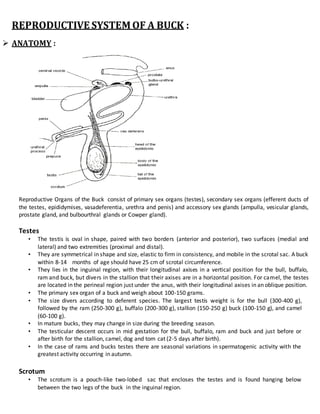
Reproductive system of a buck
- 1. REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OF A BUCK : ANATOMY : Reproductive Organs of the Buck consist of primary sex organs (testes), secondary sex organs (efferent ducts of the testes, epididymises, vasadeferentia, urethra and penis) and accessory sex glands (ampulla, vesicular glands, prostate gland, and bulbourthral glands or Cowper gland). Testes • The testis is oval in shape, paired with two borders (anterior and posterior), two surfaces (medial and lateral) and two extremities (proximal and distal). • They are symmetrical in shape and size, elastic to firm in consistency, and mobile in the scrotal sac. A buck within 8-14 months of age should have 25 cm of scrotal circumference. • They lies in the inguinal region, with their longitudinal axises in a vertical position for the bull, buffalo, ram and buck, but divers in the stallion that their axises are in a horizontal position. For camel, the testes are located in the perineal region just under the anus, with their longitudinal axises in an oblique position. • The primary sex organ of a buck and weigh about 100-150 grams. • The size divers according to deferent species. The largest testis weight is for the bull (300-400 g), followed by the ram (250-300 g), buffalo (200-300 g), stallion (150-250 g) buck (100-150 g), and camel (60-100 g). • In mature bucks, they may change in size during the breeding season. • The testicular descent occurs in mid gestation for the bull, buffalo, ram and buck and just before or after birth for the stallion, camel, dog and tom cat (2-5 days after birth). • In the case of rams and bucks testes there are seasonal variations in spermatogenic activity with the greatest activity occurring in autumn. Scrotum • The scrotum is a pouch-like two-lobed sac that encloses the testes and is found hanging below between the two legs of the buck in the inguinal region.
- 2. • The wall of the scrotum is composed of four layers; skin, tunica dartos muscle, scrotal fascia and parietal layer of vaginal tunic. The tunica dartos forms the median septum which divides the scrotum into two distinct pouches. • Improper scrotal function and poor testicular distention during hot weather may lead to temporary infertility in bucks. Epididymis • Carries the sperm from the testicle to the vas deferens then to the penis. • Length of epididymal tube in buck is about 50m. • Sperm continue to develop (mature) in the epididymis and are stored there. Vas Deferens • It is a slender, muscular tube that runs from the tail of the epididymis to the neck of the bladder, where it joins the ampulla and accessory sex glands. • Primary function is to move sperm into the urethra at the time of ejaculation. • In vasectomized animals (teaser bucks) the animal still produces testosterone and sperm cells Accessory Glands • Includes the ampulla, seminal vesicles, prostate gland and the bulbo-urethral gland • The ampullary glands contribute to the ejaculate and are present in the terminal portions of the vas deferens of bucks. • The duct of the seminal vesicles and the ductus deferens may share a common ejaculatory duct that opens into the urethra. They are pair of compact lobular glands that are easily identified because of their knobby appearance in the buck. In the stallion, they are large pyriform glandular sac that evades identification because of their thin wall • In the stallion and boar the seminal vesicles are sac-like, but in the buck the vesiclea are lobulated and firmer. • Prostate gland is a single gland with 2 parts, a body that stretches across the dorsal surface of the neck of the urinary bladder and disseminate or internal part that surrounds the pelvic urethra. The body of the prostate is small in the bull and large in the boar and camel, but absent in the ram and buck. The prostate gland in the stallion is bilobed and wholly external that can be identified by palpation per rectum. • The bulbourethral gland or Cowper's gland of the buck, stallion, bull and ram are small, round structures lying between the anus and the urethra. • Normal seminal volume during ejaculation for a buck is 0.5-1.5 ml, with a concentration of 1.5-6 billion sperm cells/ml. Penis • The penis is fibro-elastic (with sigmoid flexure) in buck, bull and camel but vascular, musclocavernosus and haemodynamic in the stallion. • The sigmoid flexure is post-scrotal for the bull and buck, but pre-scrotal for the camel and boar. • Vascular erection is not a very prominent feature of erection. The main factor, which increases the length of the penis during erection, is the obliteration of the sigmoid flexure of the organ. • In the non-erect state, the glans of the penis is contained in the sheath
