48052671.ppt
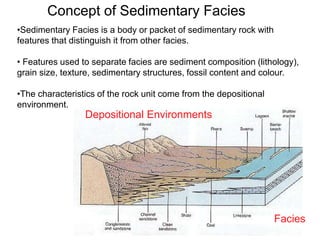
- 1. •Sedimentary Facies is a body or packet of sedimentary rock with features that distinguish it from other facies. • Features used to separate facies are sediment composition (lithology), grain size, texture, sedimentary structures, fossil content and colour. •The characteristics of the rock unit come from the depositional environment. Facies Depositional Environments Concept of Sedimentary Facies
- 2. facies: the total textural, compositional and structural characteristics of a sedimentary deposit resulting from physical, chemical and biological processes and accumulated and modified in a particular environment. Facies can be described in terms of : 1. The sediment itself: (e.g. cross-bedded sandstone facies. 2. The depositional process (e.g. stream-flood facies) 3. The depositional environment (e.g. tidal-flat facies)
- 3. Limestone Shale Siltstone Sandstone Reef Lagoon Near Shore Beach Environment Facies Lithofacies: A mappable subdivision of a stratigraphic unit that can be distinguished by its lithology- texture, mineralogy, grain size, and the depositional environment that produced it . Example: gray cross-bedded fine-grained limestone rock Facies Types • Biofacies – observations are based on fauna and flora present – Ichnofacies focuses on trace fossils – Examples • echinoid and crinoids = biofacies • burrows and tracks = ichnofacies
- 4. facies assemblage (association): collection of multiple facies resulting from genetically related accumulation and modification. EX: -lenticularly bedded stratified pebble conglomerate with planar cross-stratified sandstone -fluvial channel lithofacies assemblage Turbidite Facies Assemblage
- 5. depositional system: assemblage of multiple process-related sedimentary facies assemblages, commonly identified by the geography in which deposition occurs. EX: nearshore depositional system, deep marine depositional system.
- 6. •Facies sequences are recurring facies associations which occur in a particular order due to the inherent temporal changes in depositional conditions in particular depositional environments Facies sequences
- 7. Factors controlling sedimentary Facies 1. Depositional processes: • Sediments can be deposited by a wide range of processes including Wind, streams, tidal currents, storm and turbidity currents, waves, in-situ growth of animal skeleton as reefs, and the direct precipitation of minerals, as in evaporites. • They leave their record in the sediment in the form of sedimentary structures and textures. 2. Tectonics framework • It determines the depositional setting (e.g. stable craton, intracratonic basin or rift, continental margin, ocean floor, trench and arc-related situation • It includes rate of subsidence and uplift and volcanoes • It controls sediment supply and organic productivity 3. Climates: • It is a major factor in subaerial weathering and erosion which affect the composition of terrigenous clastic sediments • It is important in formation of some lithologies (evaporites and limestones). 4. Depositional environment
- 8. Depositional Environments • Depositional environment is an area of the Earth’s surface (geographic setting) where sediment is accumulating (deposited) as a result of distinct physical, chemical and biological processes that influence sediment deposition. • Each setting is characterized by a particular combination of geologic processes that controlled by: water type and depth (river, lake, ocean); topography; biological activity; relation to plate tectonics. • By studying present day environments, geologist can more easily interpret the rock record along the geologic time. • The geologic setting may change with time (e.g. marine to continental)
- 9. It can be determined by looking at – Texture (grain size, shape and composition, etc..) – Petrographic analyses (e.g., evaluate diagenesis) – sedimentary structures – fossils content, – bed shape and vertical sequences within the sedimentary layers How can determine the type of Depositional environment? How can Depositional environment affect the Facies? -Water depth, degree of agitation and salinity are import physical attributes of subaqueous environments and these affect and control the living organisms or forming the sediment. - Chemical factors such as Eh and pH of water affect organisms and control mineral precipitation. -Shape and location of basin of deposition affect the composition, fossil contents, and textures
- 10. Depositional Settings • Continents: Desert, glacial, fluvial (rivers), lake, swamp, cave • Mixed (Transition zone): Lagoon, river delta, beach, tidal flat • Marine : Reefs, continental shelf, continental slope, deep water
- 12. Walther’s Law Sedimentary environments that started out side-by-side will end up overlapping one another over time due to transgressions and regressions. "Facies adjacent to one another in a continuous vertical sequence also accumulated adjacent to one another laterally". the vertical succession of facies reflects lateral changes in environment
- 13. • Applies only to a section with no unconformities. •Applies to a section without rapid environmental change where non- adjacent environments may replace one another. •Gradational (vertical) transitions from one facies to another indicate original adjacency and genetic relationship during formation. •Sharp/erosional (vertical) contacts between facies provides NO evidence of contemporaneous genetic relationship of depositional environments
