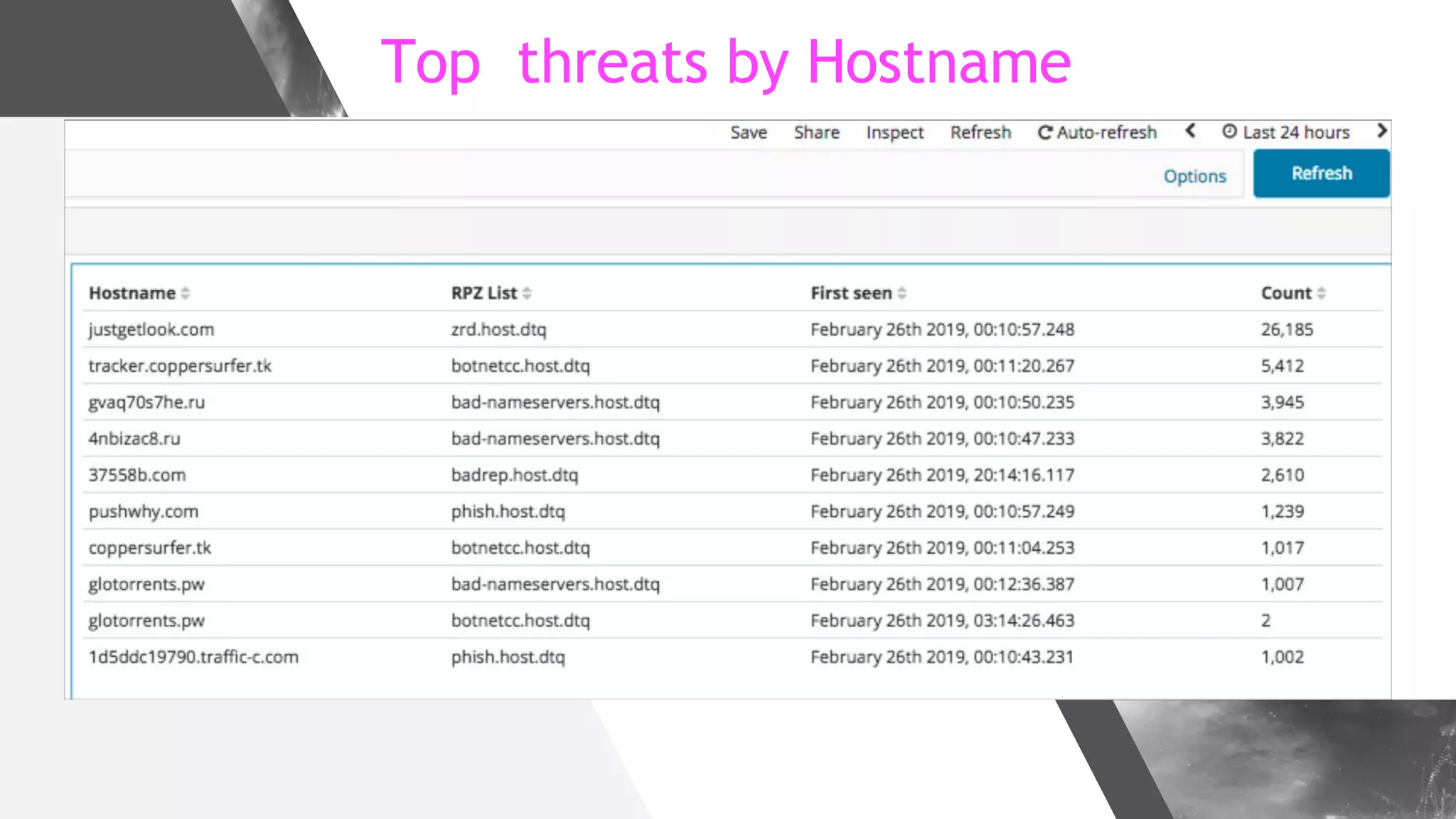
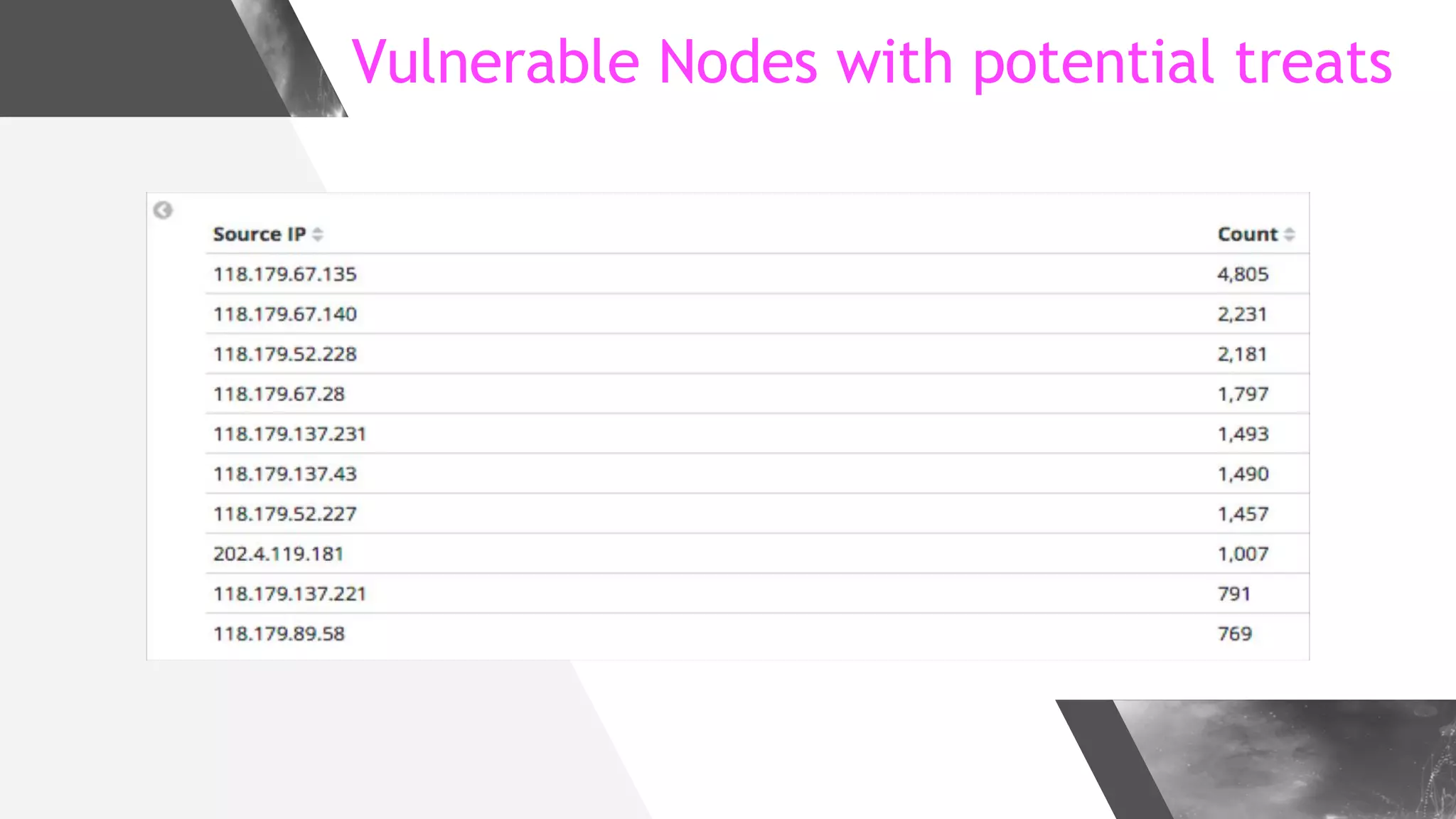
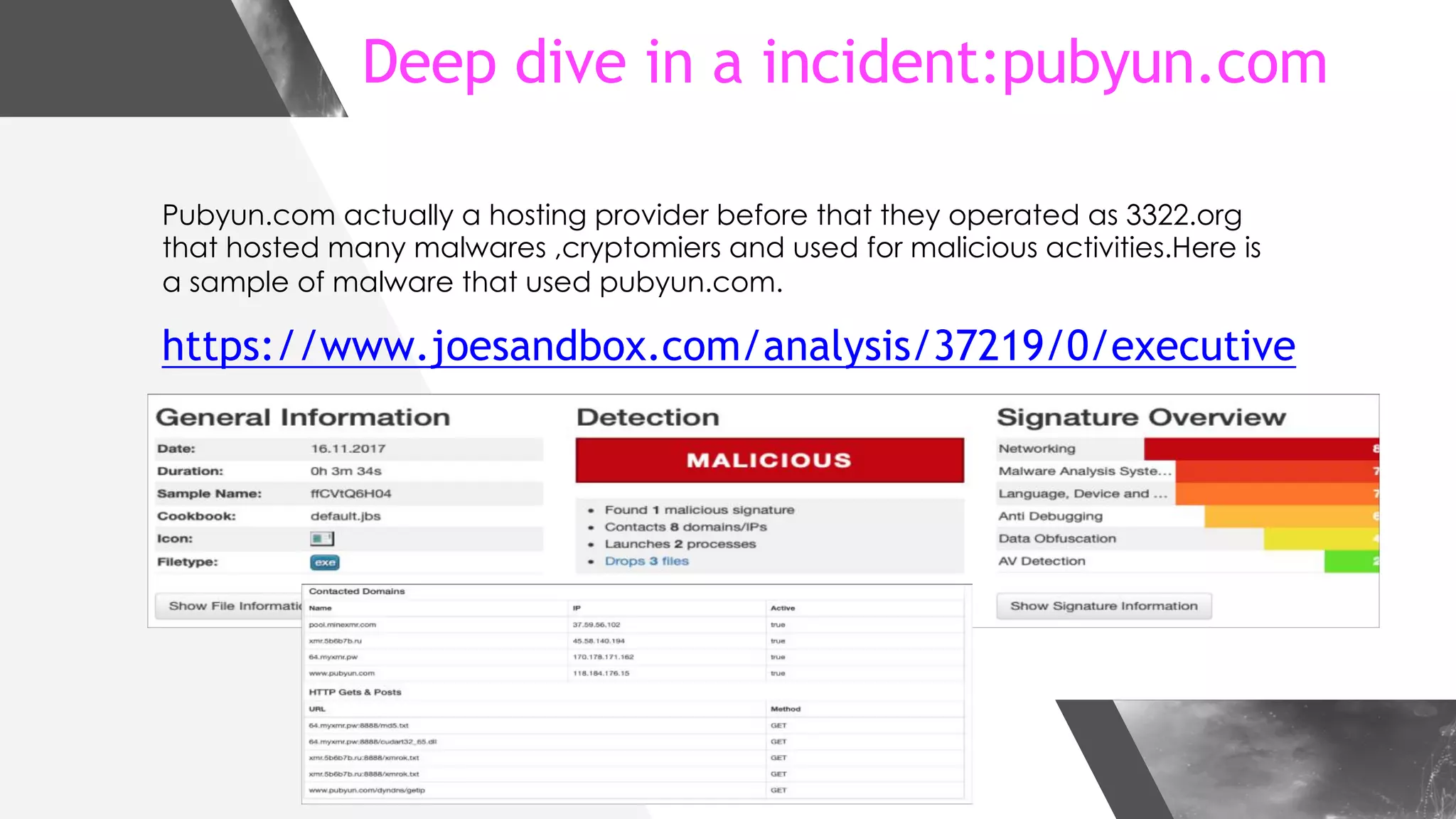
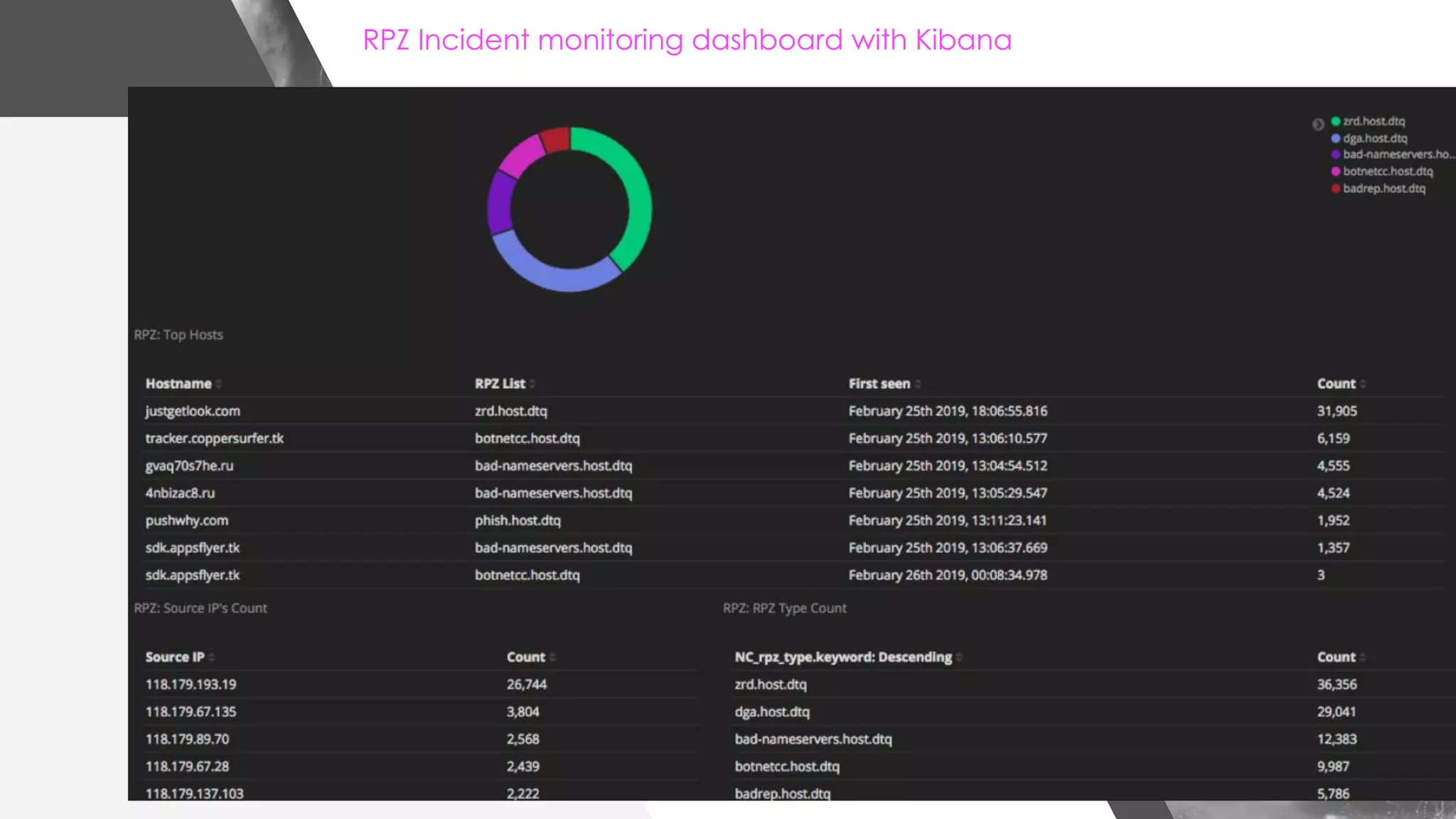
This document discusses implementing DNS Response Policy Zones (RPZ) to provide secure internet access for all users without requiring new hardware or client-side changes. It describes considerations for RPZ, how RPZ works to block malicious DNS resolutions, the components of a real-world implementation case study at a major Bangladeshi ISP, and monitoring results showing over 1.3 million queries to RPZ zones on the first day.