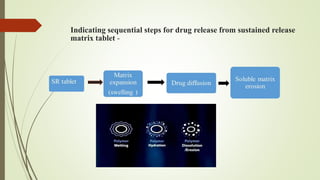
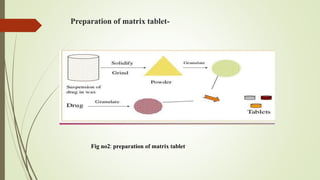
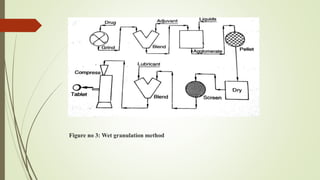
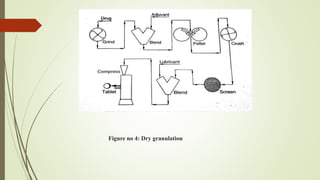
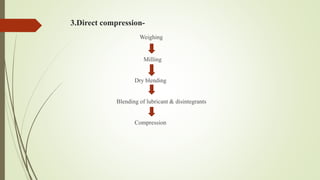
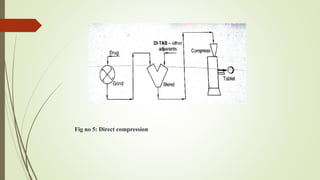
The document discusses sustained release drug delivery systems (SRDDS), highlighting their importance in improving patient compliance and reducing dosing frequency. It outlines the differences between sustained and controlled release, advantages and disadvantages of SRDDS, and the critical selection criteria for drugs and polymers used in these systems. Additionally, it covers the kinetic fundamentals of drug release, evaluation parameters, and various methods for preparing matrix tablets.































![ Friability: A tablets durability may be determined through the use of a friabilator. This apparatus
determines the tablets friability or tendency to crumble, by allowing it to roll and fall within the
drum. In general method is the 20 tablets are randomly selected, weigh before rotation and placed
in the electro lab friabilator (Roche friability teste) and apparatus rotate at specified number of
rpm for few min. After revolution the tablets weighed again and calculate the % friability. So
resistance to loss of weight indicates the tablets ability to withstand abrasion in handling,
packaging and shipment. A maximum weight loss of not more than 1 % generally is considered
acceptable for more products. It is expressed in %. The % friability is determined by using the
formula as follows
% F = [ 1- (Wt/W)] x 100
Where, %
F – Friability in percentage
W – Initial weight of tablet
Wt- - Weight of tablet after revolution
Figure no 7: Friability tester](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sustainedrelease-190523154529/85/Sustained-release-drug-deliveru-system-38-320.jpg)






