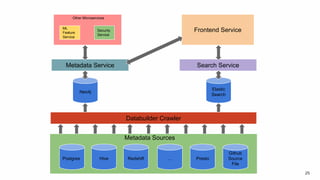
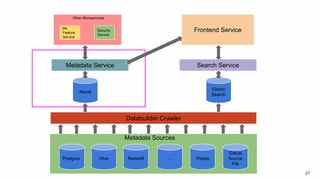
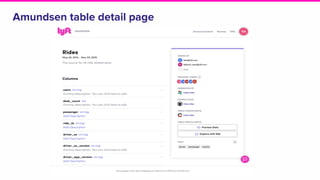
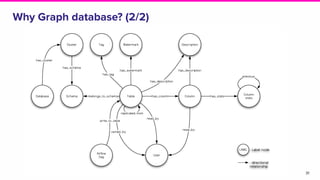
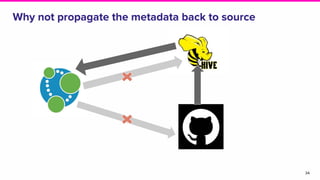
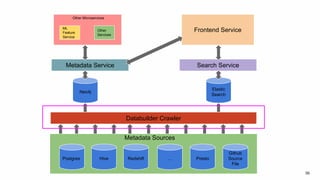
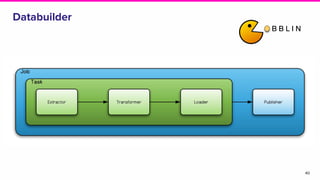
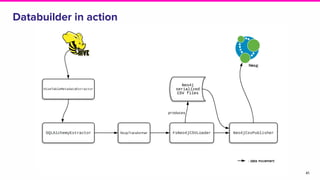
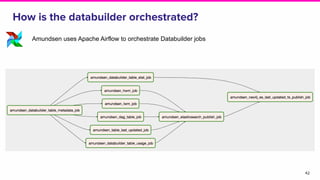
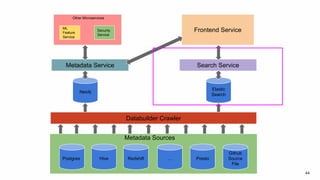
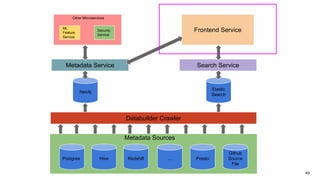
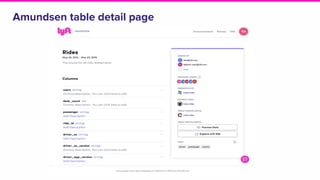
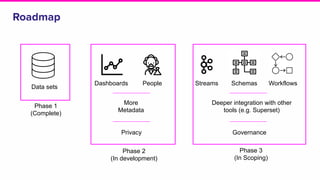
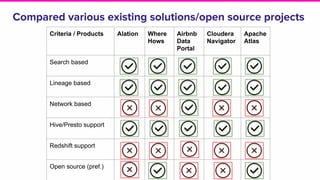
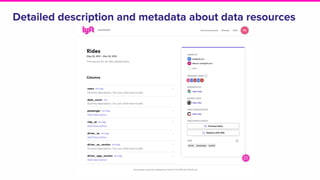
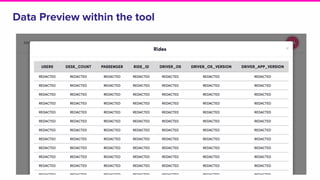
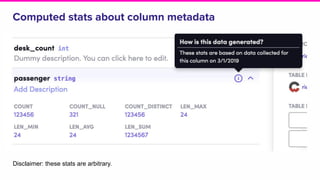
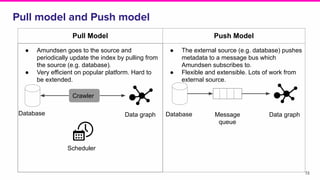
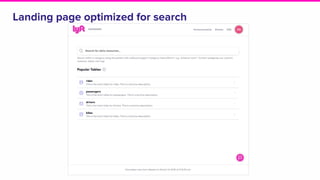
Amundsen is a metadata-driven application developed by Lyft to solve data discovery challenges. It provides a search-based UI and uses a distributed architecture with various microservices to index and serve metadata from multiple sources. Key components include a metadata service using Neo4j, a search service using Elasticsearch, and a frontend. The tool has been hugely successful at Lyft and is now open source. Future work includes expanding metadata coverage and integrating with other tools.






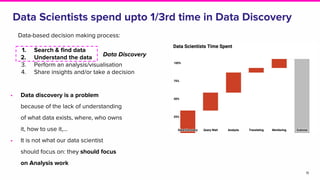









![Striking the balance
22
Relevance Popularity
● Names, Descriptions, Tags, [owners, frequent
users]
● Querying activity
● Dashboarding
● Different weights for automated vs adhoc
querying](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meetupsf-amundsenpresentation-190516010721/85/Meetup-SF-Amundsen-22-320.jpg)