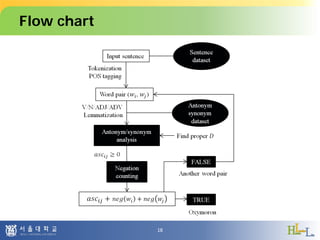
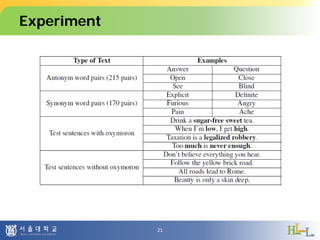
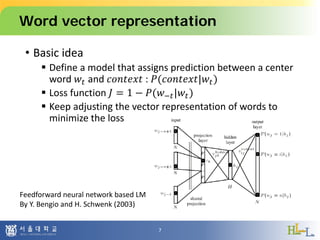
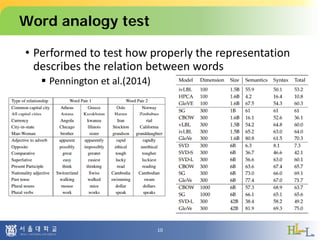
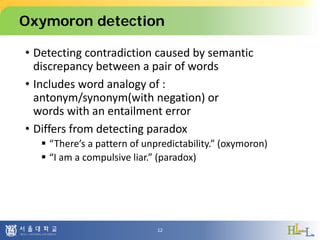
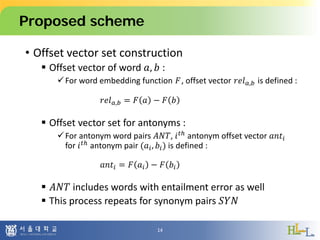
This document proposes a method to detect oxymorons in single statements by analyzing word vector representations. It introduces word vectors and word analogy tests. The proposed method constructs offset vector sets for antonyms and synonyms to check if word pairs in statements are contradictory. It applies techniques like part-of-speech tagging, lemmatization, and negation counting. The experiment uses pre-trained GloVe vectors and oxymoron/truism datasets with mixed results. Future work could apply dependency parsing and word embeddings specialized for antonyms to improve accuracy.



![Introduction
• Word meaning for computers
Use a taxonomy like WordNet that has hypernyms (is-a)
relationships and synonym sets
Problems with discreteness
Missing nuances
Missing new words
Subjective
Requires human labor
Hard to compute
accurate word similarity
4
ex) One-hot representation
hotel = [0 0 0 … 1 0 0 … 0 0 0]
motel = [0 0 0 … 0 1 0 … 0 0 0]
≈ ?
⊥ ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warnikchowdetectingoxymoronococosda-181222184306/85/DETECTING-OXYMORON-IN-A-SINGLE-STATEMENT-4-320.jpg)

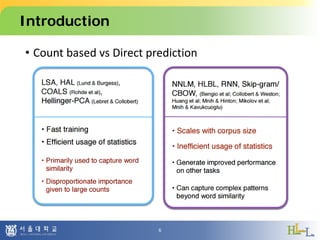




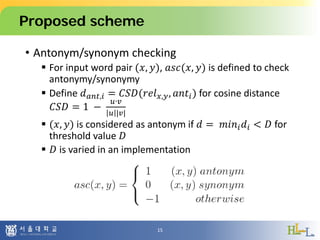
![Proposed scheme
• Checking invalid cases
Assumption :
(1) Only lexical words can have antonym/synonym relationship
(not grammatical)
(2) Contradict occurs if antonym indicate the same
object/situation simultaneously
For (1), only [verbs, nouns, adjectives, adverbs] are
analyzed, with lemmatization
For (2), dependency parsing could be applied (not in
current implementation)
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/warnikchowdetectingoxymoronococosda-181222184306/85/DETECTING-OXYMORON-IN-A-SINGLE-STATEMENT-16-320.jpg)