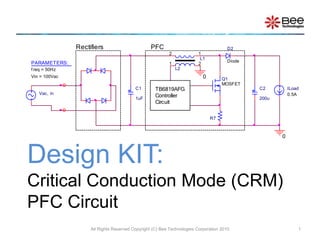
Critical Conduction Mode (CRM) PFC Circuit
- 1. Design KIT: Critical Conduction Mode (CRM) PFC Circuit All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2010 1 Vac, in C1 1uF C2 200u ILoad 0.5A L1 1 2 Diode D2 Q1 MOSFET R7 L2 1 2 0 0 Rectifiers PFC TB6819AFG Controller Circuit PARAMETERS: f req = 50Hz Vin = 100Vac
- 2. Contents • Introduction • Application Circuit • Design Specification • Time Scaling • Application Circuit with Time Scaling (tscale =10) • Common Mode Choke Coil for PFC • Design Steps (1-8) • Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Steady State • Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Start Up Appendix A.Excel Calculation Sheet B.Simulation Index All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 2
- 3. Introduction Most electronic ballasts and switching power supplies use a bridge rectifier and a bulk storage capacitor to derive raw dc voltage from the utility ac line, figure above: Vin=100Vac, 50Hz and PO=200W. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 3 Vin AC_IN1 PARAMETERS: f req = 50Hz Vin = 100Vac AC_IN2 Cbulk 2000uF 0 bulk DB1 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Load 1.414Adc Iline Vbulk
- 4. Time 160ms 164ms 168ms 172ms 176ms 180ms 184ms 188ms 192ms 196ms 200ms AVG(ABS(W(Vin)))/(RMS(ABS(V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2)))*RMS(ABS(I(Vin)))) 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 ABS( I(Vin) ) 0A 10A 20A ABS( V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) ) V(bulk) 0V 100V 200V SEL>> Introduction The Uncorrected Power Factor rectifying circuit draws current from the ac line when the ac voltage exceeds the capacitor voltage (Vbulk). The current (Iline) is non- sinusoidal. This results in a poor power factor condition where the apparent input power is much higher than the real power, figure above, power factor ratios of 0.5 to 0.7 are common. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 4 |VAC, in, 100V| (VPEAK, in=100*2=141.42V) and Vbulk |Iline| Power Factor Ratio = Pin, avg./(Vin, rms* Iin, rms)
- 5. Vac, in C1 1uF C2 200u ILoad 0.5A L1 1 2 Diode D2 Q1 MOSFET R7 L2 1 2 0 0 Rectifiers PFC TB6819AFG Controller Circuit PARAMETERS: f req = 50Hz Vin = 100Vac Introduction The Power Factor Correction (PFC) circuit, as an off-line active preconverter, is designed to draw a sinusoidal current from the AC line that is in phase with input voltage. As a result, the power factor ratio is improved to be near to ideal (1). The TB6819AFG is a critical conduction mode (CRM) PFC controller IC. The description including equation and constants as a guide to understand its designing process is included in this document. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 5 Iline VDC, OUT
- 6. Time*10 100ms 104ms 108ms 112ms 116ms 120ms 124ms 128ms 132ms 136ms 140ms AVG(ABS(W(Vin))) / (RMS(ABS(V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2)))*RMS(ABS(I(Vin)))) 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 -I(Vin) -8.0A 0A 8.0A SEL>> 1 V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) 2 V(VOUT) -160V 0V 160V 1 200V 400V 600V 2 >> Introduction The poor power factor load is corrected by keeping the ac line current sinusoidal and in phase with the line voltage. This results with power factor ratio is 0.85. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 6 VAC, in, 100V and VDC, OUT, 400V Iline Power Factor Ratio = 0.85 *simulation result at tscale = 10
- 7. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 100 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1uF 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 10nF C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 0.47uF L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 POUT R7 0.11 V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC ZCD FB_IN IS C7 8p R3 10k C4 1uF VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 200uF COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Application Circuit All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 7 VAC, in=85-265VAC PO = 200W, VDC, OUT = 400VDC *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 0 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 8. Time 10ms 11ms 12ms 13ms 14ms 15ms 16ms 17ms 18ms 19ms 20ms AVG(ABS(W(Vin)))/(RMS(ABS(V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2)))*RMS(ABS(I(Vin)))) 0 0.5 1.0 Time 0s 2ms 4ms 6ms 8ms 10ms 12ms 14ms 16ms 18ms 20ms -I(Vin) -10A 0A 10A SEL>> 1 V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) 2 V(VOUT) -200V 0V 200V 1 380V 400V 420V 2 >> Application Circuit All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 8 VAC, in, 100V and VDC, OUT, 400V Iline Power Factor Ratio = 0.85 Total simulation time = 1429.49 seconds
