CH10_2_Chemical_Equilibrium_GOB_Structures_5th_ed.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•3 views
Reverse reaction
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to CH10_2_Chemical_Equilibrium_GOB_Structures_5th_ed.pptx
Similar to CH10_2_Chemical_Equilibrium_GOB_Structures_5th_ed.pptx (20)
Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Lesson PowerPoint

Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Lesson PowerPoint
Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-important-questions.pdf

Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-important-questions.pdf
More from SilasSailasEndjala
More from SilasSailasEndjala (20)
Physics 2.3 - Thermal properties and temperature - 1.pptx

Physics 2.3 - Thermal properties and temperature - 1.pptx
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf

Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf
Vip profile Call Girls In Lonavala 9748763073 For Genuine Sex Service At Just...

Vip profile Call Girls In Lonavala 9748763073 For Genuine Sex Service At Just...
Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions

Botany krishna series 2nd semester Only Mcq type questions
All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office U.S. Department of Defense (U) Case: “Eg...

All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office U.S. Department of Defense (U) Case: “Eg...
Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b

Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b
SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE

SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE
Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf

Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf
Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)

Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)
Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks

Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks
GUIDELINES ON SIMILAR BIOLOGICS Regulatory Requirements for Marketing Authori...

GUIDELINES ON SIMILAR BIOLOGICS Regulatory Requirements for Marketing Authori...
Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR

Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR
CH10_2_Chemical_Equilibrium_GOB_Structures_5th_ed.pptx
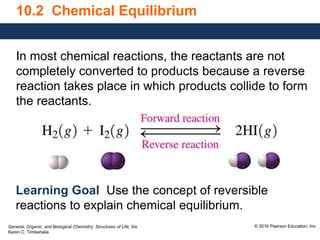
- 1. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.2 Chemical Equilibrium In most chemical reactions, the reactants are not completely converted to products because a reverse reaction takes place in which products collide to form the reactants. Learning Goal Use the concept of reversible reactions to explain chemical equilibrium.
- 2. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reversible Reactions When a reaction proceeds in both a forward and a reverse direction, it is said to be a reversible reaction. As the reactants, H2 and I2, collide, the forward reaction begins. HI molecules begin to form and collide with each other to form reactants in the reverse reaction. This reversible reaction is written with a double arrow. H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) forward reverse
- 3. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reversible Reactions A reversible reaction • occurs in both the forward and reverse direction at the same time. forward H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI (g) reverse • has two rates, a rate for the forward reaction and a rate for the reverse reaction.
- 4. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Write the forward and reverse reactions for the following: CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) CS2(g) + 4H2(g)
- 5. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Solution Write the forward and reverse reactions for the following: CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) CS2(g) + 4H2(g) The forward reaction is CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) CS2(g) + 4H2(g) The reverse reaction is CS2(g) + 4H2(g) CH4(g) + 2H2S(g)
- 6. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Rate of Reversible Reactions As the reaction progresses, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of the reverse reaction increases. At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
- 7. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Equilibrium and Reversible Reactions Equilibrium is reached when there are no further changes in the concentrations of reactants and products.
- 8. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Rates of Forward and Reverse Reactions
- 9. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Equilibrium In the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g) • the forward reaction is H2(g) + I2(g) 2HI(g). • the reverse reaction is 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g). As HI product builds up, the rate of the reverse reaction increases, while the rate of the forward reaction decreases.
- 10. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Equilibrium A reaction reaches equilibrium when no further changes take place in the concentration of the reactants and products. At equilibrium, • the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. • the forward and reverse reactions continue at the same rate.
- 11. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Complete each of the following with is/are equal or is/are not equal, change(s) or do(es) not change. A. Before equilibrium is reached, the concentrations of the reactants and products ______. B. At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction ______ to the rate of the reverse reaction.
- 12. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Forward and Reverse Reactions • If we start with reactants SO2 and O2, the reaction to form SO3 takes place until equilibrium is reached. • If we start with only the product SO3, the reaction to form SO2 and O2 takes place until equilibrium is reached.
- 13. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Study Check Complete each sentence with 1) equal 2) not equal 3) forward 4) reverse 5) changes 6) does not change A. Reactants form products in the _______ reaction. B. At equilibrium, the reactant concentration _______. C. Products form reactants in the _______ reaction.
- 14. General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry: Structures of Life, 5/e Karen C. Timberlake © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Solution Complete each sentence with 1) equal 2) not equal 3) forward 4) reverse 5) changes 6) does not change A. Reactants form products in the forward reaction. B. At equilibrium, the reactant concentration does not change. C. Products form reactants in the reverse reaction.