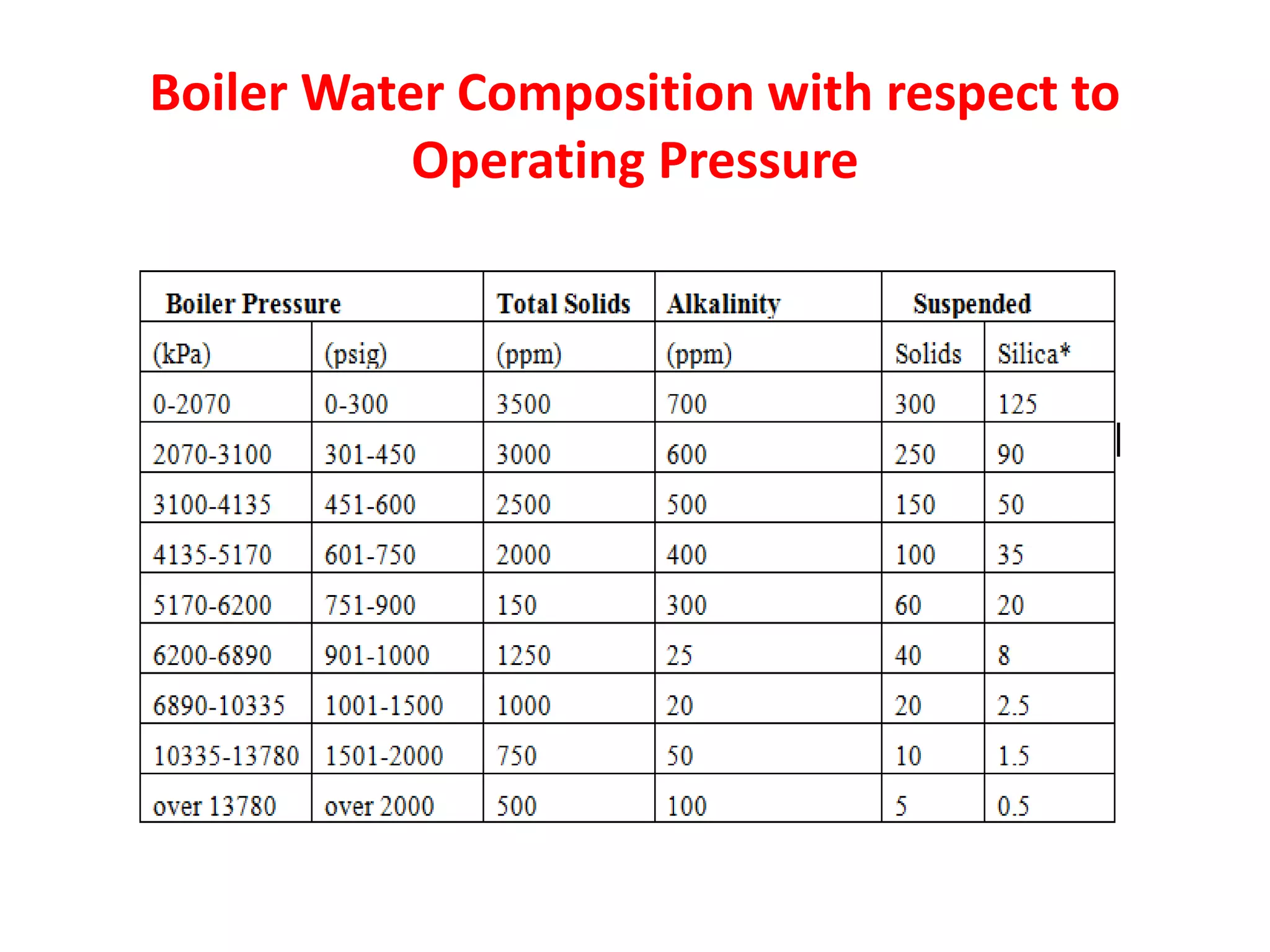
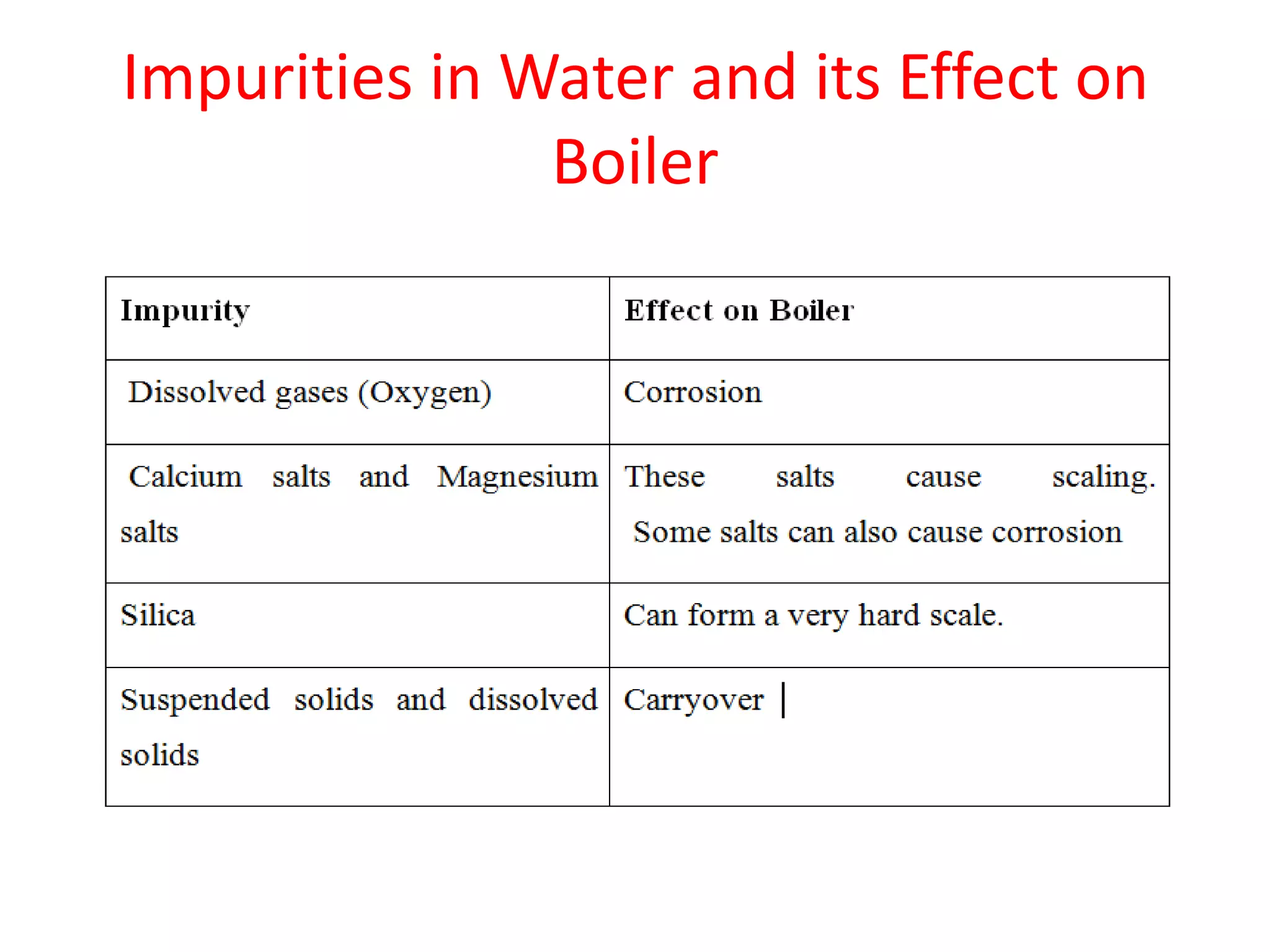
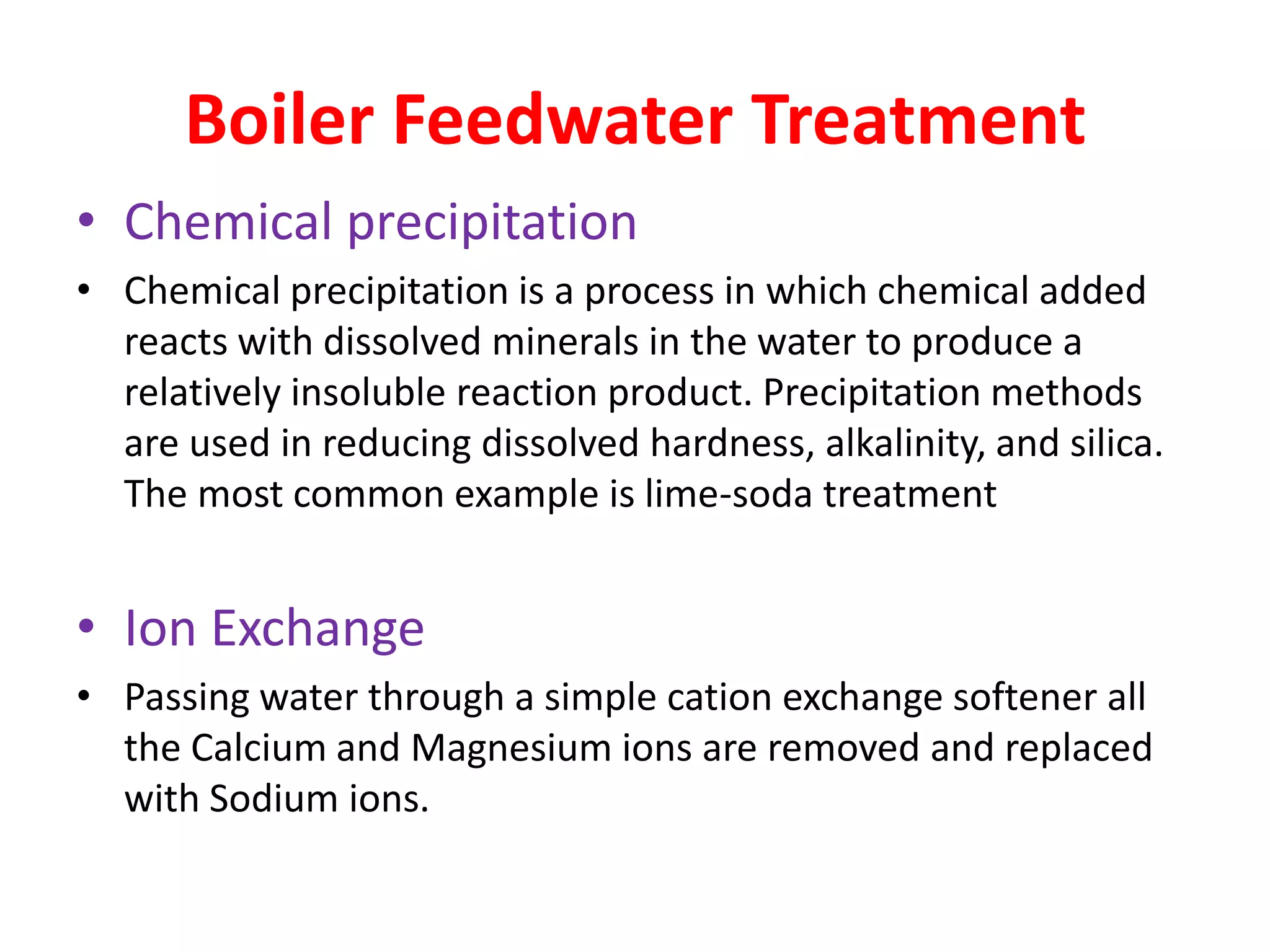
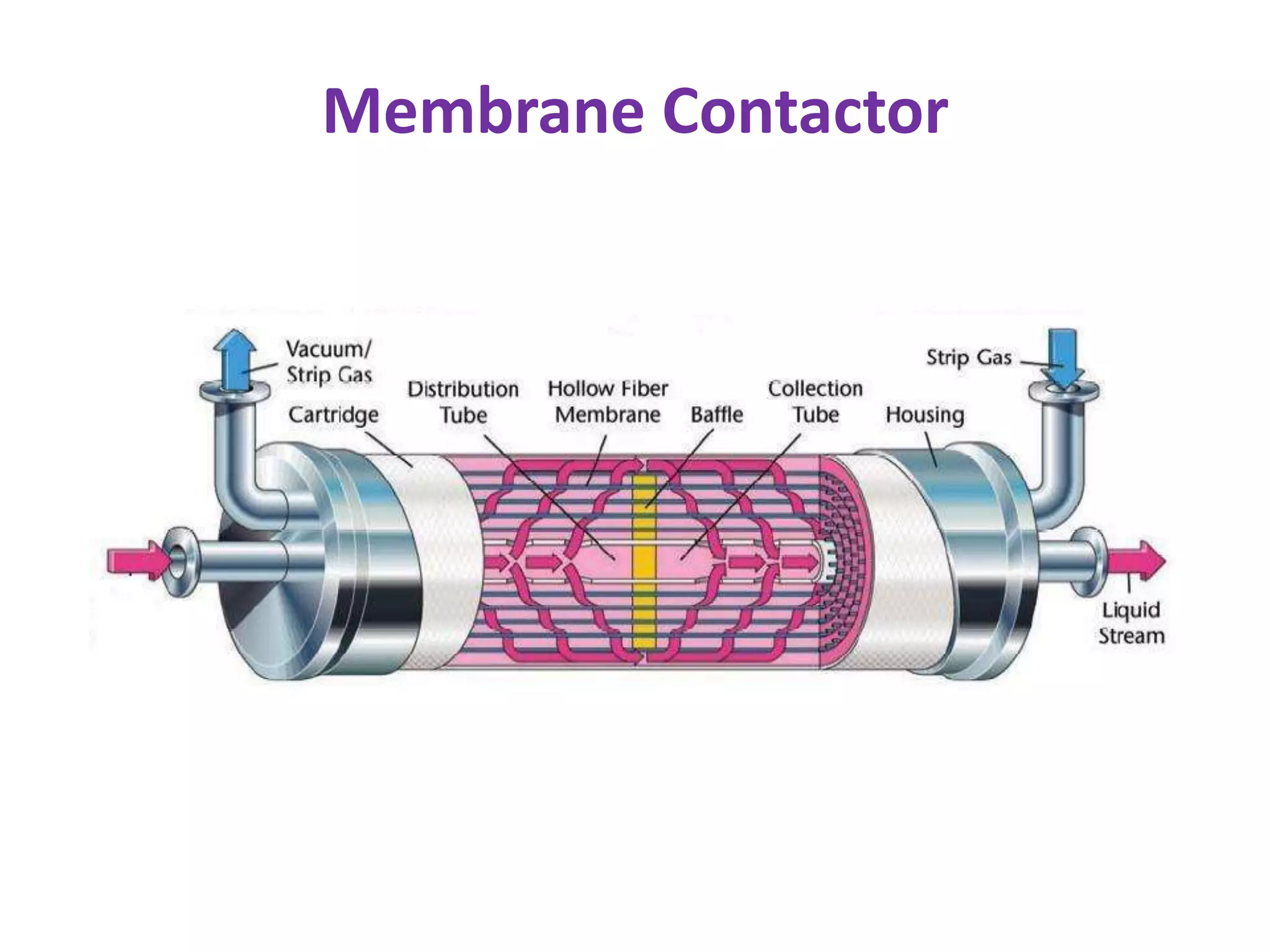
Thermal power plants require ultra pure water known as boiler feedwater that is pretreated to remove impurities which can cause scaling, corrosion, and other problems. Common pretreatment methods include filtration, coagulation, ion exchange, chemical precipitation, and deaeration to remove suspended solids, dissolved gases, and minerals. Emerging technologies like membrane contactors and reverse osmosis are also being used to further purify boiler feedwater from wastewater and other sources. Proper pretreatment is crucial to minimize damage to high pressure boilers in thermal power plants.