evolution of elephant.ppt
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•61 views
This document summarizes the evolution of elephants from early ancestors like Moeritherium through to modern species. Key developments include the emergence of a trunk or proboscis, modification of teeth into grinding molars and sharp tusks, and an increase in size and more specialized features for browsing and grazing. Major ancestral species discussed include Palaeomastodon, Dinotherium, and Mastodon, while modern elephants are represented by the mammoth, African bush elephant, and forest elephant.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to evolution of elephant.ppt
Similar to evolution of elephant.ppt (20)
Recently uploaded
Antibiotics are medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply. Bacteria are germsABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Hormones such as Growth Hormone, Prolactin, InsulinMolecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Hormones such as Growth Hormone...

Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Hormones such as Growth Hormone...Ansari Aashif Raza Mohd Imtiyaz
Recently uploaded (20)
MSC IV_Forensic medicine - Mechanical injuries.pdf

MSC IV_Forensic medicine - Mechanical injuries.pdf
Biochemistry and Biomolecules - Science - 9th Grade by Slidesgo.pptx

Biochemistry and Biomolecules - Science - 9th Grade by Slidesgo.pptx
In-pond Race way systems for Aquaculture (IPRS).pptx

In-pond Race way systems for Aquaculture (IPRS).pptx
ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...
WASP-69b’s Escaping Envelope Is Confined to a Tail Extending at Least 7 Rp

WASP-69b’s Escaping Envelope Is Confined to a Tail Extending at Least 7 Rp
Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Hormones such as Growth Hormone...

Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Action of Hormones such as Growth Hormone...
Costs to heap leach gold ore tailings in Karamoja region of Uganda

Costs to heap leach gold ore tailings in Karamoja region of Uganda
Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx

Mining Activity and Investment Opportunity in Myanmar.pptx
X-rays from a Central “Exhaust Vent” of the Galactic Center Chimney

X-rays from a Central “Exhaust Vent” of the Galactic Center Chimney
Fun for mover student's book- English book for teaching.pdf

Fun for mover student's book- English book for teaching.pdf
Alternative method of dissolution in-vitro in-vivo correlation and dissolutio...

Alternative method of dissolution in-vitro in-vivo correlation and dissolutio...
Manganese‐RichSandstonesasanIndicatorofAncientOxic LakeWaterConditionsinGale...

Manganese‐RichSandstonesasanIndicatorofAncientOxic LakeWaterConditionsinGale...
Efficient spin-up of Earth System Models usingsequence acceleration

Efficient spin-up of Earth System Models usingsequence acceleration
evolution of elephant.ppt
- 2. Characteristics Order: proboscidea Long trunk, proboscis 2 genere exist Elephas , Loxodonta Sea cows and manatees relatives Huge body 10-13 feet tall 6-7 ton weight Pillar like legs, cushionary feetb5 toes, plantigrade Skull large, air cavities: dipole Neck short
- 3. Long nose and upper lip Pharyngeal pouche store water Lophodont dentition Griding food Incisor 2nd pair modified in tusk 9 feet, 200 pound male large Molar don’t grow same time Stomach simple Liver bilobed, no gall bladder Brain small
- 4. Changes Ancestor: no proboscis, no tusk, small pig like Adapted for browsing, grazing on land Height 10-13 feet, weight 6-7 tons Large size protection from predator No natural predator now Rectigrade locomotion, pillar like leg Cushioned feet Dipole in skull Neck short support skull Upper lip, nose in proboscis
- 5. Abrasive diet Teeth lophodont with silica deposited in depressions Covered by belt system 2nd incisor in tusk Infrasonic communication Water storage in pouches Mosaic evolution in development
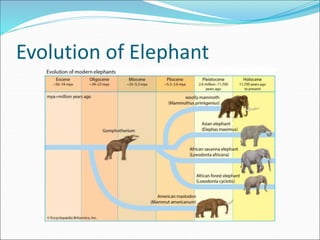
- 6. Ancestors
- 7. Moeritherium From eocene Epoch Heavy animal Size of pig, tapir, 3 feet tall No proboscis Snout long Incisor large Legs broad feet Diastema Molar low crowned
- 9. Phiomia Oligocene deposits neat Egyptian lake Moeris Shivalik Hills fossil in India Twice size of Moertherium Skull large dipole Jaws enlarged Incisor modiefed in downwardly tusk
- 11. Palaeomastodon Same time as Phiomia : oligocene epoch 6 feet Less complex
- 13. Dinotherium Lived in Miocene and Pliocene epoch Europe and India fossil No tusk in upper jaw Lower jaw tusk downward backward: digging roots of plants Small proboscis
- 15. Trilophodon/Gomphotherium In Miocene in Europe, Africa, America Large body as Asiatic elephant Upper tusk downward Lower jaw long , pair of tusk
- 17. Teralophodon Fossil in India, North America. Molar high crowned 4 crossing cups Upper tusk long straight Lower tusk small Upper jaw proboscis Lower jaw short
- 19. Dibelodon Pliocene ,fossil in North America 1st elephant in South America Short jaws Loss of lower tusk
- 21. Mastodon During oligocene to pleistocene in Africa, Europe, Eurasia Bilophodont molar True mastodonts lower jaw without tusk Molar low crowned: foliage feeder
- 23. Stegodon South and southeast Asia only Pliocene to pleistocene Short head Long proboscis Short tuskless lower jaws Molar more roof like ridges as compare to mastodont Teeth adapted to brows vegetation contain silica Modern elephant evolved from this
- 25. Mammonteus Woolly mammoth Abundant in arctic region to Spain, Italy, Europe, North Amrica, frozen sample in Siberia Tundra Lena delta Can live in cold Coat of black hairs thick Brown wool beneath Tusk were curved or long 9.5 feet
- 27. Loxodonta/ African elephant 1.5 mya, Newest Male and female tusks Largest Loxodonta africana Smaller forest Loxodonta cyclotic West and central Africa forest Small round eyes Dark skin Found only in Sahara south Can use infrasonic waves for talk