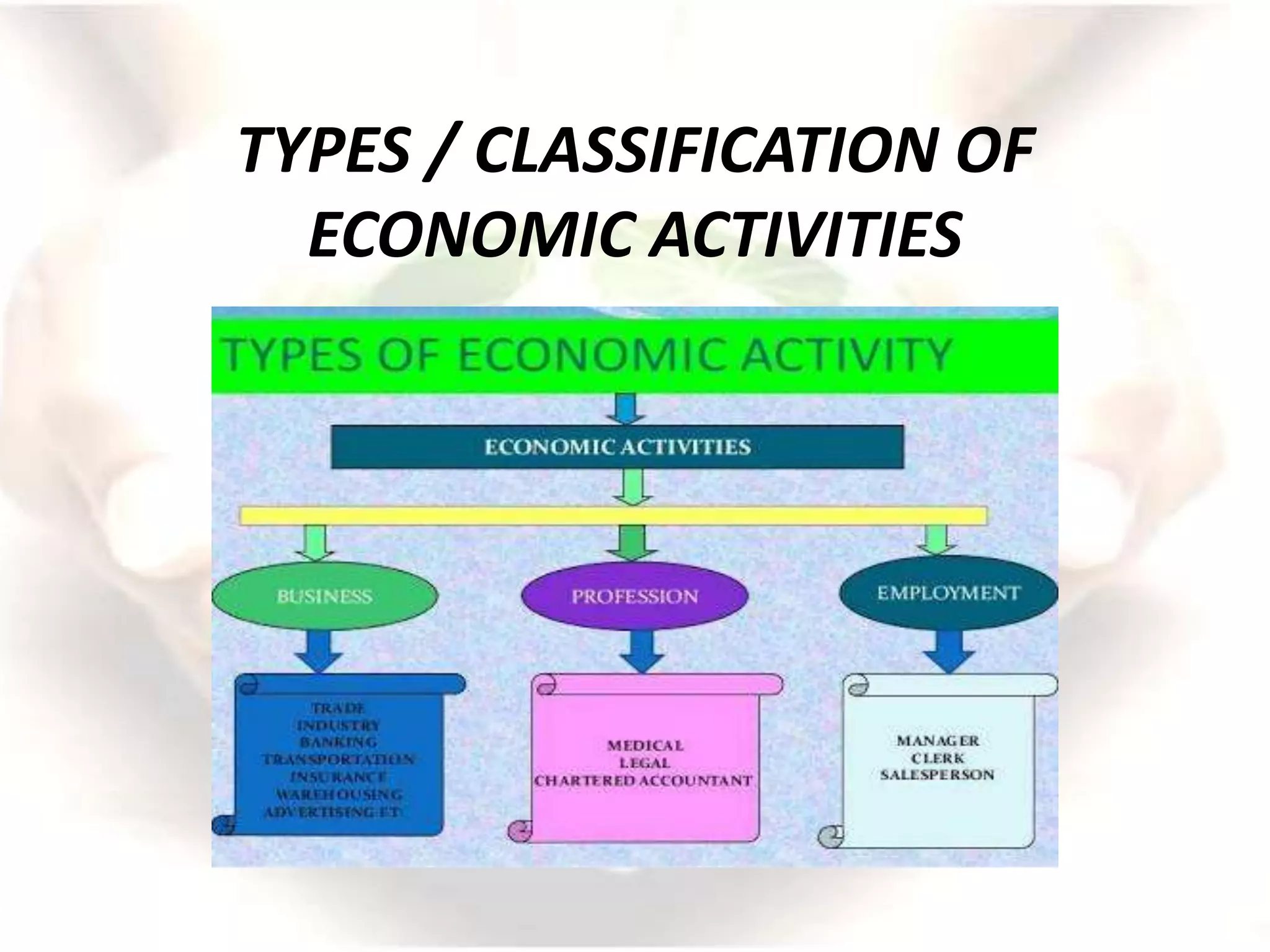
The document outlines economic activities, categorizing them into production, distribution, exchange, and consumption of goods and services, with the primary aim being to satisfy human wants. It distinguishes between economic activities, which involve monetary transactions, and non-economic activities, performed out of altruism or personal satisfaction. The text further elaborates on various objectives, characteristics, parts, classifications, and sectors of economic activities.