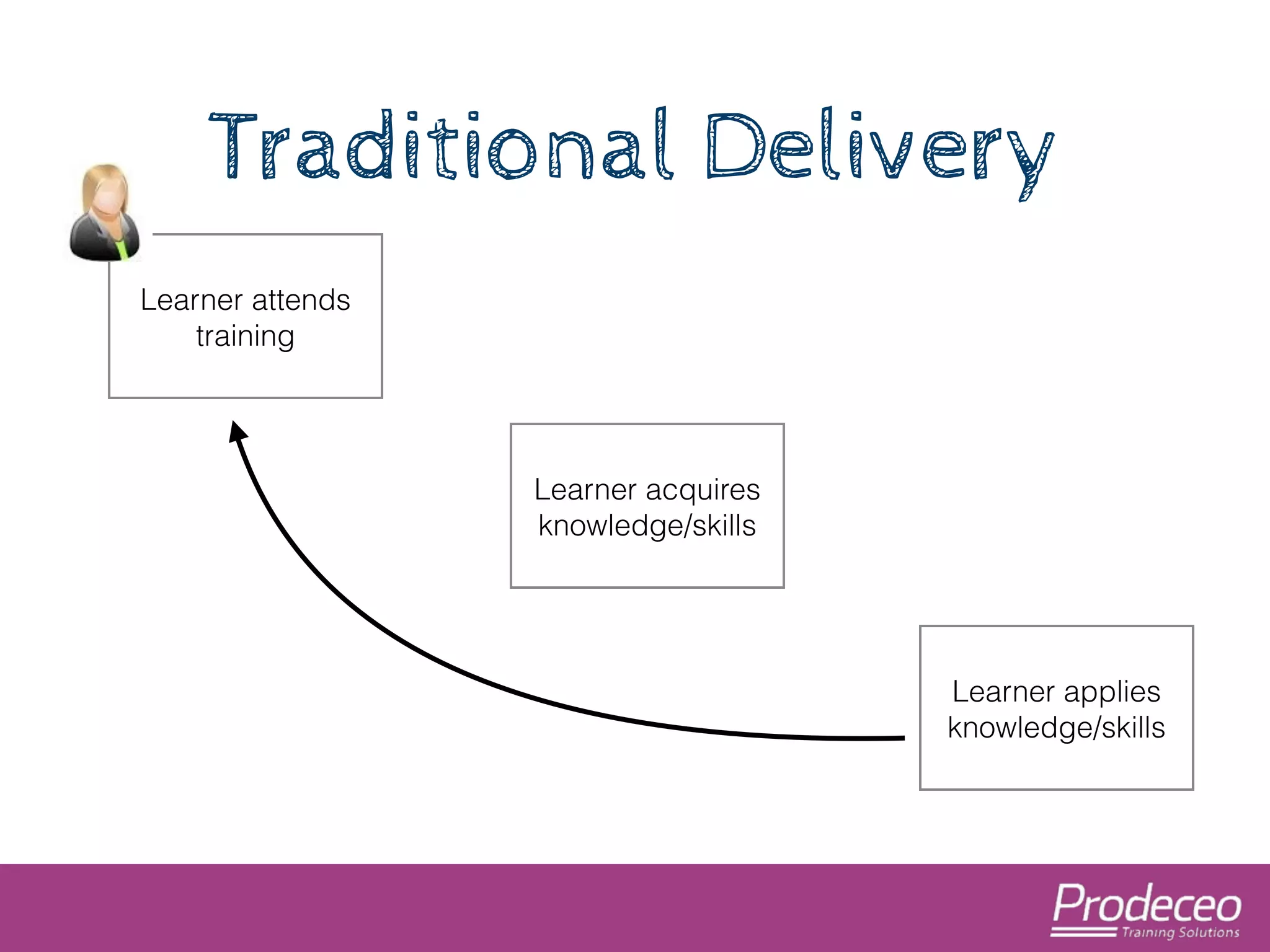
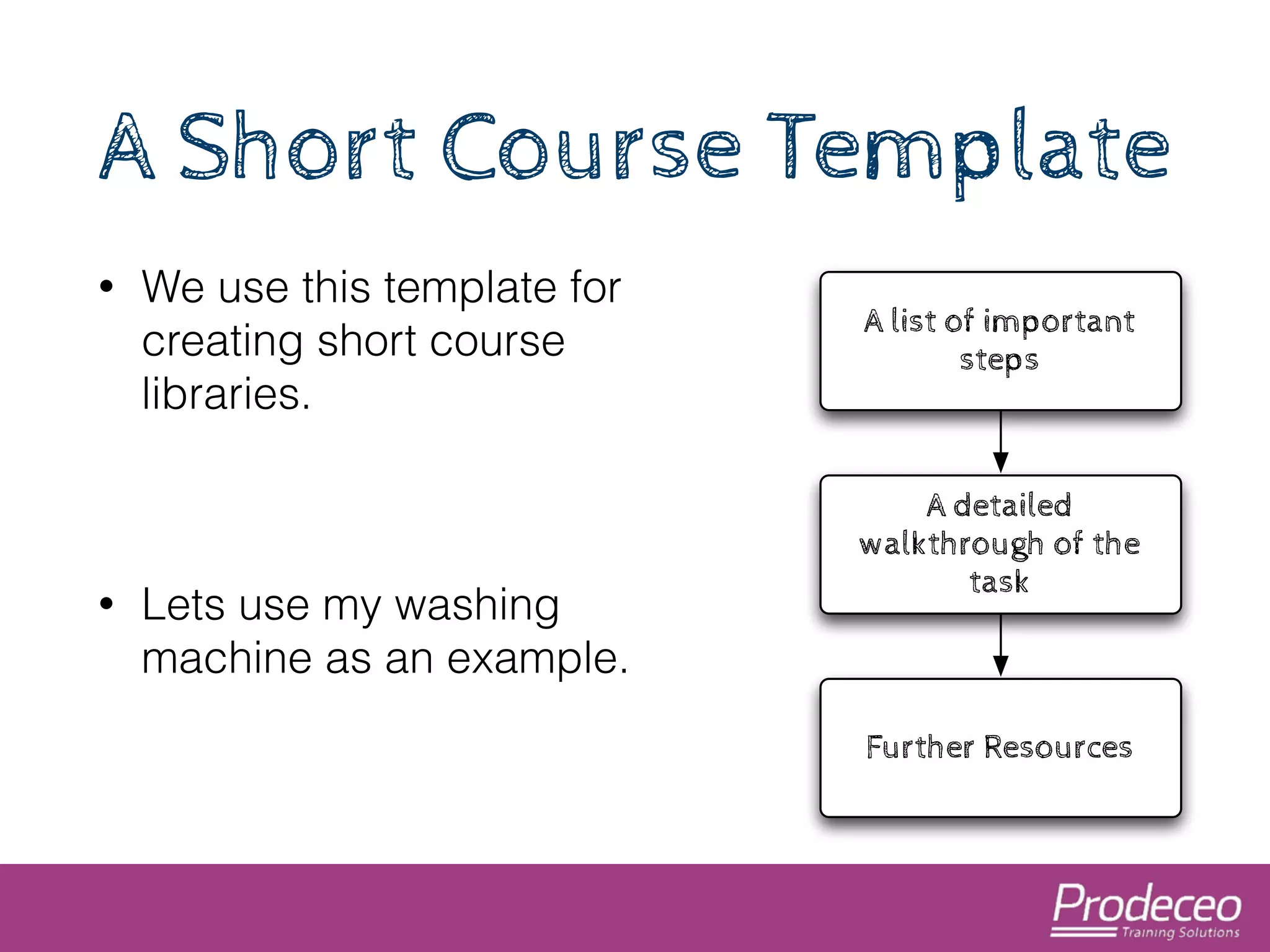
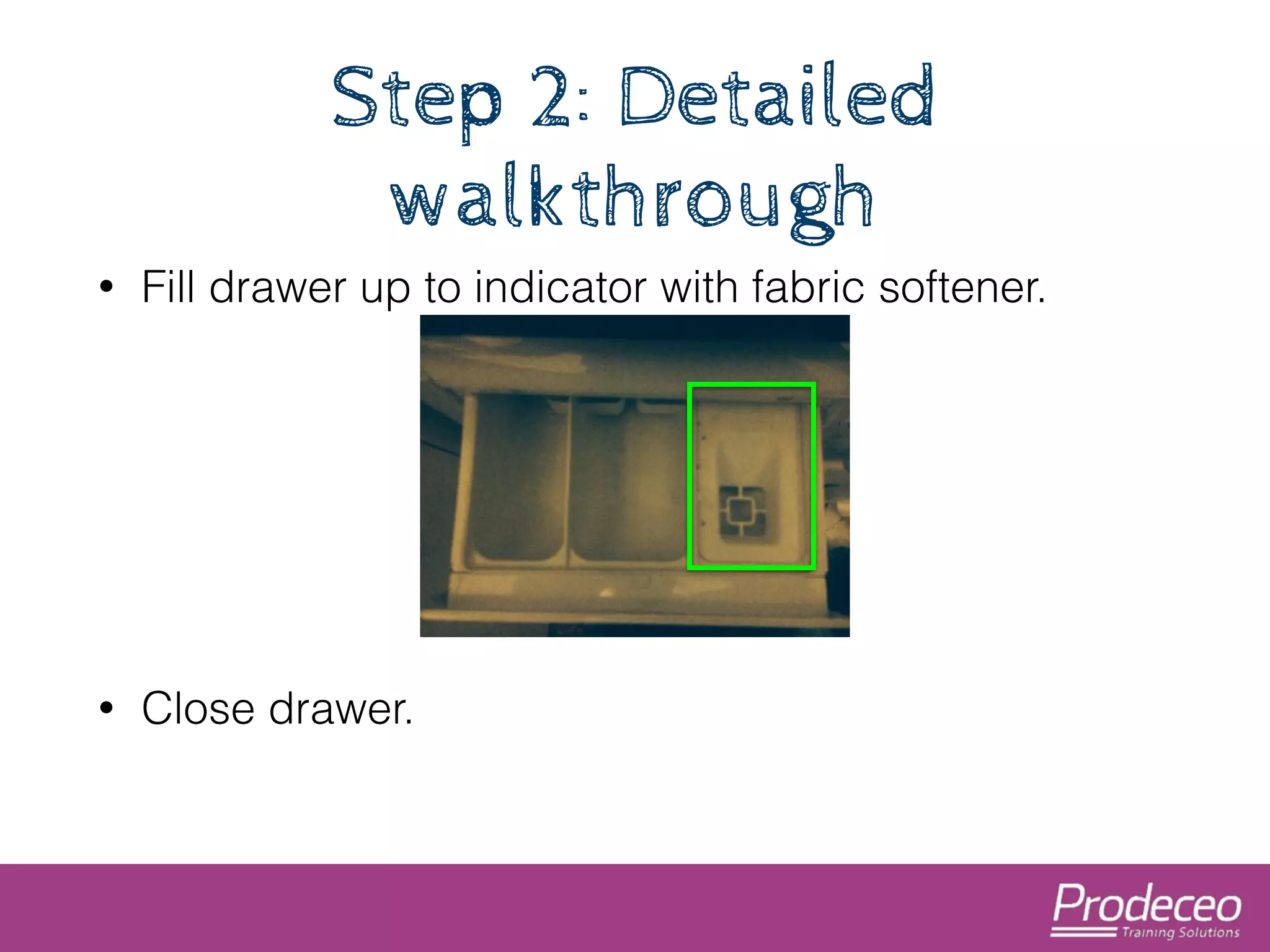
