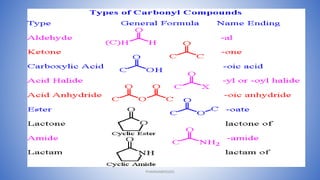
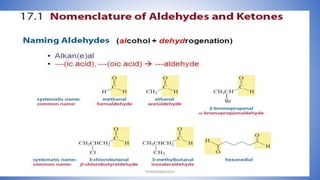
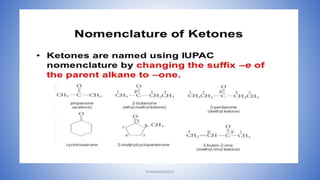
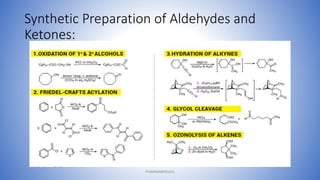
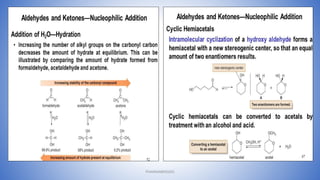
The document discusses carbonyl compounds, which contain a carbon-oxygen double bond carbonyl group. The carbonyl group is a constituent of important organic compound classes like carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes, and ketones. Compounds containing a carbonyl group have higher melting and boiling points than hydrocarbons with the same number of carbon atoms because the carbonyl group is polar. The carbonyl carbon acquires a partial positive charge while the oxygen acquires a partial negative charge due to differences in electron affinity. Nomenclature assigns characteristic suffixes like "al" to aldehydes and "one" to ketones. Chain numbering starts from the end nearest the carbonyl group.