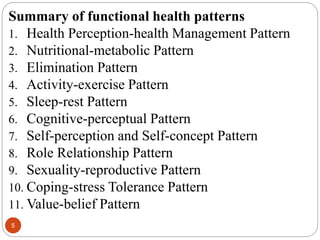
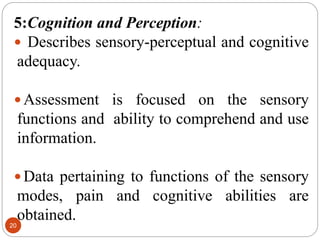
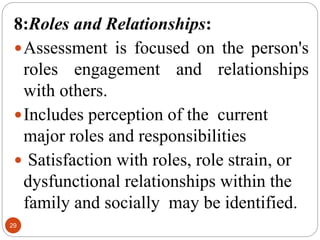
The document describes Marjorie Gordon's Functional Health Patterns (GFHP) which proposes 11 functional health patterns that are common to all humans and contribute to their health. The 11 patterns provide a framework for comprehensive nursing assessment and include: 1) health perception/management, 2) nutrition, 3) elimination, 4) activity/exercise, 5) sleep/rest, 6) cognition/perception, 7) self-perception, 8) roles/relationships, 9) sexuality/reproduction, 10) coping/stress, and 11) values/beliefs. The patterns allow nurses to systematically collect subjective and objective health data to identify strengths, problems, and nursing diagnoses.