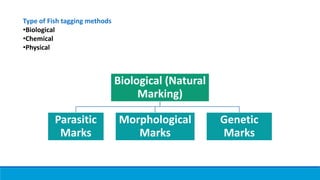
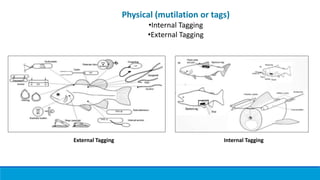
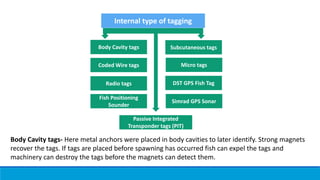
Fish tagging methods allow biologists to gather information about fish populations. There are biological, chemical, and physical tagging methods. Biological methods use natural marks like parasites or morphology. Chemical methods involve immersing, injecting, or feeding fish dye to mark them. Physical methods include internal tags like coded wire tags or PIT tags, and external tags like strap tags, dart tags, and anchor tags. Tagging provides data on movement patterns, population estimates, growth, and mortality to further understanding of fisheries.