- 9. Design Specification This application circuit is for 400VDC/200W output Critical Conduction Mode (CRM) PFC Circuit : • VAC, in,min = 85 (VAC) • VAC, in,max = 265 (VAC) • VO = 400 (VDC) • Po = 200 (W) • fs = 20kHz ~ 150kHz, 50kHz • (assumed) = 90% Control IC : • Part # TTB6819AFG (PFC Controller IC) • Switching Technique: Critical Conduction Mode (CRM) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 9
- 10. Time Scaling The transient (cycle-by-cycle) simulation of PFC circuits is really time (and memory) consuming exercise, even with a fast computer. There is a way to speed up simulations by artificially altering some of the key element values by using of time scaling ratio (tscale), passed as a parameter to the simulation engine: • F line = F line tscale • C 2 = C 2 tscale • C 3 = C 3 tscale • C 4 = C 4 tscale • C 5 = C 5 tscale All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 10
- 11. Application Circuit with Time Scaling (tscale =10) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 11 VAC, in=85-265VAC PO = 200W, VDC, OUT = 400VDC *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 2ms 0 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 100 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 3.74 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10
- 12. Time*10 10ms 11ms 12ms 13ms 14ms 15ms 16ms 17ms 18ms 19ms 20ms AVG(ABS(W(Vin)))/(RMS(ABS(V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2)))*RMS(ABS(I(Vin)))) 0 0.5 1.0 Time*10 0s 2ms 4ms 6ms 8ms 10ms 12ms 14ms 16ms 18ms 20ms -I(Vin) -10A 0A 10A SEL>> 1 V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) 2 V(VOUT) -200V 0V 200V 1 380V 400V 420V 2 >> Application Circuit with Time Scaling (tscale =10) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 12 VAC, in, 100V and VDC, OUT, 400V Iline Power Factor Ratio = 0.85 Total simulation time = 132.41 seconds
- 13. Common Mode Choke Coil for PFC To model a simple common mode choke coil, the SPICE primitive k, which describes the coupling ratio between L1 and L2, can be used. COUPLING=1 of K_Linear means there is no leakage inductance in the common mode choke coil model. N is a ratio of L2 turns and L1 turns, or N2/N1 Input the parameters: L as an L1 inductance value and N, then L2 is calculated using equation: L2 = N2L1 All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 13 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2
- 14. Design Steps (1-8) (1) Output Voltage and Feedback Circuit (2) Output Capacitor (3) L1 Inductance (4) Input Capacitor (5) Auxiliary Winding L2 (6) Multiplier Input Circuit (MULT) (7) Current Detection Circuit (IS) (8) Zero Current Detection Circuit (ZCD) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 14
- 15. (1) Output Voltage and Feedback Circuit The output voltage is resistively divided and applied to the error amplifier, to set the VO the R1 and R2 resistor value should satisfy the following equation : *With VO=400V and R2=1.5M, R1 is calculated to be 9.47k, however a resistor of 9.53k , which is available in the E96 series, is used as R1 (actual). All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 15 2.51 R R R V 2 1 1 O Output DC Voltage, VO 400 V Error Amplifier Reference Voltage Verr 2.51 V R2 1.5 M R1 9.47 k R1 (actual) 9.53* k
- 16. (2) Output Capacitor The output capacitance C2 is determined so that the PFC output ripple voltage dose not exceed the VOPV-2, for the capacitor selection, the following equation should be satisfied: The value of VOVP-2, min and Verr, min are inform in the TB6819AFG datasheet. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 16 PO 200 W fin 50 Hz VO 400 V VOVP-2, min 2.63 V Verr, min 2.46 V C2 41 F C2used 200 F 1 - /V V V 2 2 P C2 err 2 - OVP 2 O O in f