- 3. • The ram and buck have urethral process known as a filiform appendage extending beyond the glans penis. • The end of the buck penis is coiled, especially during copulation. • Mating time is very short in bucks. Intromission usually lasts less than 5 seconds. Bucks will generally throw their head back at ejaculation. Prepuce • The prepuce is the sheath or foreskin that protects the penis. • Shorter in buck, surrounded by tuft of hair. AFFECTIONS : Castration Small goats are held, head down, between the operator’s knees or head up with the front and hind limbs on each side held together. Animals younger than one month of age are usually restrained in lateral recumbency. Typically, older ones are put into a squeeze chute or stocks. Many operators elect to use a local anesthetic in the skin and/or spermatic cord, although some young goats and lambs receive operations with only physical restraint. For a standing animal in stocks or head catch, the operator’s hand is placed at the base of the tail so that it can be lifted over the animal’s back. Lamb or kid sensitivity to local anesthetics necessitates reduction of the concentration of a local anesthetic being administered; lidocaine should be diluted from 2% to 0.5% or 1%.The lower range should be used on goats and debilitated, aged, young, or depressed animals. Another drug combination that works well on goats is midazolam (0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg IV) in combination with butorphanol (0.02 mg/kg IV). For animals less than 150 kg, the distal portion of the scrotum is grasped and pulled distally, thus displacing the testes proximally. The distal third of the scrotum is excised to expose the testes. Traction is applied to each testis, and the spermatic cord is freed by stripping the fascia proximally. At this point, the cord can be ligated and transected, emasculated, or stretched until the vasculature ruptures. The latter technique results in vasospasm, which is usually adequate hemostasis for smaller animals but could damage the inguinal ring in kids and lead to a hernia. For this reason, use of a technique that closes (use of emasculator or ligation) the spermatic cord is preferable. The wound is usually left open to heal by second intention. Older animals are occasionally castrated, with the best results obtained when they are restrained in chutes or on a tilt table. Local anesthetic in the scrotal skin and spermatic cord is appropriate. The operator’s preferences dictate the surgical approach. The distal scrotum can be removed, or vertical incisions can be made on either side of the median raphe. Regardless, the testis is identified and freed from its surrounding fascia with blunt dissection. Once isolated, the spermatic cord is ligated and transected or emasculated. Generally, the vaginal tunic is not incised and is removed en bloc with the testis. If the vaginal tunic is incised, the testis and spermatic cord are ligated (or emasculated). Transfixation sutures help prevent ligature slippage. Cryptorchidism/Testicular Anomaly The left testis is more often retained in cattle, while a predilection for right cryptorchids has been reported in goats. Cryptorchid testes are very rare in ruminants, but ectopic testes are more common. The clinical diagnosis of undescended testis is made by physical examination where the absence of a testis in the scrotum is detected. To identify the location of the undescended testis one should palpate for (perhaps also search with ultrasound examination) the testis not only on the abdomen and inguinal canal but also in the subcutaneous tissues in the inguinal region, the fold of the flank, and alongside the penis. In addition, rectal examination may identify an abdominal testis.