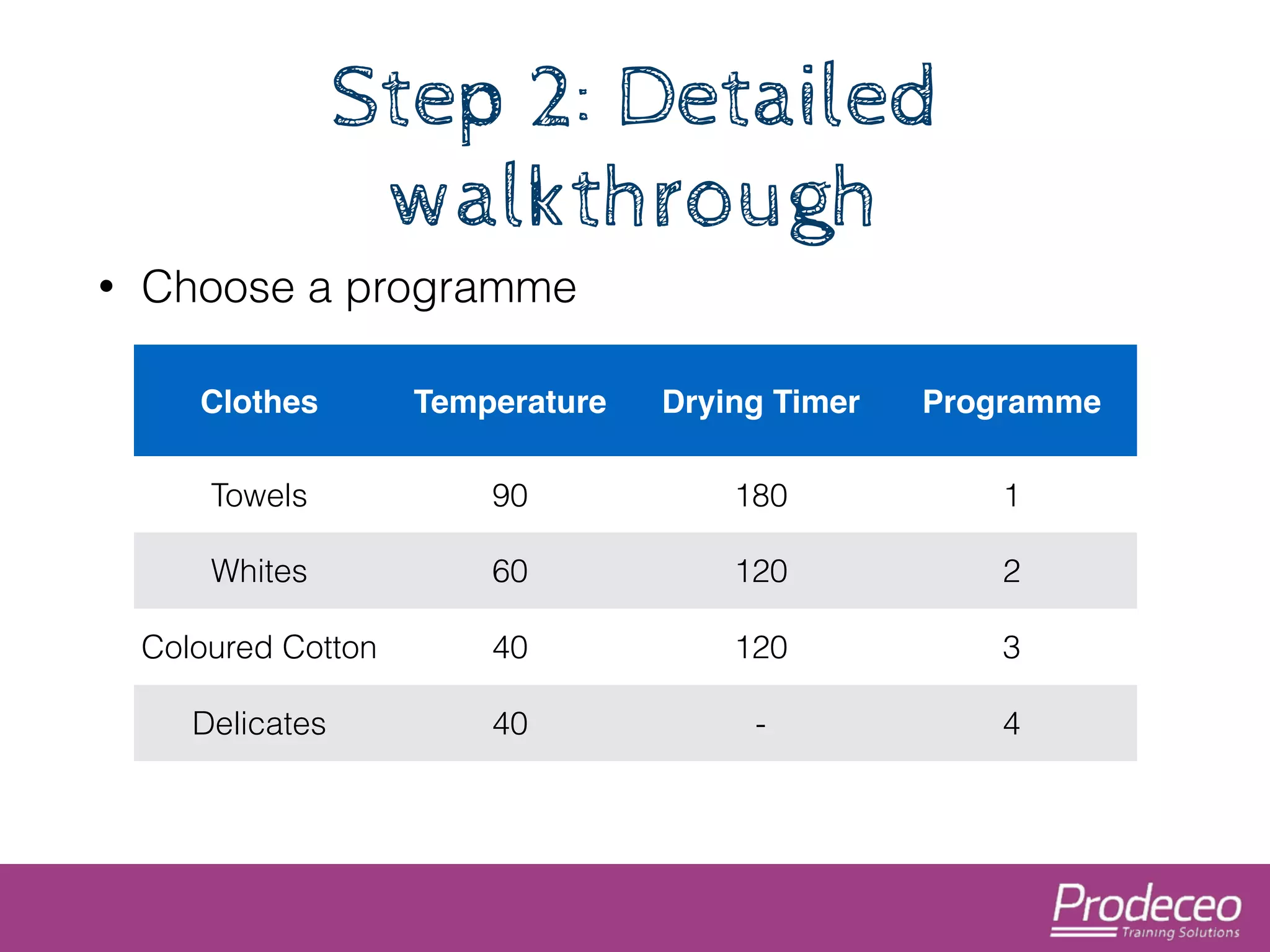
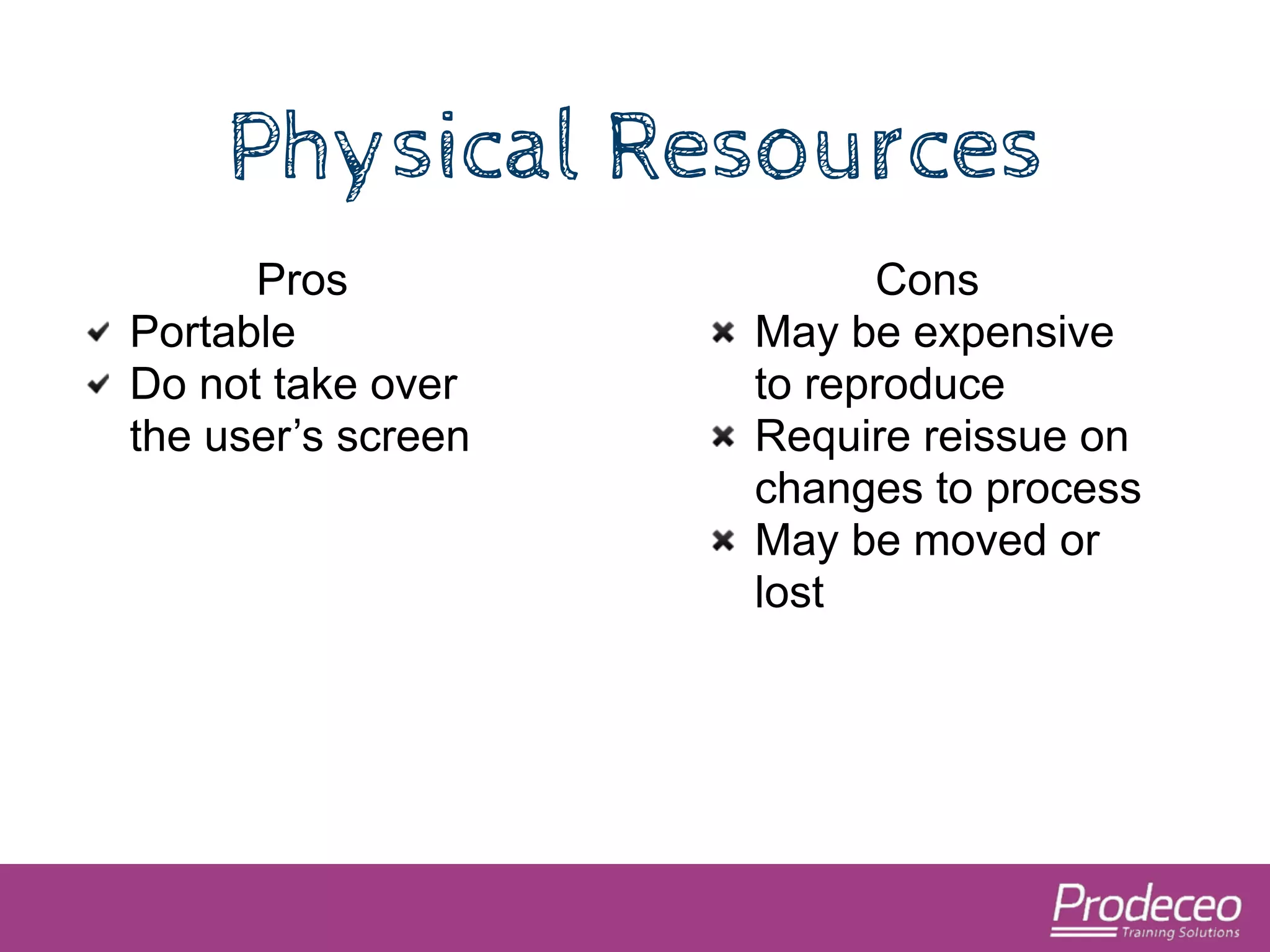
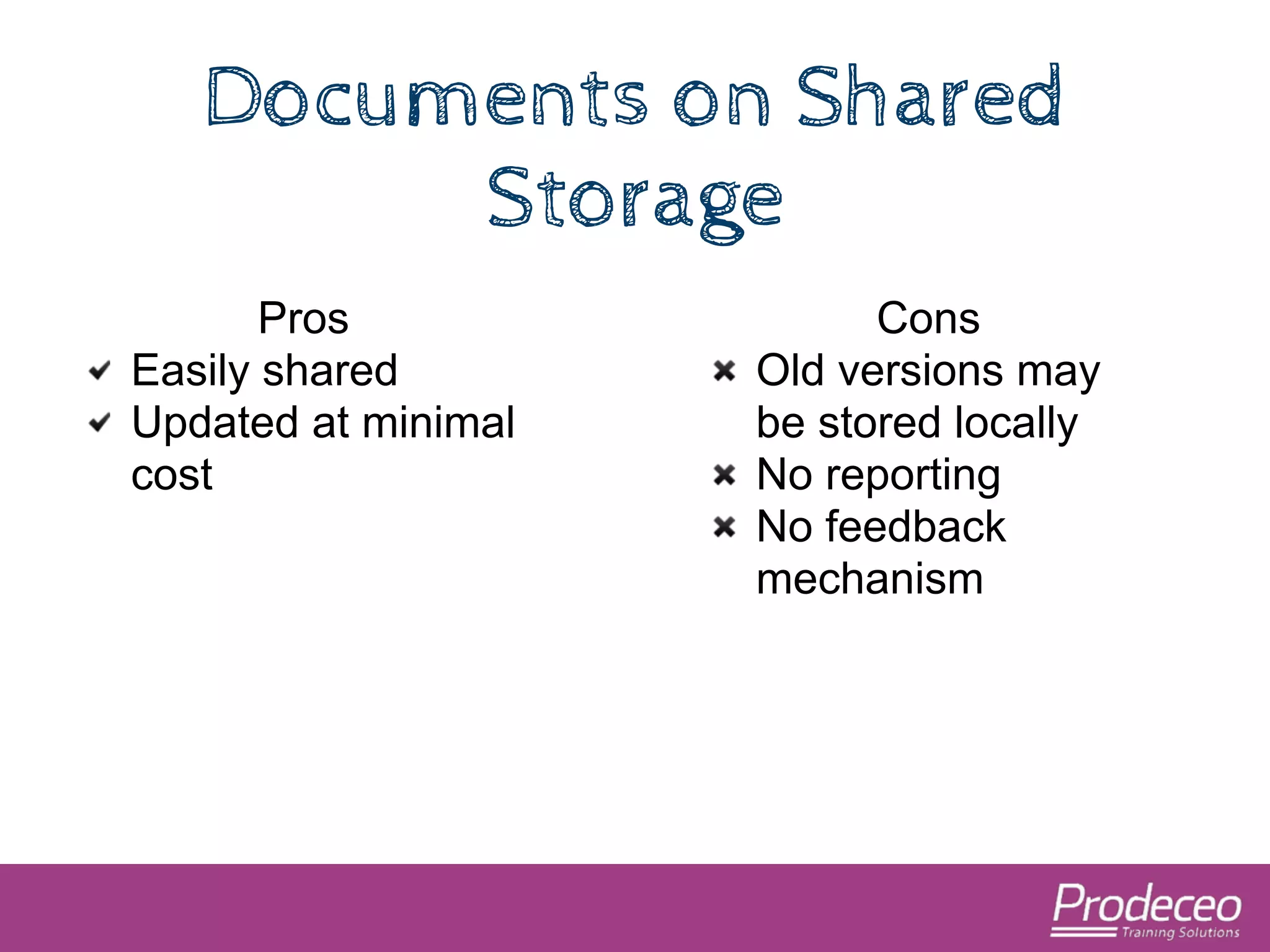
The document explores how technology, particularly the internet, is impacting our cognitive functions, including memory and attention spans, which are now shorter. It suggests that traditional learning methods are insufficient as people forget information quickly and advocates for creating concise, topic-focused short courses for efficient learning. The document also provides practical tips for distributing these courses effectively and emphasizes the importance of keeping resources updated and accessible.