- 17. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 100 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 3.85 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (1) and (2) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 17 Vin = 100Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 R1=9.53k and R2=1.5M Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V C2 = 200F *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 4ms 0 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 18. Time*10 0s 5ms 10ms 15ms 20ms 25ms 30ms 35ms 40ms V(FB_IN) 2.63 2.46 2.4 2.6 2.8 V(VOUT) 380V 400V 420V SEL>> V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) -200V 0V 200V Simulation of Step (1) and (2) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 18 VAC, in,=100V (VPEAK, in,=100*1.4142=141.4V) V(FB IN), VOVP-2, min.(2.63V), and Verr,min(2.46V) VO=400Vdc with 2fline ripple Total simulation time = 270.61 seconds
- 19. (3) L1 Inductance The switching frequencyfs (Hz) depends on the L1 inductance and input/output condition which the equation and the calculation data are as shown below. *The fs value should be within 20kHz and 150kHz, to avoid an occurrence of EMI problem, fs=50kHz is used. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 19 O O 2 min in, AC, min in, AC, O P V fs 100 2 V ) V 2 (V L1 η Output DC Voltage, VO 400 V Minimum AC Input Voltage, VAC, in, min 85 V Power Efficiency, (assumed) 90 % Switching Frequency, fs* 50 kHz Output Power, PO 200 W Calculated Inductance, L1(calculated) 227 H Selected (Actual) Inductance, L1(actual) 230 H
- 20. (4) Input Capacitor C1 should be capable of supplying energy stored in the L1 while the FET is on. Assumed that the on/off duty is 50%, the C1 should be temporarily able to supply twice the current. A current reaches its maximum at the VAC, in, min. Thus, the following relationship should be satisfied: All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 20 L1 230 H PO 200 W VAC, in, min 85 V C1 0.35 F C1used 1 F 4 min in, AC, 2 O V P L1 2 C1
- 21. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 4.22 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (3) and (4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 21 Vin, min = 85Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V The Calculated L1 value 227H (adjusted 230H is used) I(L1) C1 = 1F *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 16m 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 22. Time 16.45ms 16.46ms 16.47ms 16.48ms 16.49ms 16.50ms 16.51ms 16.52ms 16.53ms 16.54ms 16.55ms V(POUT) 0V 10V 20V -I(L1) 0A 5A 10A V(VOUT) 395V 400V 405V SEL>> Simulation of Step (3) and (4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 22 VO=400Vdc with high switching ripple I(L1) Switching Control Signal, fs = 48.4 kHz Total simulation time = 1056.11 seconds
- 23. (5) Auxiliary Winding L2 The auxiliary winding L2 is used to detect the zero inductor current condition of the inductor L1. Since the maximum reference voltage for the ZCD comparator is 1.9V (the IC specification) , N1/N2 should meet the following condition: Where N1 is the number of winding of turns of L1, N2 is that of L2 *To ensure that the design requirements are met, N1/N2 should preferably about 10 (9.6 is used) to allow for design margins. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 23 9 . 1 max in, AC, O V 2 V N1/N2 Output DC Voltage, VO 400 V Maximum AC Input Voltage, VAC, in, max 265 V Calculated Turn Number Ratio, N1/N2 < 14 Selected Transformer Turn Ratio, N1/N2 (actual) 9.6*
- 24. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 265 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 2.533 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (5) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 24 N1/N2=9.6, input parameter N = N2/N1 = 1/9.6 I(L1) Vin, min = 265Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 4ms 2ms 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 25. Time*10 20ms 22ms 24ms 26ms 28ms 30ms 32ms 34ms 36ms 38ms 40ms V(ZCD) 1.9 0 2.5 5.0 7.5 -I(L1) 0A 2.5A 5.0A V(VOUT) 375V 400V 425V SEL>> V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) -400V 0V 400V Simulation of Step (5) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 25 VO=400V and PO=200W VAC, in, min=265V (VPEAK, in, min=265*1.4142=374.8V) I(L1) V(ZCD) and the maximum reference voltage of the TB6819AFG’s ZCD comparator, 1.9V Total simulation time = 1012.86 seconds
