1. A tourism destination is defined as a physical space where tourists spend at least one night and includes attractions, amenities, and resources to meet tourist needs.
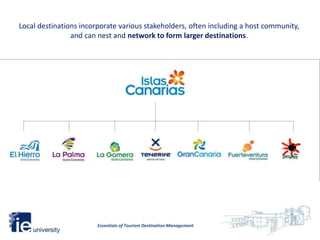
2. Destinations can be any scale from a country down to a specific town or site and incorporate various stakeholders like communities and businesses.
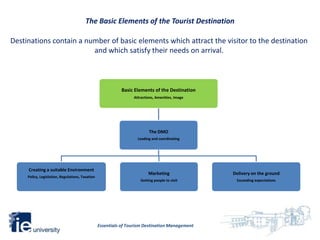
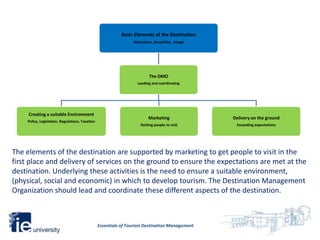
3. Destination management coordinates all elements of a destination including creating an environment, marketing, and delivering experiences to attract visitors and meet their expectations. The destination management organization leads these efforts.