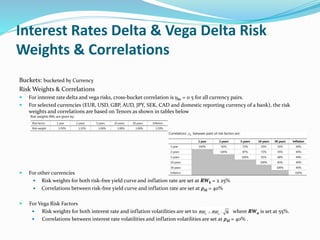
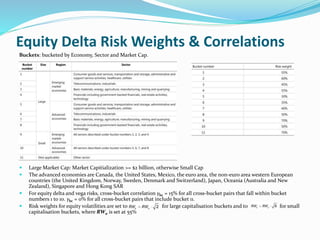
The document discusses the standardized approach for calculating counterparty credit valuation adjustment (SA-CVA) capital under Basel regulations. It provides details on the sensitivities based charge calculation method for SA-CVA, including delta and vega risk charges across different risk classes. It also outlines the risk weights and correlations used to calculate delta and vega risk charges for various risk factors like interest rates, credit spreads, equities, foreign exchange, and commodities.