- 26. (6) Multiplier Input Circuit (MULT) The AC input supply voltage (sinewave) is applied to the multiplier by dividing a full-wave rectified voltage waveform. The IC startup threshold voltages of the Brown Out Protection (BOP) function = 0.75V and the MULT linear input voltage range of the multiplier = 0 to 3V, the R9 and R10 resistor should satisfy the following condition: with excel calculation sheet PFC_Cal-Sht.xlsx you can input R9 and R10 values, then check the calculated BOP and Linear MULT values to be within the maximum values. All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 26 10 9 10 min in, AC, R R R 2 V 0 75 . Maximum AC Input Voltage, VAC, in, min 400 V Maximum AC Input Voltage, VAC, in, max 265 V R9 3 M R10 22 k Minimum Condition for BOP 0.875 > 0.75 Maximum Condition for Linear MULT 2.728 < 3 3 10 9 10 max in, AC, R R R 2 V and
- 27. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 4.22 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, min All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 27 R10=3M and R11=22k Vin, min = 85Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 16m 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 28. Time*10 180ms 182ms 184ms 186ms 188ms 190ms 192ms 194ms 196ms 198ms 200ms V(MULT) 0.75 0 0.5 1.0 V(Rtf) 0V 40V 80V 120V SEL>> V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) -200V 0V 200V Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, min All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 28 Full-wave rectified voltage VAC, in, min=85V (VPEAK, in, min=85*1.4142=120.2V) V(MULT) > BOP threshold voltage (0.75V) Total simulation time = 1056.11 seconds
- 29. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 265 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 2.533 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, max All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 29 Vin, max = 265Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V R10=3M and R11=22k *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 4ms 2ms 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 30. Time*10 20ms 22ms 24ms 26ms 28ms 30ms 32ms 34ms 36ms 38ms 40ms V(MULT) 3 0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 V(Rtf) 0V 100V 200V 300V 400V V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) -400V -200V 0V 200V 400V SEL>> Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, max All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 30 Full-wave rectified voltage VAC, in, max=265V (VPEAK, in, min=265*1.4142=374.8V) V(MULT) < MULT linear input maximum voltage (3V) Total simulation time = 1012.86 seconds
- 31. (7) Current Detection Circuit (IS) Iq1 (power switch current) is converted into voltage by R7, then applied to the IS pin. The R7 resistor value calculation follows these steps: 1) The maximum current of the Q1 current, Iq1 (max) should allow the output power PO to meet the specification. Therefore, the following equation should be satisfied: 2) the IS pin peak voltage (Visp) is calculated using the following equation: 3) R7 = Visp / Iq1(max.). All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 31 R10 R9 R10 2 V 0.65 Visp min in, AC, Minimum ac input voltage, VAC, in, min 85 V Output power, PO 200 W Power efficiency, (assumed) 90 % R9 3 M R10 22 k Power switch current, Iq1(max.) 5.23 A TB6819AFG IS pin peak voltage Visp 0.57 V R7 0.11 ) 2 V ( η 2 2 100 P Iq1(max.) min in, AC, O
- 32. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 4.22 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (7) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 32 Iq1 R7 = 0.11 Vin, min = 85Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V R10=3M and R11=22k *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 16m 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 33. Simulation of Step (7) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 33 Time*10 180ms 182ms 184ms 186ms 188ms 190ms 192ms 194ms 196ms 198ms 200ms V(IS) 0V 0.5V 1.0V ID(Q1) 0A 2.0A 4.0A 6.0A 8.0A SEL>> V(MULT) 0V 0.5V 1.0V Iq1 V(MULT) V(IS) Total simulation time = 1056.11 seconds