- 14. The facies within this succession will represent conformable deposits that accumulated through time in progressively shallower water depths, and thus the vertical succession through the parasequence is: -shallowing-upward, -usually coarsening-upward, and - as higher, younger sediments are deposited under progressively more proximal, higher-energy conditions Shallowing-upward cycle
- 15. The facies within this succession will represent conformable deposits that accumulated through time in progressively deepnming water depths, and thus the vertical succession through the parasequence is: -deepening-upward, -usually finning-upward, and - as higher, younger sediments are deposited under progressively more deeper, lower-energy conditions Deepening-upward cycle
- 16. Facies Analysis • The interpretation of strata in terms of depositional environments • How? – Recognize sedimentary environments – Interpret rocks based on facies – Rely heavily on facies associations – Vertical – Horizontal – Can use idealized model to assist in analysis
- 18. • According to this classification, sandstones are divided into two major groups based on texture (matrix content): Sandstone Classification The widely used classification is that presented by Pettijohn et al., (1973) and based on Dott (1964). This classification is based on: 1. the mineralogy of the sediment (the three mineral components: Quartz plus chert, feldspar, and lithic fragments (Q, F & R) and 2. presence or absence of a matrix (matrix content). (a) matrix-poor sandstones, the arenites, where the rocks are composed of grains only or contain less than 15% matrix. Arenites are texturally mature and clean sandstones. Their lithification is due to cement precipitates in the primary intergranular pores. (b) matrix-rich sandstones, the wackes, where the rocks contain 15-75% matrix. Wackes are argillaceous, texturally immature, or “dirty” sandstones. • Each one of these two groups is subdivided into various rock-types based on mineral composition.
- 19. • The percentage of quartz, feldspar and rock fragments allow the arenites and wackes to be further subdivided. Of the arenites, the term quartz arenite is applied to those with 95% or more quartz grains. Arkosic arenite refers to an arenite with more than 25% feldspar, which exceeds the rock fragments content, and litharenite is applied where the rock fragments content 25% and is greater than feldspar. Other transitional rock-types are present as arkose, lithic arkose, subarkose,… The wackes are the transitional group between arenites and mudrocks. They include 1. greywacke where two types are distinguished: feldspathic and lithic greywacke, and 2. quartz wacke, a rock- type rich in quartz with some matrix. From Boggs, Principles of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy, 4th ed., Figure 5.5, p. 130
- 20. Quartz
- 21. Carbonate Rocks Constituents I- Allochemical Particles (allochems) – framework grains of a mechanically deposited limestone – four main types: - Skeletal grains (fossil and fossil fragments, - Non-skeletal grains: Ooliths, Peloids, Intraclasts •II. Orthochemical Particles (orthochems) – matrix and cement that fill spaces, bind allochems together and lithify the sediment Pores Cement Non-skeletal grains Matrix (<20 m) Skeletal grains
- 22. 1. Intraclasts (rock fragments): • formed, transported and redeposited within the basin 2. Ooliths: concentrically laminated carbonate structures, including: • oolites -concentrically laminated structures,less than 2mm in diameter, thought to be abiogenic in origin • pisolites - same as oolites, but greater than 2mm in diameter • oncolites - spheroidal stromatolites (> 1-2 cm) 3. Peloids: • silt to fine grained sand sized carbonate particles with no distinctive internal structure; most thought to be fecal pellets 4. Skeletal particles (bioclasts): • whole microfossils, whole megafossils, broken shell fragments – algae, forams, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, gastropods, pelecypods, ostracods, etc.
- 23. • Type I limestone, Sparry Allochemical rocks: - allochems > 50%, - spar cement > micrite mud - 4 rock types - more energetic environment, some sorting • Type II limestone, Micritic Allochemical rocks: – allochems >10%, – micrite mud > spar cement – 4 rock types – lower energy environment, more poorly sorted than Type I • Type III limestone: Micrite - allochems < 10% - very low energy at the site of deposition (carbonate mudrock) • Type IV limestone “Biolithite”: Reef rock , - a separate categories were proposed for rocks formed by organic growth Folk Classification (1959, 1962)
- 24. • Folk proposed a textural spectrum that incorporated textural parameters: Mud component (matrix %), Sorting, Rounding and packing of grains • Carbonate rocks with component grains coarser than sand size (>2 mm) are differentiated as rudites, Oosparrudite, biomicrudite,…
- 25. • Dunham Classification – Based on depositional Texture • depositional texture recognizable or not recognized (crystalline) • mud-bearing vs mud-free sediment • Grain support vs mud support • sediment deposited in calm vs agitated waters • bound (biologically) (presence or absence of organic binding)