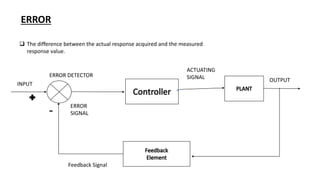
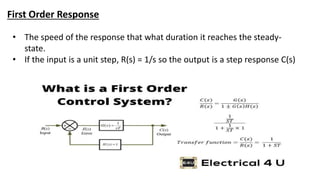
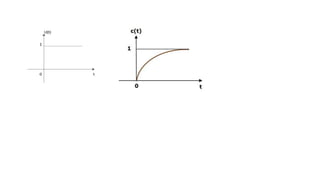
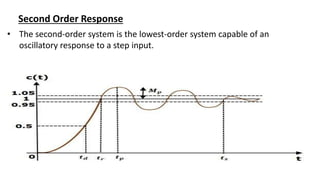
This document discusses types of errors, accuracy, sensitivity, resolution, and linearity in measurements. It defines random error, systematic error including environmental, instrumental and observational errors. Gross errors are discussed. Accuracy is defined as closeness to a true value. Sensitivity is a measure of output change for input change. Resolution is the ability to detect small changes. Linearity refers to how measurement bias is affected by the measurement range. First order response reaches steady state for a step input. Second order response can oscillate to a step input due to overshoot and damping effects.