- 34. (8) Zero Current Detection Circuit (ZCD) The auxiliary winding L2 is connected to the ZCD pin. The current through L2 is limited to ZCD pin rated current (3mA) by using the current limiting resistor R6. The following relationship should be satisfied depending on whether the external FET is on or off: FET = On: FET = Off: A resistor of 68k is used for limiting the current to 1/5 of the rated current All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 34 VAC, in, max 265 V N2/N1 1/9.6 W VO 400 V FET = ON, R6 > 13.0 k FET = OFF, R6 > 13.9 k R6 (actual) 68 k 3mA (N2/N1) 2 V R6 max. in, AC, 3mA (N2/N1) V R6 O
- 35. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 4.22 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Simulation of Step (8) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 35 ON/OFF R6 = 68k Vin, max = 265Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V R10=3M and R11=22k *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 4ms 2ms 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u
- 36. Time*10 20ms 22ms 24ms 26ms 28ms 30ms 32ms 34ms 36ms 38ms 40ms I(R6) 3m/5 -1.0m 0 1.0m V(VOUT) 375V 400V 425V V(AC_IN1,AC_IN2) -400V 0V 400V SEL>> Simulation of Step (8) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 36 VAC, in, max=265V V(VOUT) I(R6) and 1/5 of the ZCD rated current (3mA/5) Total simulation time = 1012.86 seconds
- 37. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 4.22 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} IC = {2.51*1509.53/9.53} PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Steady State All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 37 Vin, min = 85Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 10 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V I(D2) Switching Diode, D2 *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 16m 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u ID(Q1) Switching MOSFET, Q1
- 38. Time 18.00ms 18.25ms 18.50ms 18.75ms 19.00ms 19.25ms 19.50ms 19.75ms 20.00ms ID(Q1) -6A 0A 6A 12A V(Q1:d,Q1:s) 0V 200V 400V 600V I(D2) 8A 16A -2A SEL>> V(D2:2,D2:1) 0V 200V 400V 600V Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Steady State All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 38 D2 VKA, Peak ≈ 400V at steady state Total simulation time = 1056.11 seconds D2 IF, Peak ≈ 12A at steady state Q1 VDS, Peak ≈ 400V at steady state Q1 ID, Peak ≈ 7.2A at steady state
- 39. Load 0.5A R12 39k C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 85 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k C2 {200u/tscale} PARAMETERS: tscale = 40 COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 DB1 Diode D2 Diode D3 Diode D4 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 Q1 MOSFET R5 10 Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Start Up All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 39 Vin, min = 85Vac with frequency 50Hz, tscale = 40 Iload = 0.5A as PO=200W at VO=400V I(D2) Switching Diode, D2 *Analysis directives: .TRAN 0 20ms 16m 100n .OPTIONS ABSTOL= 100n .OPTIONS GMIN= 1.0E-8 .OPTIONS ITL1= 500 .OPTIONS ITL2= 200 .OPTIONS ITL4= 40 .OPTIONS RELTOL= 0.01 .OPTIONS VNTOL= 100u ID(Q1) Switching MOSFET, Q1 Rectifier Diode, DB1-4
- 40. Time*40 0s 40ms 80ms 120ms 160ms 200ms 240ms 280ms 320ms 360ms 400ms 1 V(Q1:d,Q1:s) 2 ID(Q1) -500V 0V 500V 1 -10A 0A 10A 2 >> 1 V(D2:2,D2:1) 2 I(D2) 0V 200V 400V 600V 1 SEL>> 0A 6A 12A 18A 2 SEL>> 1 V(DB1:2,DB1:1) 2 I(DB1) 100V 200V -10V 1 >> 0A 8A 16A 2 V(VOUT) 0V 200V 400V 600V Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Start Up All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 40 V(VOUT) at start up Total simulation time = 1056.11 seconds D2 VKA, Peak ≈ 400V and IF, Peak ≈ 16A at start up Q1 VDS, Peak ≈ 400V and ID, Peak ≈ 10A at start up DB1-4 IF, Peak ≈ 10A at start up