- 4. With undescended testes the approach is made directly over the testis, if possible. The animal should be restrained appropriately, usually in dorsal recumbency for testes on the ventral abdomen and inguinal canal. Abdominal testes are best removed via a flank celiotomy. In the latter case, closure of the vaginal ring is needed to prevent formation of an inguinal hernia. Vasectomy Vasectomy (removal of a segment of the ductus (formerly vas) deferens to render a male animal infertile) is generally a management technique used to produce teaser males or as an adjunct to such methods. Vasectomy is usually performed with the aid of a local block at the surgical site. It can be done with the animal standing or restrained in lateral recumbency. Goats can be operated on in a sitting position, restrained by an assistant. The conventional technique involves incision of the neck of the scrotum cranially, caudally, or even laterally. In bucks and rams, the incisions need to be about 2 cm in length to allow exteriorization of the cord. The skin and parietal layer of the vaginal tunic are incised in a vertical fashion. The ductus deferens is located by palpation because it is firmer than the surrounding vasculature and membranes. Incision of the vessels of the cord leads to considerable hemorrhage that is difficult to control and can obscure the other structures of the cord. Care should be taken to identify the ductus deferens, isolate it via delicate blunt dissection, and remove a 3-cm piece of it after 3-0 absorbable ligatures have been placed on each end. The procedure is repeated on the opposite side. Administration of tetanus toxoid is wise after vasectomy, especially in bucks and rams. Persistent Frenulum Some bucks (or rams) retain one or more discrete bands of tissue that connect the free end of the shaft of the penis to the lamina interna of the prepuce. In young animals the penis can often be extended manually with no or little sedation. Application of a dorsal nerve block is often sufficient to perform this procedure. With the penis extended as far as possible by traction on its free end, a fine needle is inserted through the lamina interna at the dorsal aspect of the preputial orifice. Lidocaine (2%) is injected under the lamina interna and is deposited in a semicircle to cover the dorsal aspect of the penis. This will render the free end of the shaft of the penis insensitive by blocking the dorsal penile nerve before it splits into its terminal branches. Preputial Erosions In rams and bucks a unique form of decubital lesion occurs dorsal to the preputial orifice (between the prepuce and the abdominal wall). This occurs only in heavy show animals that are confined in small pens. Because they are recumbent much of the time, pressure of the preputial orifice on the body wall results in a chronic ulcer. This lesion is resistant to conservative treatment, and the only successful approach is surgical resection. OTHER CONDITIONS Congenital phimosis inbucks - It is a permanent unsoundness Enzootic balanoposthitis ("pizzlerot") - occurs in rams and castrated male sheep and goats (wethers), and can occasionally affect steers, bulls, or the vulva of ewes - results from high protein diets. The causative bacteria (Corynebacterium renale) breaks down the urea in the prepuce to ammonia, which causes ulceration. - discomfort and reduced libido can result, and phimosis can occur in severe cases
- 5. - the condition can often be controlled by temporari ly restricting the diet, supplying ad libitum water, trimming the wool around the prepuce, etc., disposing of all infected materials, and isolating affected animals. Increasing the amount of grass hay in the diet and decreasing the amount of legume will also be beneficial. - individual animals can be treated by cleaning the affected area and applying topical antibacterial ointment as needed. Ammonium chloride per os @ 1-3 gm, 2-3 times daily, will help to acidify the urine and therefore may be beneficial. Ulcerative dermatosis of sheep andgoat - caused by a virus similar to the one that causes contagious ecthyma (sore mouth) - described in the western U.S.A., Europe, and South Africa - transmitted by physical contact, probably through a break in the skin or mucous membranes - causes ulcers of the lips, face, legs, feet, and external genital organs of both sexes (i.e., deeper lesions than for contagious ecthyma, which has not been reported to affect the genitals) - no vaccine or effective therapy; therefore, control by management. Damage to the urethral process - a result of inflammation and necrosis, amputation for the removal of calculi, shearing accident, etc. - may not significantly affect fertility if it is absent, but should be noted when evaluating a valuable animal. Intersexes - relatively common in polled goats Dr. Urfeya Mirza
