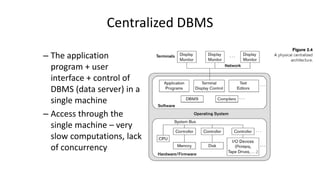
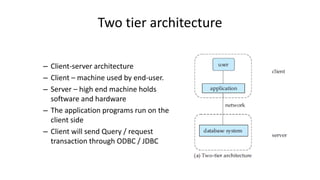
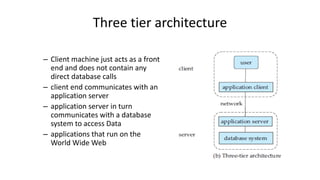
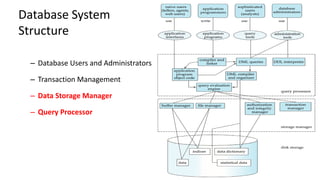
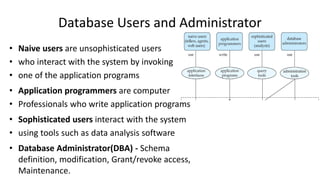
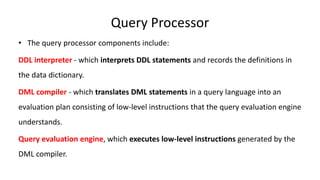
The document outlines different architectures of database management systems, including centralized, two-tier, and three-tier architectures, emphasizing their structure and user interaction. It details the roles of database users, administrators, and various managers within the system, such as storage and transaction managers. Additionally, it describes the importance of the query processor and transaction management, including properties like atomicity, consistency, and durability.