- 41. Simulation with Models from the SpicePark (1/4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 41 Load 0.5A R12 39k Q2 2SK2611 C9 0.1uF Vin FREQ = {f req*tscale} VAMPL = {Vin*1.414} AC_IN1 R4 100 PARAMETERS: f req = 50 Vin = 100 C6 3300p AC_IN2 C1 1u 0 0 R9 3MEG R10 22k C5 {10n/tscale} C8 47.1uF IC = 17.9 D5 DZ18V R11 360k R6 68k R8 100k MULT Rtf C3 {0.47u/tscale} IC = 3.74 L1 {L} 1 2 PARAMETERS: L = 230u N = {1/9.6} N=N2/N1, L2=(N^2)*L1 VCC V1 R7 0.11 POUT V2 U1 TB6819AFG FB_IN COMP MULT IS ZCD GND POUT VCC FB_IN IS ZCD C7 8p R3 10k C4 {1u/tscale} VOUT R2 1.5MEG R1 9.53k COMP L2 {N*N*L} 1 2 K K1 COUPLING = 1 K_Linear L1 = L1 L2 = L2 C2 RJJ-35V221MG5-T20 D2 SCS110AG DB1 Diode D3 Diode D4 PARAMETERS: tscale = 10 DB2 DB3 Diode DB4 R5 10 Capacitor model MOSFET professional model Schottky diode model Replace some default model with models from SpicePark
- 42. Time 484us 488us 492us 496us 500us 504us 508us 512us 516us 520us 524us V(V2) 0V 40V -I(L1) 0A 5A 10A V(V1) 0V 250V 500V V(Q2:g) 10V 20V SEL>> Time 0s 0.2ms 0.4ms 0.6ms 0.8ms 1.0ms 1.2ms 1.4ms 1.6ms 1.8ms 2.0ms V(VOUT) 392V 400V Simulation with Models from the SpicePark (2/4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 42 V(VOUT) with high frequency ripple which is caused by ESR and ESL of the capacitor model. Gate charge characteristics is include in the MOSFET Professional model. V(V1) I (L1) V(V2)
- 43. Time 480us 485us 490us 495us 500us 505us 510us 515us 476us V(V2) 40V -20V SEL>> -I(L1) 0A 5A 10A V(V1) 0V 250V 500V V(Q1:g) 0V 10V 20V Time 0s 0.5ms 1.0ms 1.5ms 2.0ms V(VOUT) 392V 400V Simulation with Models from the SpicePark (3/4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 43 The Simulation Waveform with the defaults models V(V1) I (L1) V(V2) V(VOUT) without high frequency ripple which is caused by ESR and ESL of the capacitor model. Gate charge characteristics is not include in the default model.
- 44. Simulation with Models from the SpicePark (1/4) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 44 SpicePark of MOSFET model Select the device which is capable of handling the simulated peak values.
- 45. Excel Calculation Sheet (1/2) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 45 Design Specification VAC, in,min 85 V VAC, in,max 265 V fin 50 Hz VO 400 V PO 200 W fs 50 kHz (assumed) 90 % (1) Output Voltage & Feedback Circuit R2 1.5 MW ; Input R2 value, the R1 for the VO specification is auto-calculated R1 9.47 kW R1 (actual) 9.53 kW (2) Output Capacitor VOVP-2, MIN. 2.63 V ; VOVP-2, MIN. and Verr, MIN. are TB6819AFG electrical characteristics Verr, MIN. 2.46 V C2 ³ 41 mF (3) L1 Inductance L1 227 mH L1(actual) 230 mH
- 46. Excel Calculation Sheet (2/2) All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 46 (4) Input Capacitor C1 ³ 0.35 F C1(actual) 1 F (5) Auxiliary Winding L2 N1/N2 < 14 N1/N2(actual) 9.6 (6) Multiplier Input Circuit (MULT) R9 3 MW ; Input R9 and R10 values, then check the BOP and the Linear MULT values R10 22 kW Codition: BOP 0.875 > 0.75 Linear MULT 2.728 < 3 (7) Current Detection Circuit (IS) Iq1(max.) 5.23 A Visp 0.57 V R7 0.11 (8) Zero Current Detection Circuit (ZCD) FET=ON, R8 > 13.0 k FET=OFF, R8 > 13.9 k R8 (actual) 68 k ; limiting the current to 1/5 of the rated current. Remark Input your design specification and your selected parameters. The numbers in the green font are auto- calculated numbers. The numbers in the blue font are the design actual selected (used) number.
- 47. Simulation Index All Rights Reserved Copyright (C) Bee Technologies Corporation 2012 47 Simulations Folder name 1. Application Circuit....................................................................... 2. Application Circuit with Time Scaling (tscale =10)......................... 3. Simulation of Step (1) and (2)..................................................... 4. Simulation of Step (3) and (4)..................................................... 5. Simulation of Step (5)................................................................. 6. Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, min................................................... 7. Simulation of Step (6) at Vin, max.................................................. 8. Simulation of Step (7)................................................................. 9. Simulation of Step (8)................................................................. 10. Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Steady State................... 11. Switching Devices VPEAK and IPEAK at Start Up........................... APPCKT APPCKT_tscale STEP1-2 STEP3-4 STEP5 STEP6_INMIN STEP6_INMAX STEP7 STEP8 IVPEAK-SS IVPEAK-SU Libraries : 1. ..parttb6819afgtb6819afg.lib 2. ..partparts.lib
