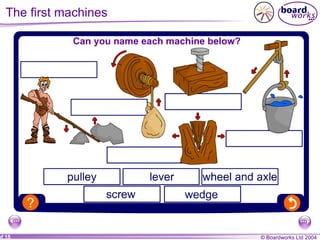
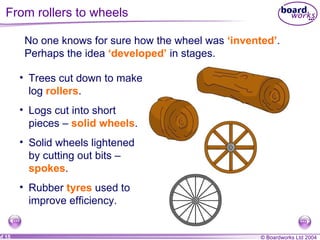
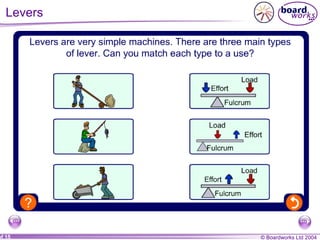
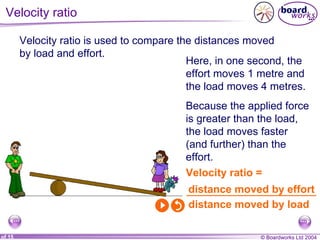
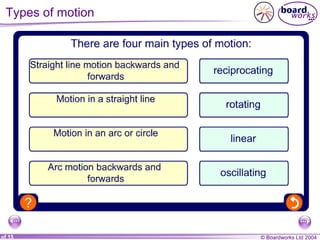
This document discusses different types of simple machines and mechanisms that make life easier for humans. It describes how wheels were developed over time from log rollers to solid wheels to spoked wheels. It also mentions the use of animal power and levers as simple machines that increase mechanical advantage. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of gears and motions like linear and rotational.